Serhii Hamotskyi
NLP-based Decision Support System for Examination of Eligibility Criteria from Securities Prospectuses at the German Central Bank
Feb 09, 2023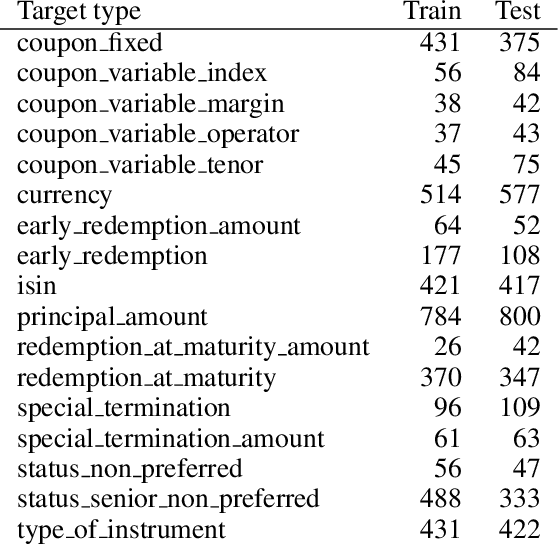
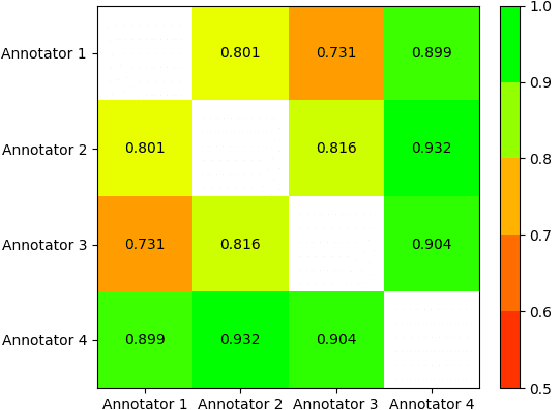
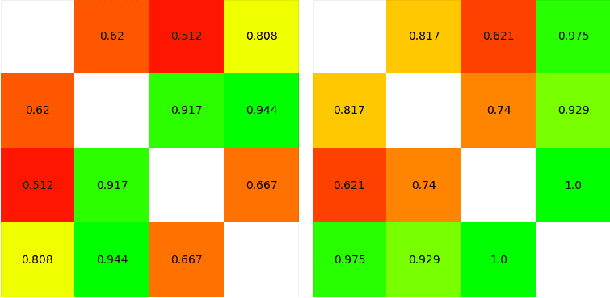
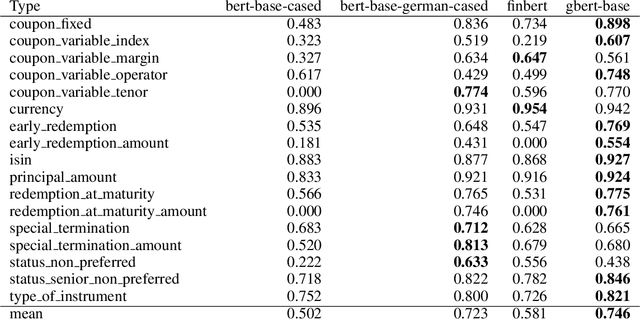
Abstract:As part of its digitization initiative, the German Central Bank (Deutsche Bundesbank) wants to examine the extent to which natural Language Processing (NLP) can be used to make independent decisions upon the eligibility criteria of securities prospectuses. Every month, the Directorate General Markets at the German Central Bank receives hundreds of scanned prospectuses in PDF format, which must be manually processed to decide upon their eligibility. We found that this tedious and time-consuming process can be (semi-)automated by employing modern NLP model architectures, which learn the linguistic feature representation in text to identify the present eligible and ineligible criteria. The proposed Decision Support System provides decisions of document-level eligibility criteria accompanied by human-understandable explanations of the decisions. The aim of this project is to model the described use case and to evaluate the extent to which current research results from the field of NLP can be applied to this problem. After creating a heterogeneous domain-specific dataset containing annotations of eligible and non-eligible mentions of relevant criteria, we were able to successfully build, train and deploy a semi-automatic decider model. This model is based on transformer-based language models and decision trees, which integrate the established rule-based parts of the decision processes. Results suggest that it is possible to efficiently model the problem and automate decision making to more than 90% for many of the considered eligibility criteria.
Generating and Estimating Nonverbal Alphabets for Situated and Multimodal Communications
Dec 12, 2017
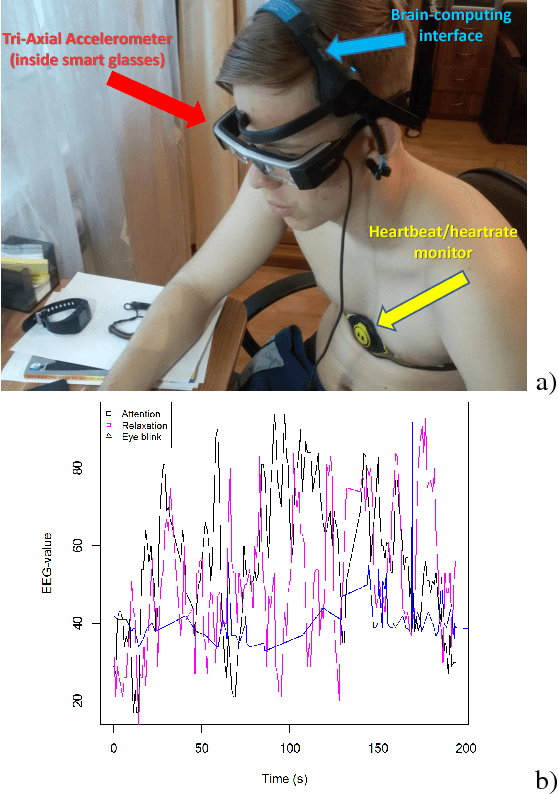
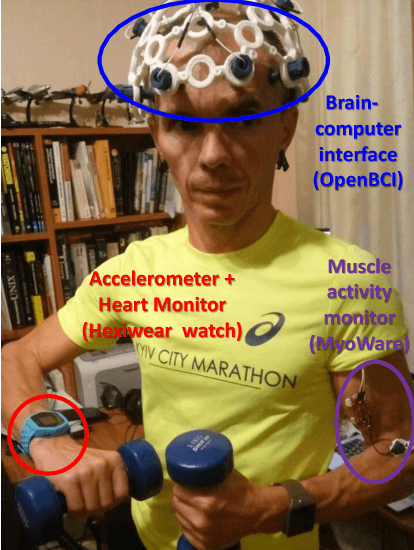

Abstract:In this paper, we discuss the formalized approach for generating and estimating symbols (and alphabets), which can be communicated by the wide range of non-verbal means based on specific user requirements (medium, priorities, type of information that needs to be conveyed). The short characterization of basic terms and parameters of such symbols (and alphabets) with approaches to generate them are given. Then the framework, experimental setup, and some machine learning methods to estimate usefulness and effectiveness of the nonverbal alphabets and systems are presented. The previous results demonstrate that usage of multimodal data sources (like wearable accelerometer, heart monitor, muscle movements sensors, braincomputer interface) along with machine learning approaches can provide the deeper understanding of the usefulness and effectiveness of such alphabets and systems for nonverbal and situated communication. The symbols (and alphabets) generated and estimated by such methods may be useful in various applications: from synthetic languages and constructed scripts to multimodal nonverbal and situated interaction between people and artificial intelligence systems through Human-Computer Interfaces, such as mouse gestures, touchpads, body gestures, eyetracking cameras, wearables, and brain-computing interfaces, especially in applications for elderly care and people with disabilities.
* 5 pages, 5 figures
Automatized Generation of Alphabets of Symbols
Jul 16, 2017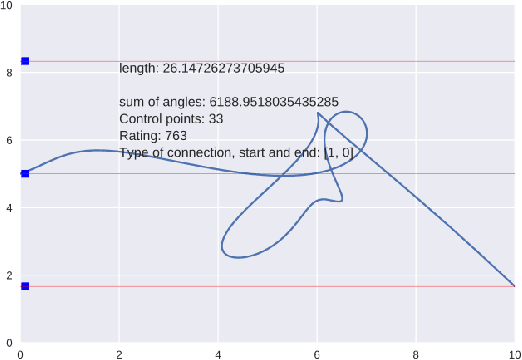
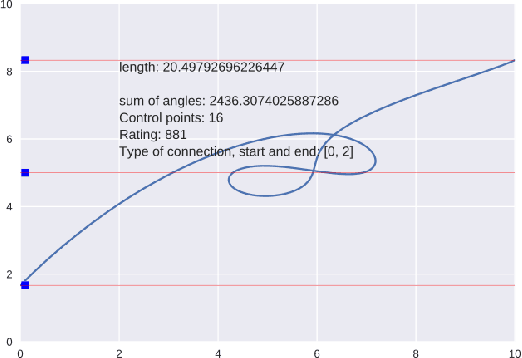
Abstract:In this paper, we discuss the generation of symbols (and alphabets) based on specific user requirements (medium, priorities, type of information that needs to be conveyed). A framework for the generation of alphabets is proposed, and its use for the generation of a shorthand writing system is explored. We discuss the possible use of machine learning and genetic algorithms to gather inputs for generation of such alphabets and for optimization of already generated ones. The alphabets generated using such methods may be used in very different fields, from the creation of synthetic languages and constructed scripts to the creation of sensible commands for multimodal interaction through Human-Computer Interfaces, such as mouse gestures, touchpads, body gestures, eye-tracking cameras, and brain-computing Interfaces, especially in applications for elderly care and people with disabilities.
* 4 pages, 3 figures; Federated Conference on Computer Science and Information Systems, Prague (FedCSIS-2017) (Prague, Czech Republic)
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge