Sanket Thakur
Leveraging Next-Active Objects for Context-Aware Anticipation in Egocentric Videos
Aug 16, 2023



Abstract:Objects are crucial for understanding human-object interactions. By identifying the relevant objects, one can also predict potential future interactions or actions that may occur with these objects. In this paper, we study the problem of Short-Term Object interaction anticipation (STA) and propose NAOGAT (Next-Active-Object Guided Anticipation Transformer), a multi-modal end-to-end transformer network, that attends to objects in observed frames in order to anticipate the next-active-object (NAO) and, eventually, to guide the model to predict context-aware future actions. The task is challenging since it requires anticipating future action along with the object with which the action occurs and the time after which the interaction will begin, a.k.a. the time to contact (TTC). Compared to existing video modeling architectures for action anticipation, NAOGAT captures the relationship between objects and the global scene context in order to predict detections for the next active object and anticipate relevant future actions given these detections, leveraging the objects' dynamics to improve accuracy. One of the key strengths of our approach, in fact, is its ability to exploit the motion dynamics of objects within a given clip, which is often ignored by other models, and separately decoding the object-centric and motion-centric information. Through our experiments, we show that our model outperforms existing methods on two separate datasets, Ego4D and EpicKitchens-100 ("Unseen Set"), as measured by several additional metrics, such as time to contact, and next-active-object localization. The code will be available upon acceptance.
Guided Attention for Next Active Object @ EGO4D STA Challenge
May 25, 2023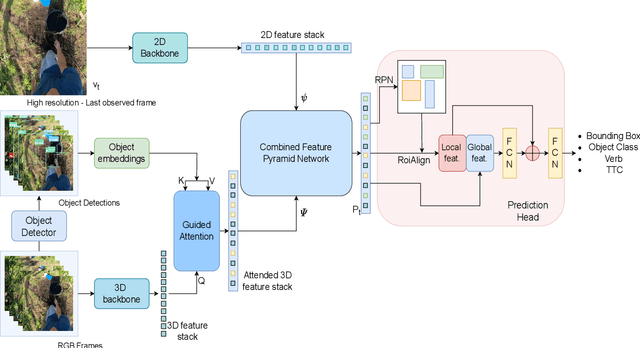
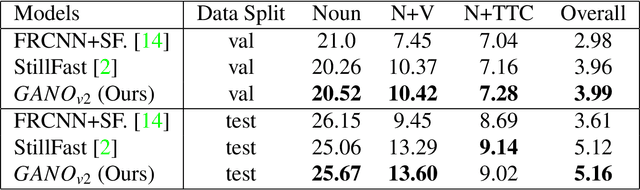
Abstract:In this technical report, we describe the Guided-Attention mechanism based solution for the short-term anticipation (STA) challenge for the EGO4D challenge. It combines the object detections, and the spatiotemporal features extracted from video clips, enhancing the motion and contextual information, and further decoding the object-centric and motion-centric information to address the problem of STA in egocentric videos. For the challenge, we build our model on top of StillFast with Guided Attention applied on fast network. Our model obtains better performance on the validation set and also achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) results on the challenge test set for EGO4D Short-Term Object Interaction Anticipation Challenge.
Enhancing Next Active Object-based Egocentric Action Anticipation with Guided Attention
May 22, 2023

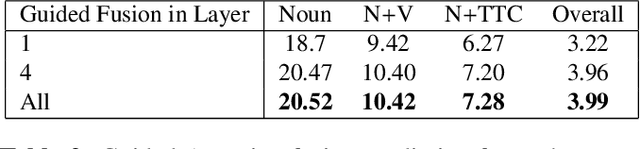
Abstract:Short-term action anticipation (STA) in first-person videos is a challenging task that involves understanding the next active object interactions and predicting future actions. Existing action anticipation methods have primarily focused on utilizing features extracted from video clips, but often overlooked the importance of objects and their interactions. To this end, we propose a novel approach that applies a guided attention mechanism between the objects, and the spatiotemporal features extracted from video clips, enhancing the motion and contextual information, and further decoding the object-centric and motion-centric information to address the problem of STA in egocentric videos. Our method, GANO (Guided Attention for Next active Objects) is a multi-modal, end-to-end, single transformer-based network. The experimental results performed on the largest egocentric dataset demonstrate that GANO outperforms the existing state-of-the-art methods for the prediction of the next active object label, its bounding box location, the corresponding future action, and the time to contact the object. The ablation study shows the positive contribution of the guided attention mechanism compared to other fusion methods. Moreover, it is possible to improve the next active object location and class label prediction results of GANO by just appending the learnable object tokens with the region of interest embeddings.
Anticipating Next Active Objects for Egocentric Videos
Feb 14, 2023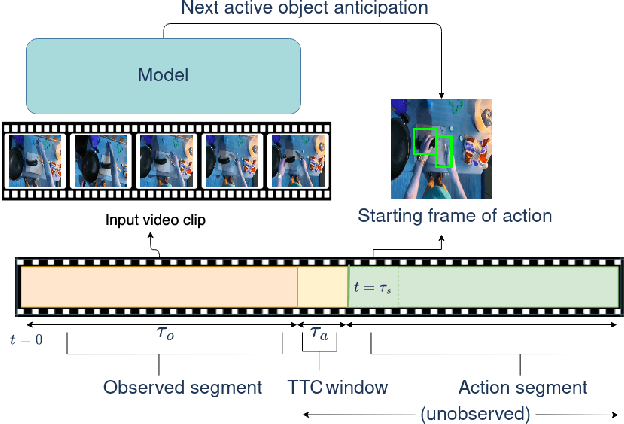
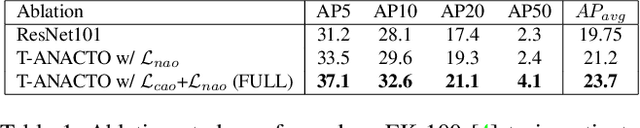
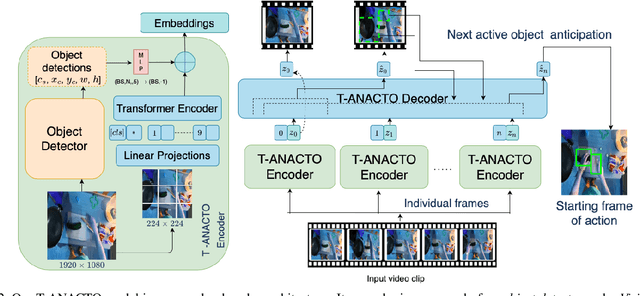
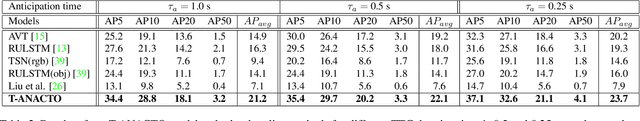
Abstract:This paper addresses the problem of anticipating the next-active-object location in the future, for a given egocentric video clip where the contact might happen, before any action takes place. The problem is considerably hard, as we aim at estimating the position of such objects in a scenario where the observed clip and the action segment are separated by the so-called ``time to contact'' (TTC) segment. Many methods have been proposed to anticipate the action of a person based on previous hand movements and interactions with the surroundings. However, there have been no attempts to investigate the next possible interactable object, and its future location with respect to the first-person's motion and the field-of-view drift during the TTC window. We define this as the task of Anticipating the Next ACTive Object (ANACTO). To this end, we propose a transformer-based self-attention framework to identify and locate the next-active-object in an egocentric clip. We benchmark our method on three datasets: EpicKitchens-100, EGTEA+ and Ego4D. We also provide annotations for the first two datasets. Our approach performs best compared to relevant baseline methods. We also conduct ablation studies to understand the effectiveness of the proposed and baseline methods on varying conditions. Code and ANACTO task annotations will be made available upon paper acceptance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge