Sandeep Ramachandra
Perfectly predicting ICU length of stay: too good to be true
Nov 10, 2022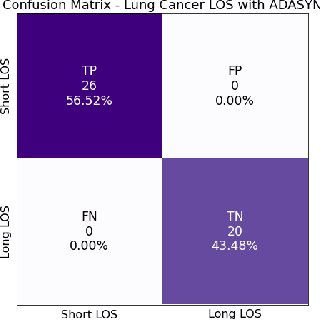
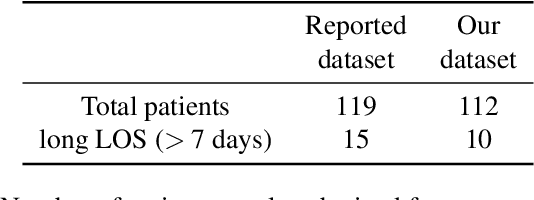

Abstract:A paper of Alsinglawi et al was recently accepted and published in Scientific Reports. In this paper, the authors aim to predict length of stay (LOS), discretized into either long (> 7 days) or short stays (< 7 days), of lung cancer patients in an ICU department using various machine learning techniques. The authors claim to achieve perfect results with an Area Under the Receiver Operating Characteristic curve (AUROC) of 100% with a Random Forest (RF) classifier with ADASYN class balancing over sampling technique, which if accurate could have significant implications for hospital management. However, we have identified several methodological flaws within the manuscript which cause the results to be overly optimistic and would have serious consequences if used in a clinical practice. Moreover, the reporting of the methodology is unclear and many important details are missing from the manuscript, which makes reproduction extremely difficult. We highlight the effect these oversights have had on the result and provide a more believable result of 88.91% AUROC when these oversights are corrected.
Transformer Networks for Data Augmentation of Human Physical Activity Recognition
Sep 04, 2021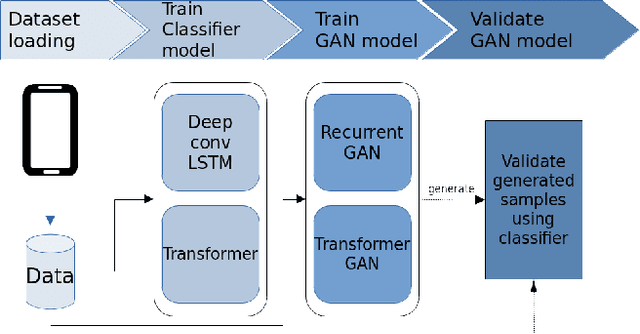
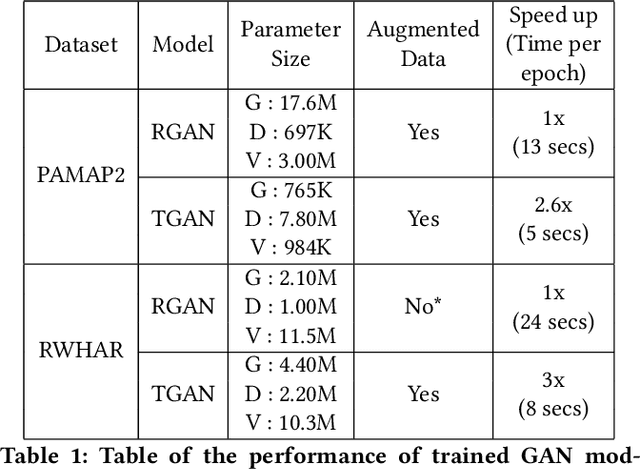

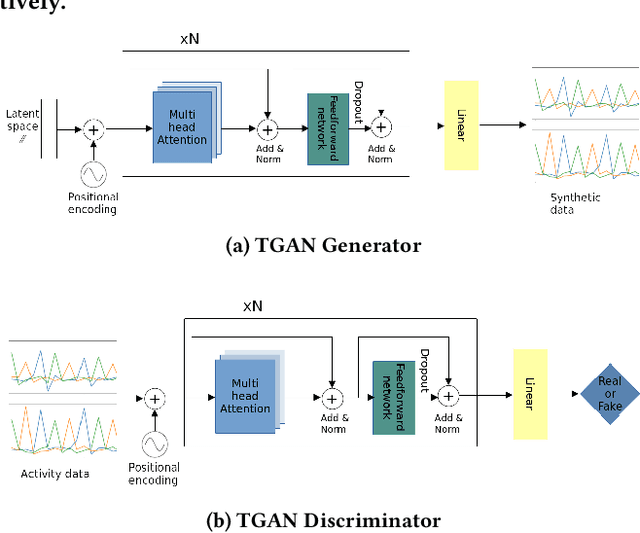
Abstract:Data augmentation is a widely used technique in classification to increase data used in training. It improves generalization and reduces amount of annotated human activity data needed for training which reduces labour and time needed with the dataset. Sensor time-series data, unlike images, cannot be augmented by computationally simple transformation algorithms. State of the art models like Recurrent Generative Adversarial Networks (RGAN) are used to generate realistic synthetic data. In this paper, transformer based generative adversarial networks which have global attention on data, are compared on PAMAP2 and Real World Human Activity Recognition data sets with RGAN. The newer approach provides improvements in time and savings in computational resources needed for data augmentation than previous approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge