Seth Roffe
Neutron-Induced, Single-Event Effects on Neuromorphic Event-based Vision Sensor: A First Step Towards Space Applications
Jan 29, 2021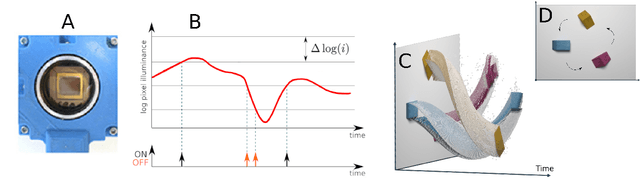
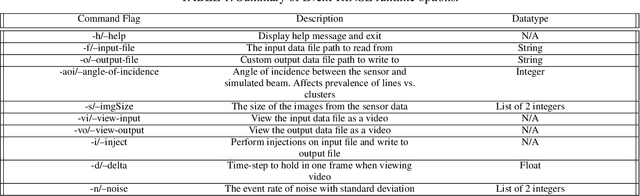
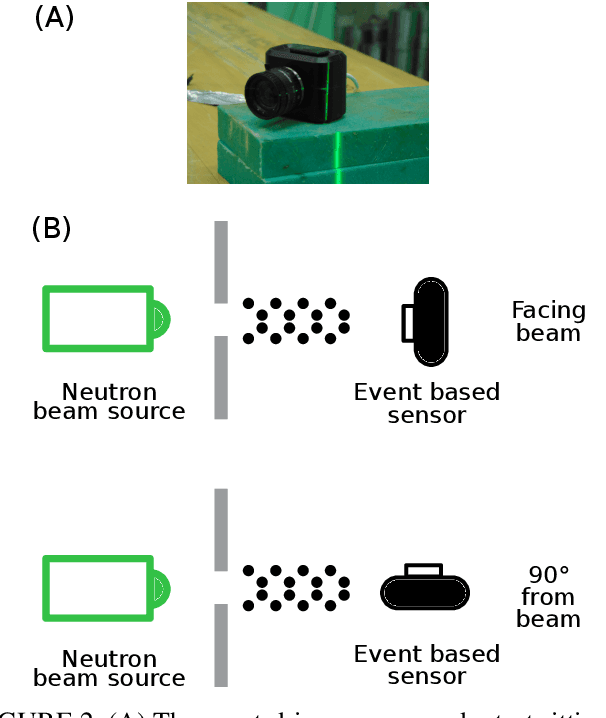
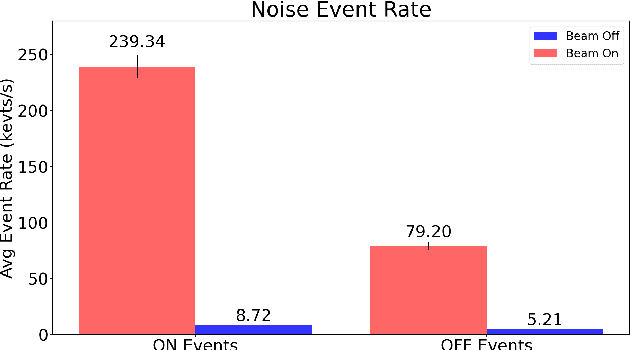
Abstract:This paper studies the suitability of neuromorphic event-based vision cameras for spaceflight, and the effects of neutron radiation on their performance. Neuromorphic event-based vision cameras are novel sensors that implement asynchronous, clockless data acquisition, providing information about the change in illuminance greater than 120dB with sub-millisecond temporal precision. These sensors have huge potential for space applications as they provide an extremely sparse representation of visual dynamics while removing redundant information, thereby conforming to low-resource requirements. An event-based sensor was irradiated under wide-spectrum neutrons at Los Alamos Neutron Science Center and its effects were classified. We found that the sensor had very fast recovery during radiation, showing high correlation of noise event bursts with respect to source macro-pulses. No significant differences were observed between the number of events induced at different angles of incidence but significant differences were found in the spatial structure of noise events at different angles. The results show that event-based cameras are capable of functioning in a space-like, radiative environment with a signal-to-noise ratio of 3.355. They also show that radiation-induced noise does not affect event-level computation. We also introduce the Event-based Radiation-Induced Noise Simulation Environment (Event-RINSE), a simulation environment based on the noise-modelling we conducted and capable of injecting the effects of radiation-induced noise from the collected data to any stream of events in order to ensure that developed code can operate in a radiative environment. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first time such analysis of neutron-induced noise analysis has been performed on a neuromorphic vision sensor, and this study shows the advantage of using such sensors for space applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge