Sanchari Das
POSTER: A Multi-Signal Model for Detecting Evasive Smishing
May 23, 2025Abstract:Smishing, or SMS-based phishing, poses an increasing threat to mobile users by mimicking legitimate communications through culturally adapted, concise, and deceptive messages, which can result in the loss of sensitive data or financial resources. In such, we present a multi-channel smishing detection model that combines country-specific semantic tagging, structural pattern tagging, character-level stylistic cues, and contextual phrase embeddings. We curated and relabeled over 84,000 messages across five datasets, including 24,086 smishing samples. Our unified architecture achieves 97.89% accuracy, an F1 score of 0.963, and an AUC of 99.73%, outperforming single-stream models by capturing diverse linguistic and structural cues. This work demonstrates the effectiveness of multi-signal learning in robust and region-aware phishing.
Natural Language Processing of Privacy Policies: A Survey
Jan 17, 2025Abstract:Natural Language Processing (NLP) is an essential subset of artificial intelligence. It has become effective in several domains, such as healthcare, finance, and media, to identify perceptions, opinions, and misuse, among others. Privacy is no exception, and initiatives have been taken to address the challenges of usable privacy notifications to users with the help of NLP. To this aid, we conduct a literature review by analyzing 109 papers at the intersection of NLP and privacy policies. First, we provide a brief introduction to privacy policies and discuss various facets of associated problems, which necessitate the application of NLP to elevate the current state of privacy notices and disclosures to users. Subsequently, we a) provide an overview of the implementation and effectiveness of NLP approaches for better privacy policy communication; b) identify the methodologies that can be further enhanced to provide robust privacy policies; and c) identify the gaps in the current state-of-the-art research. Our systematic analysis reveals that several research papers focus on annotating and classifying privacy texts for analysis but need to adequately dwell on other aspects of NLP applications, such as summarization. More specifically, ample research opportunities exist in this domain, covering aspects such as corpus generation, summarization vectors, contextualized word embedding, identification of privacy-relevant statement categories, fine-grained classification, and domain-specific model tuning.
The State of Lithium-Ion Battery Health Prognostics in the CPS Era
Mar 28, 2024Abstract:Lithium-ion batteries (Li-ion) have revolutionized energy storage technology, becoming integral to our daily lives by powering a diverse range of devices and applications. Their high energy density, fast power response, recyclability, and mobility advantages have made them the preferred choice for numerous sectors. This paper explores the seamless integration of Prognostics and Health Management within batteries, presenting a multidisciplinary approach that enhances the reliability, safety, and performance of these powerhouses. Remaining useful life (RUL), a critical concept in prognostics, is examined in depth, emphasizing its role in predicting component failure before it occurs. The paper reviews various RUL prediction methods, from traditional models to cutting-edge data-driven techniques. Furthermore, it highlights the paradigm shift toward deep learning architectures within the field of Li-ion battery health prognostics, elucidating the pivotal role of deep learning in addressing battery system complexities. Practical applications of PHM across industries are also explored, offering readers insights into real-world implementations.This paper serves as a comprehensive guide, catering to both researchers and practitioners in the field of Li-ion battery PHM.
Substituting Restorative Benefits of Being Outdoors through Interactive Augmented Spatial Soundscapes
Jul 28, 2020
Abstract:Geriatric depression is a common mental health condition affecting majority of older adults in the US. As per Attention Restoration Theory (ART), participation in outdoor activities is known to reduce depression and provide restorative benefits. However, many older adults, who suffer from depression, especially those who receive care in organizational settings, have less access to sensory experiences of the outdoor natural environment. This is often due to their physical or cognitive limitations and from lack of organizational resources to support outdoor activities. To address this, we plan to study how technology can bring the restorative benefits of outdoors to the indoor environments through augmented spatial natural soundscapes. Thus, we propose an interview and observation-based study at an assisted living facility to evaluate how augmented soundscapes substitute for outdoor restorative, social, and experiential benefits. We aim to integrate these findings into a minimally intrusive and intuitive design of an interactive augmented soundscape, for indoor organizational care settings.
MFA is a Waste of Time! Understanding Negative Connotation Towards MFA Applications via User Generated Content
Aug 16, 2019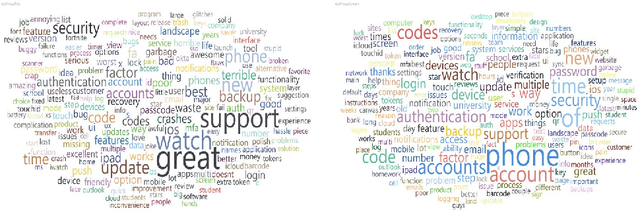

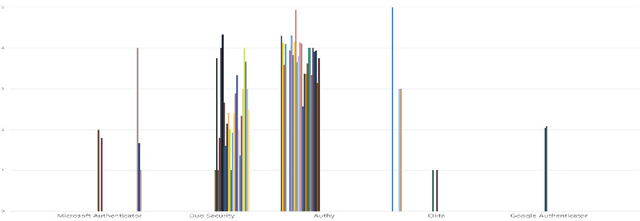
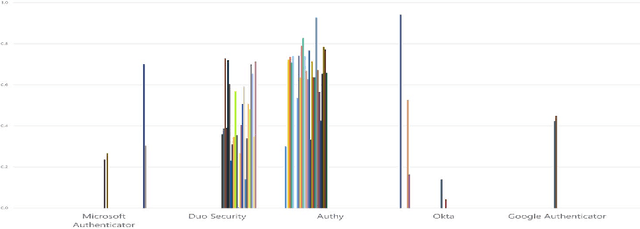
Abstract:Traditional single-factor authentication possesses several critical security vulnerabilities due to single-point failure feature. Multi-factor authentication (MFA), intends to enhance security by providing additional verification steps. However, in practical deployment, users often experience dissatisfaction while using MFA, which leads to non-adoption. In order to understand the current design and usability issues with MFA, we analyze aggregated user generated comments (N = 12,500) about application-based MFA tools from major distributors, such as, Amazon, Google Play, Apple App Store, and others. While some users acknowledge the security benefits of MFA, majority of them still faced problems with initial configuration, system design understanding, limited device compatibility, and risk trade-offs leading to non-adoption of MFA. Based on these results, we provide actionable recommendations in technological design, initial training, and risk communication to improve the adoption and user experience of MFA.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge