Sarah Kobir
Enhanced Speech Emotion Recognition with Efficient Channel Attention Guided Deep CNN-BiLSTM Framework
Dec 13, 2024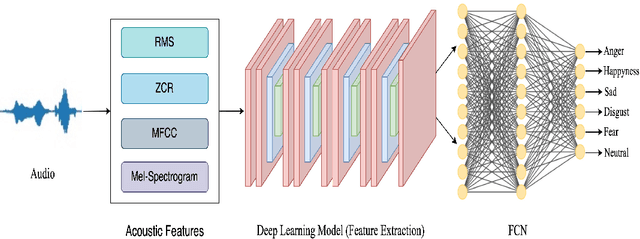
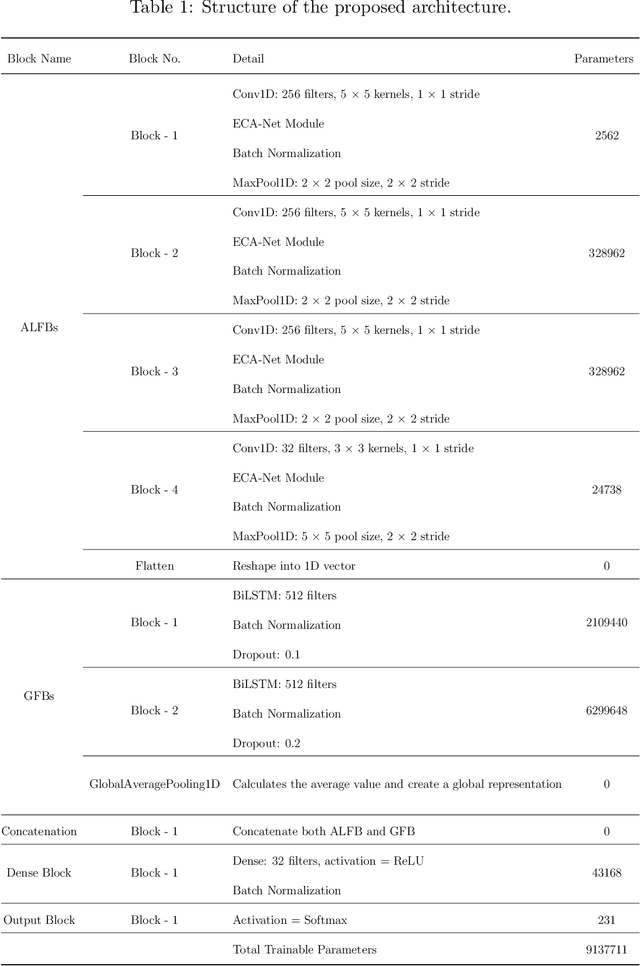
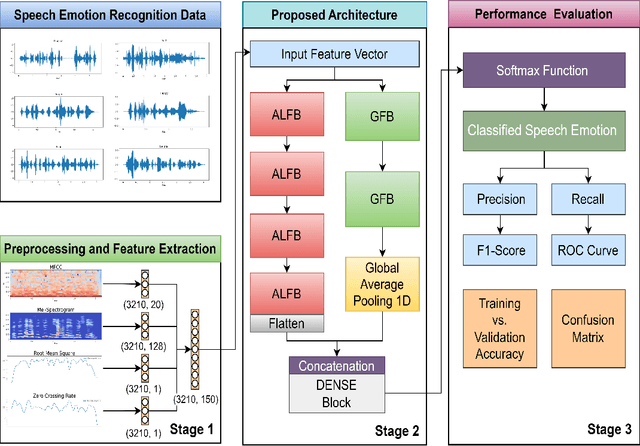
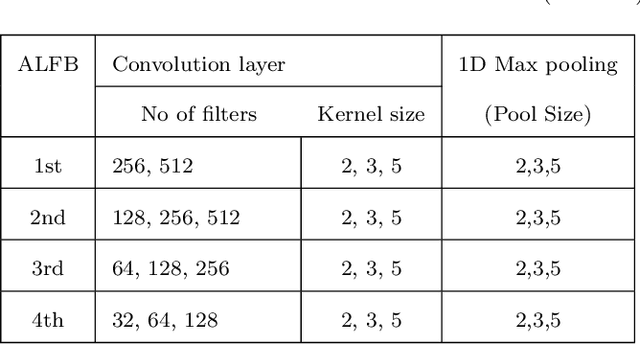
Abstract:Speech emotion recognition (SER) is crucial for enhancing affective computing and enriching the domain of human-computer interaction. However, the main challenge in SER lies in selecting relevant feature representations from speech signals with lower computational costs. In this paper, we propose a lightweight SER architecture that integrates attention-based local feature blocks (ALFBs) to capture high-level relevant feature vectors from speech signals. We also incorporate a global feature block (GFB) technique to capture sequential, global information and long-term dependencies in speech signals. By aggregating attention-based local and global contextual feature vectors, our model effectively captures the internal correlation between salient features that reflect complex human emotional cues. To evaluate our approach, we extracted four types of spectral features from speech audio samples: mel-frequency cepstral coefficients, mel-spectrogram, root mean square value, and zero-crossing rate. Through a 5-fold cross-validation strategy, we tested the proposed method on five multi-lingual standard benchmark datasets: TESS, RAVDESS, BanglaSER, SUBESCO, and Emo-DB, and obtained a mean accuracy of 99.65%, 94.88%, 98.12%, 97.94%, and 97.19% respectively. The results indicate that our model achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance compared to most existing methods.
Attention Based Feature Fusion Network for Monkeypox Skin Lesion Detection
Aug 13, 2024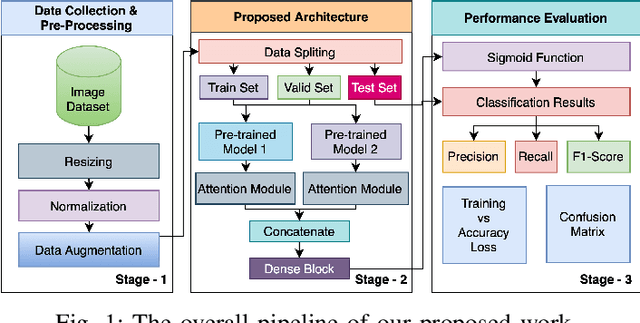
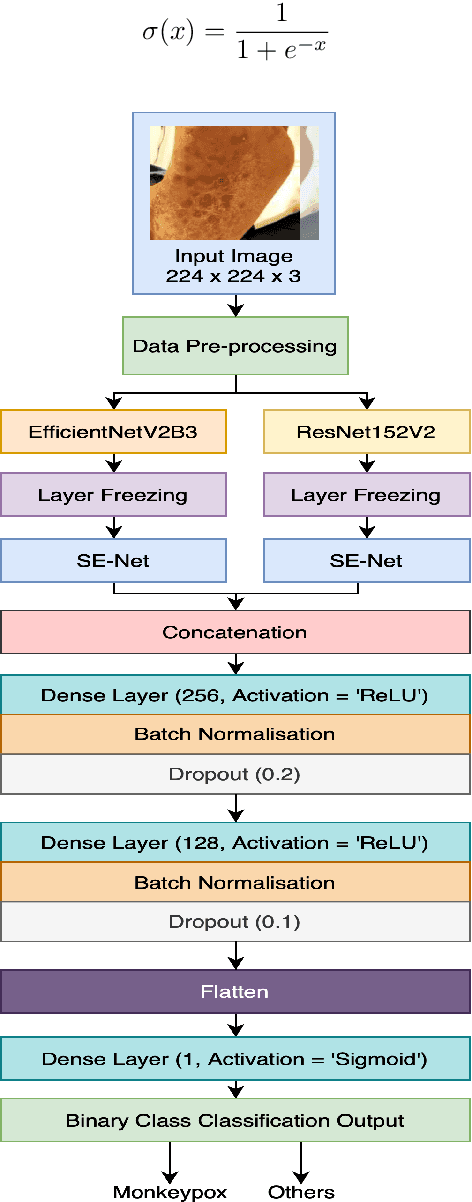
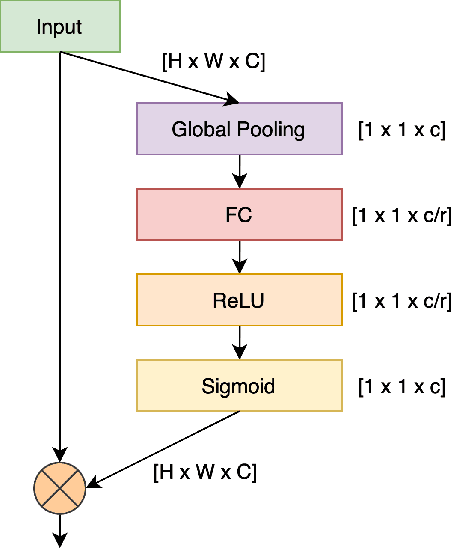
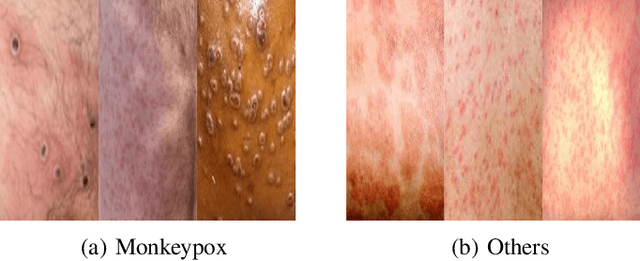
Abstract:The recent monkeypox outbreak has raised significant public health concerns due to its rapid spread across multiple countries. Monkeypox can be difficult to distinguish from chickenpox and measles in the early stages because the symptoms of all three diseases are similar. Modern deep learning algorithms can be used to identify diseases, including COVID-19, by analyzing images of the affected areas. In this study, we introduce a lightweight model that merges two pre-trained architectures, EfficientNetV2B3 and ResNet151V2, to classify human monkeypox disease. We have also incorporated the squeeze-and-excitation attention network module to focus on the important parts of the feature maps for classifying the monkeypox images. This attention module provides channels and spatial attention to highlight significant areas within feature maps. We evaluated the effectiveness of our model by extensively testing it on a publicly available Monkeypox Skin Lesions Dataset using a four-fold cross-validation approach. The evaluation metrics of our model were compared with the existing others. Our model achieves a mean validation accuracy of 96.52%, with precision, recall, and F1-score values of 96.58%, 96.52%, and 96.51%, respectively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge