Satyabrata Maity
Fault Matters: Sensor Data Fusion for Detection of Faults using Dempster-Shafer Theory of Evidence in IoT-Based Applications
Jun 24, 2019
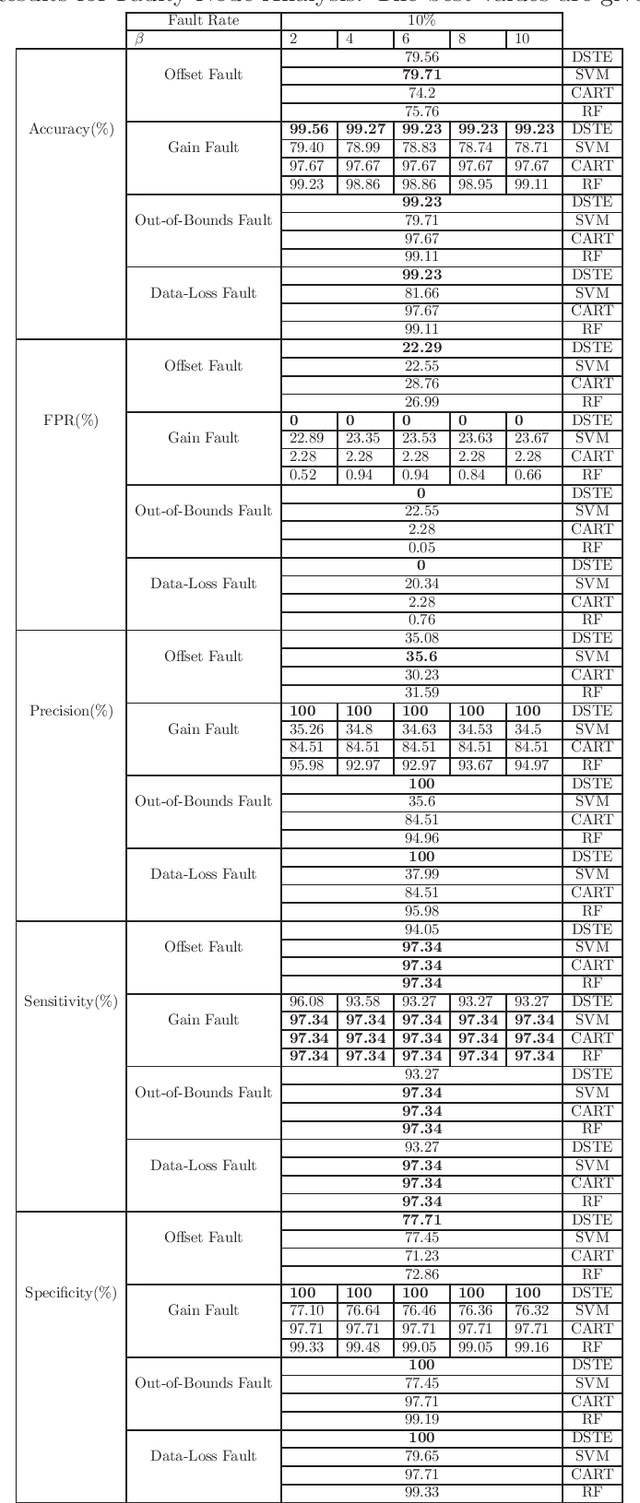
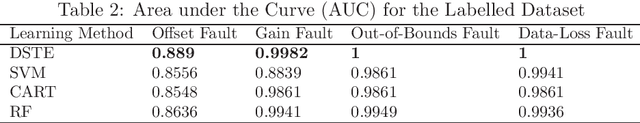
Abstract:Fault detection in sensor nodes is a pertinent issue that has been an important area of research for a very long time. But it is not explored much as yet in the context of Internet of Things. Internet of Things work with a massive amount of data so the responsibility for guaranteeing the accuracy of the data also lies with it. Moreover, a lot of important and critical decisions are made based on these data, so ensuring its correctness and accuracy is also very important. Also, the detection needs to be as precise as possible to avoid negative alerts. For this purpose, this work has adopted Dempster-Shafer Theory of Evidence which is a popular learning method to collate the information from sensors to come up with a decision regarding the faulty status of a sensor node. To verify the validity of the proposed method, simulations have been performed on a benchmark data set and data collected through a test bed in a laboratory set-up. For the different types of faults, the proposed method shows very competent accuracy for both the benchmark (99.8%) and laboratory data sets (99.9%) when compared to the other state-of-the-art machine learning techniques.
A Novel Approach for Human Action Recognition from Silhouette Images
Oct 15, 2015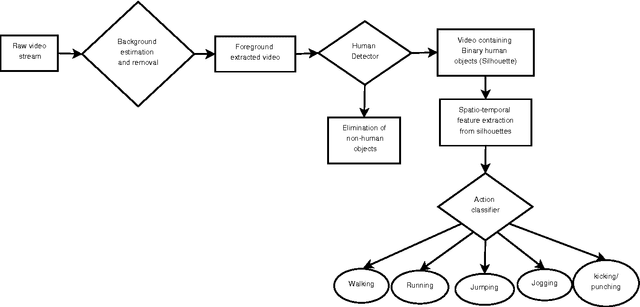
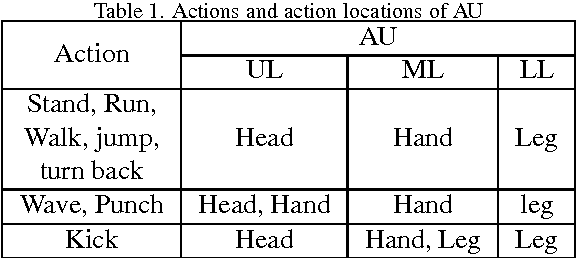
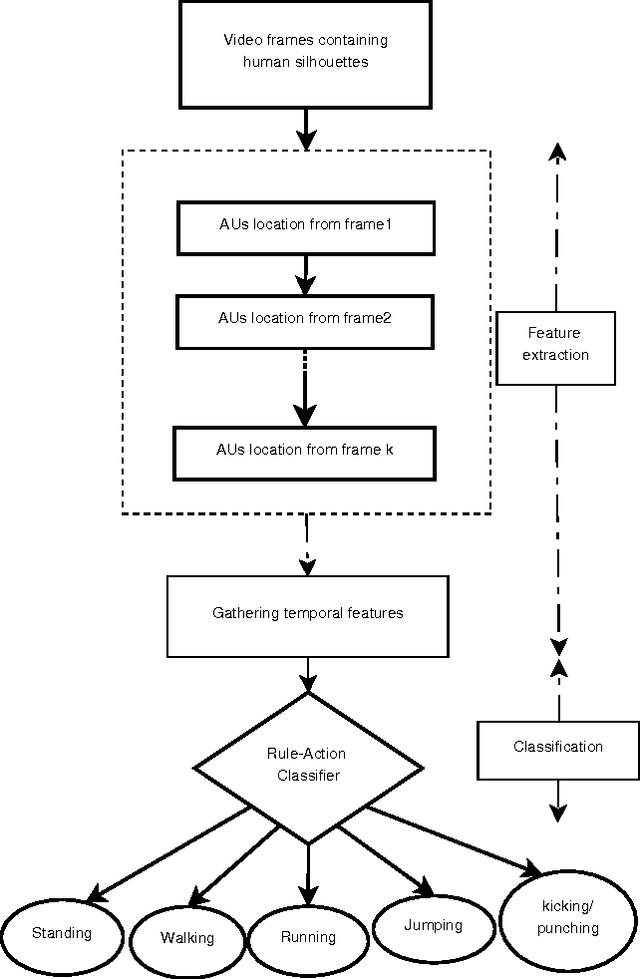
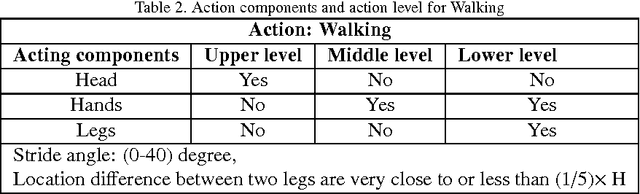
Abstract:In this paper, a novel human action recognition technique from video is presented. Any action of human is a combination of several micro action sequences performed by one or more body parts of the human. The proposed approach uses spatio-temporal body parts movement (STBPM) features extracted from foreground silhouette of the human objects. The newly proposed STBPM feature estimates the movements of different body parts for any given time segment to classify actions. We also proposed a rule based logic named rule action classifier (RAC), which uses a series of condition action rules based on prior knowledge and hence does not required training to classify any action. Since we don't require training to classify actions, the proposed approach is view independent. The experimental results on publicly available Wizeman and MuHVAi datasets are compared with that of the related research work in terms of accuracy in the human action detection, and proposed technique outperforms the others.
A brief experience on journey through hardware developments for image processing and its applications on Cryptography
Dec 27, 2012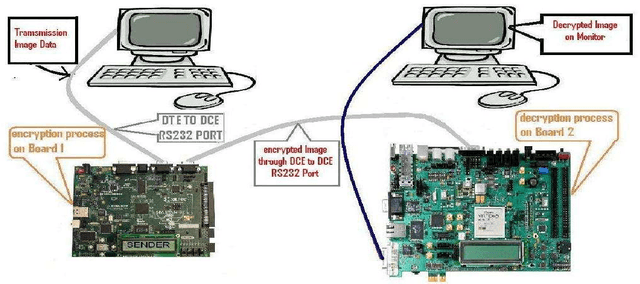
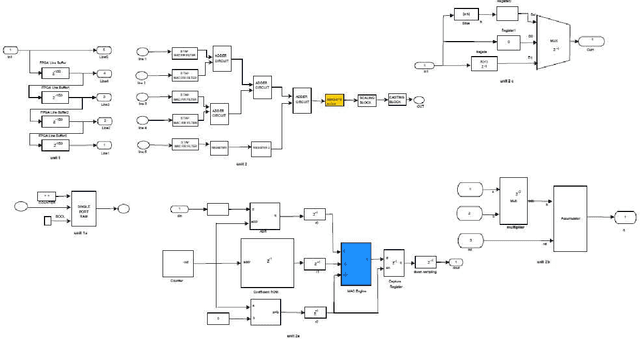
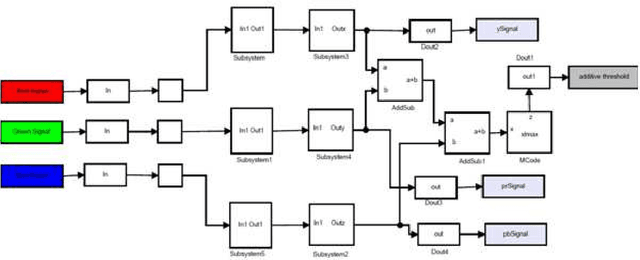
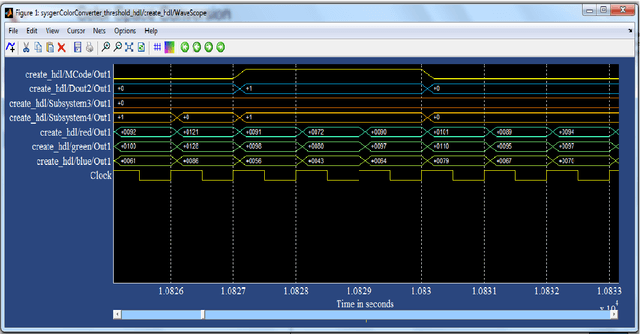
Abstract:The importance of embedded applications on image and video processing,communication and cryptography domain has been taking a larger space in current research era. Improvement of pictorial information for betterment of human perception like deblurring, de-noising in several fields such as satellite imaging, medical imaging etc are renewed research thrust. Specifically we would like to elaborate our experience on the significance of computer vision as one of the domains where hardware implemented algorithms perform far better than those implemented through software. So far embedded design engineers have successfully implemented their designs by means of Application Specific Integrated Circuits (ASICs) and/or Digital Signal Processors (DSP), however with the advancement of VLSI technology a very powerful hardware device namely the Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) combining the key advantages of ASICs and DSPs was developed which have the possibility of reprogramming making them a very attractive device for rapid prototyping.Communication of image and video data in multiple FPGA is no longer far away from the thrust of secured transmission among them, and then the relevance of cryptography is indeed unavoidable. This paper shows how the Xilinx hardware development platform as well Mathworks Matlab can be used to develop hardware based computer vision algorithms and its corresponding crypto transmission channel between multiple FPGA platform from a system level approach, making it favourable for developing a hardware-software co-design environment.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge