Saowanee Ngamruengphong
Multi-contrast laser endoscopy for in vivo gastrointestinal imaging
May 15, 2025



Abstract:White light endoscopy is the clinical gold standard for detecting diseases in the gastrointestinal tract. Most applications involve identifying visual abnormalities in tissue color, texture, and shape. Unfortunately, the contrast of these features is often subtle, causing many clinically relevant cases to go undetected. To overcome this challenge, we introduce Multi-contrast Laser Endoscopy (MLE): a platform for widefield clinical imaging with rapidly tunable spectral, coherent, and directional illumination. We demonstrate three capabilities of MLE: enhancing tissue chromophore contrast with multispectral diffuse reflectance, quantifying blood flow using laser speckle contrast imaging, and characterizing mucosal topography using photometric stereo. We validate MLE with benchtop models, then demonstrate MLE in vivo during clinical colonoscopies. MLE images from 31 polyps demonstrate an approximate three-fold improvement in contrast and a five-fold improvement in color difference compared to white light and narrow band imaging. With the ability to reveal multiple complementary types of tissue contrast while seamlessly integrating into the clinical environment, MLE shows promise as an investigative tool to improve gastrointestinal imaging.
GAN Inversion for Data Augmentation to Improve Colonoscopy Lesion Classification
May 04, 2022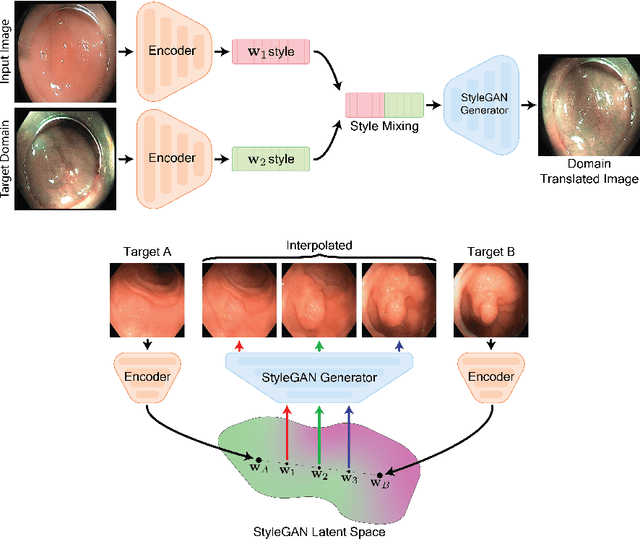

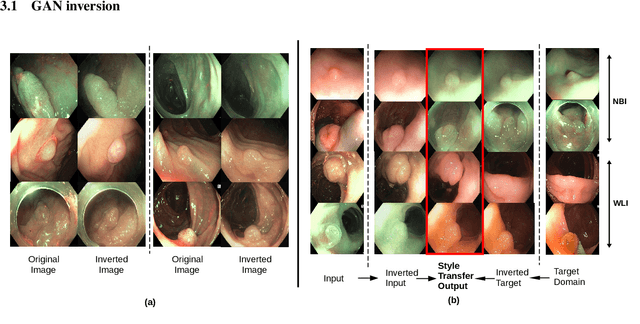
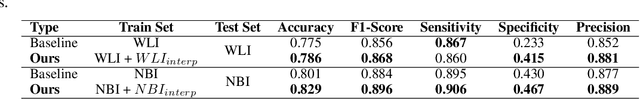
Abstract:A major challenge in applying deep learning to medical imaging is the paucity of annotated data. This study demonstrates that synthetic colonoscopy images generated by Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) inversion can be used as training data to improve the lesion classification performance of deep learning models. This approach inverts pairs of images with the same label to a semantically rich & disentangled latent space and manipulates latent representations to produce new synthetic images with the same label. We perform image modality translation (style transfer) between white light and narrowband imaging (NBI). We also generate realistic-looking synthetic lesion images by interpolating between original training images to increase the variety of lesion shapes in the training dataset. We show that these approaches outperform comparative colonoscopy data augmentation techniques without the need to re-train multiple generative models. This approach also leverages information from datasets that may not have been designed for the specific colonoscopy downstream task. E.g. using a bowel prep grading dataset for a polyp classification task. Our experiments show this approach can perform multiple colonoscopy data augmentations, which improve the downstream polyp classification performance over baseline and comparison methods by up to 6%.
Improving colonoscopy lesion classification using semi-supervised deep learning
Sep 07, 2020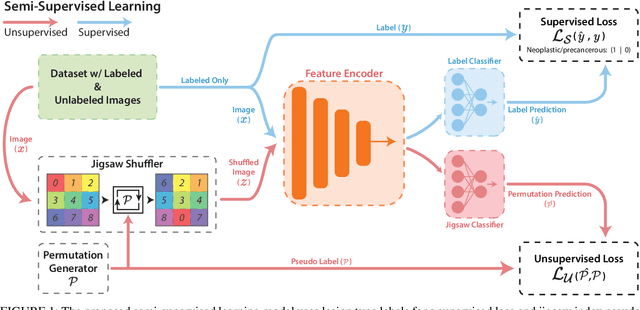

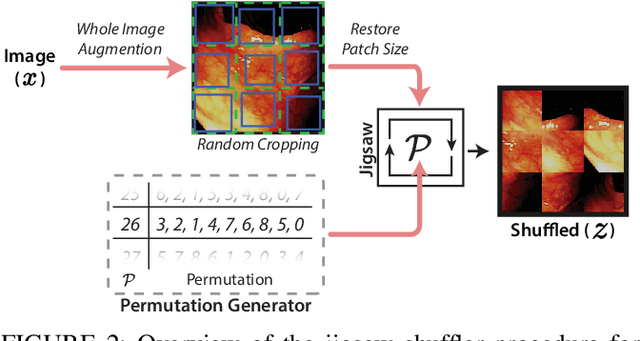
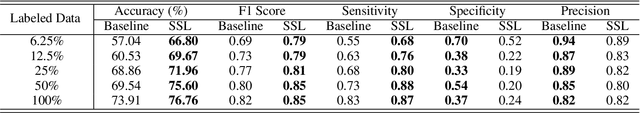
Abstract:While data-driven approaches excel at many image analysis tasks, the performance of these approaches is often limited by a shortage of annotated data available for training. Recent work in semi-supervised learning has shown that meaningful representations of images can be obtained from training with large quantities of unlabeled data, and that these representations can improve the performance of supervised tasks. Here, we demonstrate that an unsupervised jigsaw learning task, in combination with supervised training, results in up to a 9.8% improvement in correctly classifying lesions in colonoscopy images when compared to a fully-supervised baseline. We additionally benchmark improvements in domain adaptation and out-of-distribution detection, and demonstrate that semi-supervised learning outperforms supervised learning in both cases. In colonoscopy applications, these metrics are important given the skill required for endoscopic assessment of lesions, the wide variety of endoscopy systems in use, and the homogeneity that is typical of labeled datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge