Sebastian Krebs
DenseBEV: Transforming BEV Grid Cells into 3D Objects
Dec 18, 2025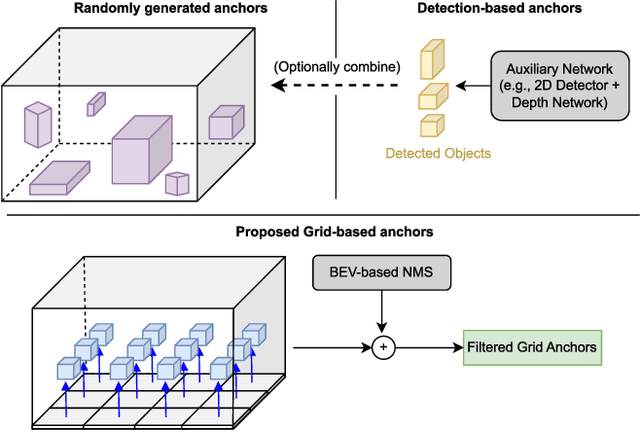
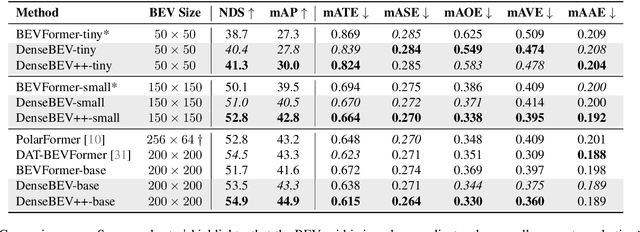
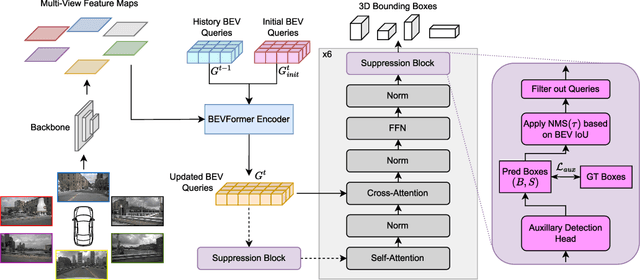
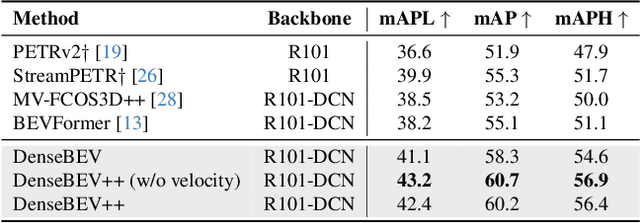
Abstract:In current research, Bird's-Eye-View (BEV)-based transformers are increasingly utilized for multi-camera 3D object detection. Traditional models often employ random queries as anchors, optimizing them successively. Recent advancements complement or replace these random queries with detections from auxiliary networks. We propose a more intuitive and efficient approach by using BEV feature cells directly as anchors. This end-to-end approach leverages the dense grid of BEV queries, considering each cell as a potential object for the final detection task. As a result, we introduce a novel two-stage anchor generation method specifically designed for multi-camera 3D object detection. To address the scaling issues of attention with a large number of queries, we apply BEV-based Non-Maximum Suppression, allowing gradients to flow only through non-suppressed objects. This ensures efficient training without the need for post-processing. By using BEV features from encoders such as BEVFormer directly as object queries, temporal BEV information is inherently embedded. Building on the temporal BEV information already embedded in our object queries, we introduce a hybrid temporal modeling approach by integrating prior detections to further enhance detection performance. Evaluating our method on the nuScenes dataset shows consistent and significant improvements in NDS and mAP over the baseline, even with sparser BEV grids and therefore fewer initial anchors. It is particularly effective for small objects, enhancing pedestrian detection with a 3.8% mAP increase on nuScenes and an 8% increase in LET-mAP on Waymo. Applying our method, named DenseBEV, to the challenging Waymo Open dataset yields state-of-the-art performance, achieving a LET-mAP of 60.7%, surpassing the previous best by 5.4%. Code is available at https://github.com/mdaehl/DenseBEV.
CrowdQuery: Density-Guided Query Module for Enhanced 2D and 3D Detection in Crowded Scenes
Sep 10, 2025Abstract:This paper introduces a novel method for end-to-end crowd detection that leverages object density information to enhance existing transformer-based detectors. We present CrowdQuery (CQ), whose core component is our CQ module that predicts and subsequently embeds an object density map. The embedded density information is then systematically integrated into the decoder. Existing density map definitions typically depend on head positions or object-based spatial statistics. Our method extends these definitions to include individual bounding box dimensions. By incorporating density information into object queries, our method utilizes density-guided queries to improve detection in crowded scenes. CQ is universally applicable to both 2D and 3D detection without requiring additional data. Consequently, we are the first to design a method that effectively bridges 2D and 3D detection in crowded environments. We demonstrate the integration of CQ into both a general 2D and 3D transformer-based object detector, introducing the architectures CQ2D and CQ3D. CQ is not limited to the specific transformer models we selected. Experiments on the STCrowd dataset for both 2D and 3D domains show significant performance improvements compared to the base models, outperforming most state-of-the-art methods. When integrated into a state-of-the-art crowd detector, CQ can further improve performance on the challenging CrowdHuman dataset, demonstrating its generalizability. The code is released at https://github.com/mdaehl/CrowdQuery.
Ultra-Wideband Positioning System Based on ESP32 and DWM3000 Modules
Mar 15, 2024Abstract:In this paper, an Ultra-Wideband (UWB) positioning system is introduced, that leverages six identical custom-designed boards, each featuring an ESP32 microcontroller and a DWM3000 module from Quorvo. The system is capable of achieving localization with an accuracy of up to 10 cm, by utilizing Two-Way-Ranging (TWR) measurements between one designated tag and five anchor devices. The gathered distance measurements are subsequently processed by an Extended Kalman Filter (EKF) running locally on the tag board, enabling it to determine its own position, relying on fixed, a priori known positions of the anchor boards. This paper presents a comprehensive overview of the systems architecture, the key components, and the capabilities it offers for indoor positioning and tracking applications.
The EuroCity Persons Dataset: A Novel Benchmark for Object Detection
Jun 05, 2018
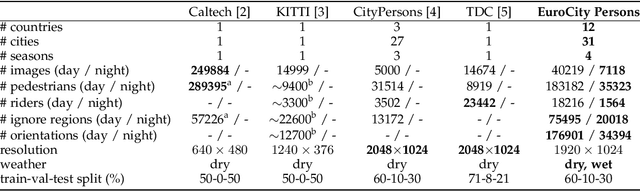
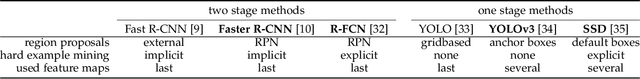
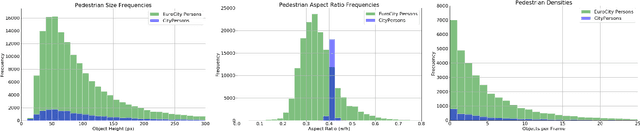
Abstract:Big data has had a great share in the success of deep learning in computer vision. Recent works suggest that there is significant further potential to increase object detection performance by utilizing even bigger datasets. In this paper, we introduce the EuroCity Persons dataset, which provides a large number of highly diverse, accurate and detailed annotations of pedestrians, cyclists and other riders in urban traffic scenes. The images for this dataset were collected on-board a moving vehicle in 31 cities of 12 European countries. With over 238200 person instances manually labeled in over 47300 images, EuroCity Persons is nearly one order of magnitude larger than person datasets used previously for benchmarking. The dataset furthermore contains a large number of person orientation annotations (over 211200). We optimize four state-of-the-art deep learning approaches (Faster R-CNN, R-FCN, SSD and YOLOv3) to serve as baselines for the new object detection benchmark. In experiments with previous datasets we analyze the generalization capabilities of these detectors when trained with the new dataset. We furthermore study the effect of the training set size, the dataset diversity (day- vs. night-time, geographical region), the dataset detail (i.e. availability of object orientation information) and the annotation quality on the detector performance. Finally, we analyze error sources and discuss the road ahead.
Use of semantic technologies for the development of a dynamic trajectories generator in a Semantic Chemistry eLearning platform
Dec 07, 2010
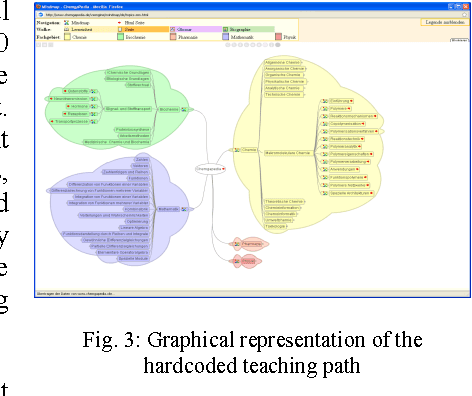

Abstract:ChemgaPedia is a multimedia, webbased eLearning service platform that currently contains about 18.000 pages organized in 1.700 chapters covering the complete bachelor studies in chemistry and related topics of chemistry, pharmacy, and life sciences. The eLearning encyclopedia contains some 25.000 media objects and the eLearning platform provides services such as virtual and remote labs for experiments. With up to 350.000 users per month the platform is the most frequently used scientific educational service in the German spoken Internet. In this demo we show the benefit of mapping the static eLearning contents of ChemgaPedia to a Linked Data representation for Semantic Chemistry which allows for generating dynamic eLearning paths tailored to the semantic profiles of the users.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge