Sankarshanaa Sagaram
SolarPanel Segmentation :Self-Supervised Learning for Imperfect Datasets
Feb 20, 2024

Abstract:The increasing adoption of solar energy necessitates advanced methodologies for monitoring and maintenance to ensure optimal performance of solar panel installations. A critical component in this context is the accurate segmentation of solar panels from aerial or satellite imagery, which is essential for identifying operational issues and assessing efficiency. This paper addresses the significant challenges in panel segmentation, particularly the scarcity of annotated data and the labour-intensive nature of manual annotation for supervised learning. We explore and apply Self-Supervised Learning (SSL) to solve these challenges. We demonstrate that SSL significantly enhances model generalization under various conditions and reduces dependency on manually annotated data, paving the way for robust and adaptable solar panel segmentation solutions.
ReFuSeg: Regularized Multi-Modal Fusion for Precise Brain Tumour Segmentation
Aug 26, 2023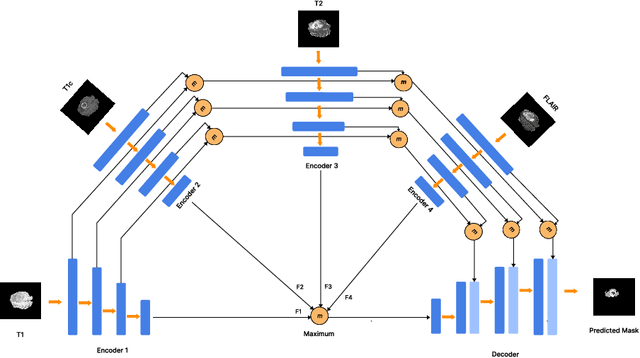
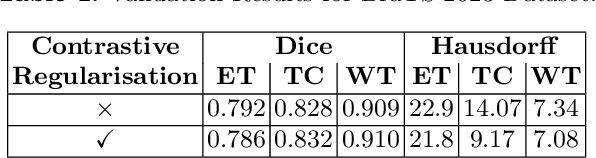
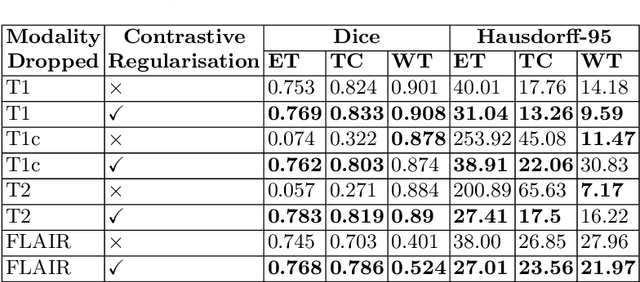
Abstract:Semantic segmentation of brain tumours is a fundamental task in medical image analysis that can help clinicians in diagnosing the patient and tracking the progression of any malignant entities. Accurate segmentation of brain lesions is essential for medical diagnosis and treatment planning. However, failure to acquire specific MRI imaging modalities can prevent applications from operating in critical situations, raising concerns about their reliability and overall trustworthiness. This paper presents a novel multi-modal approach for brain lesion segmentation that leverages information from four distinct imaging modalities while being robust to real-world scenarios of missing modalities, such as T1, T1c, T2, and FLAIR MRI of brains. Our proposed method can help address the challenges posed by artifacts in medical imagery due to data acquisition errors (such as patient motion) or a reconstruction algorithm's inability to represent the anatomy while ensuring a trade-off in accuracy. Our proposed regularization module makes it robust to these scenarios and ensures the reliability of lesion segmentation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge