Samyak Prajapati
OGInfra: Geolocating Oil & Gas Infrastructure using Remote Sensing based Active Fire Data
Oct 30, 2022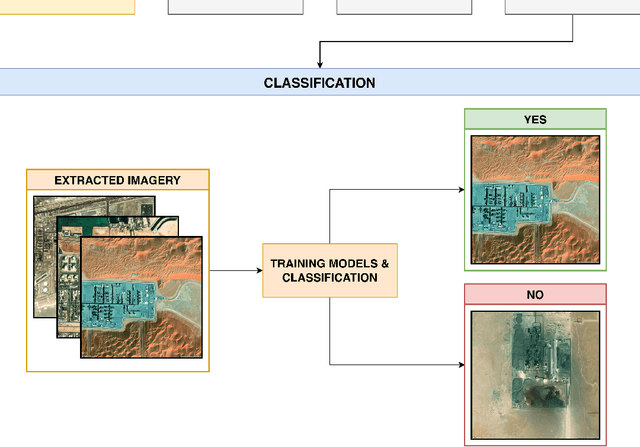
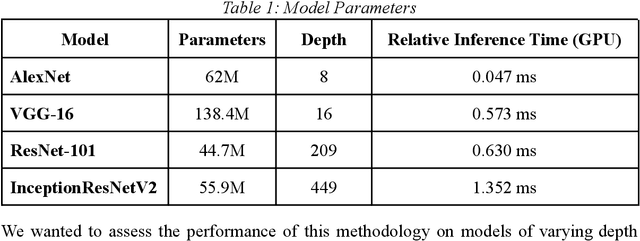
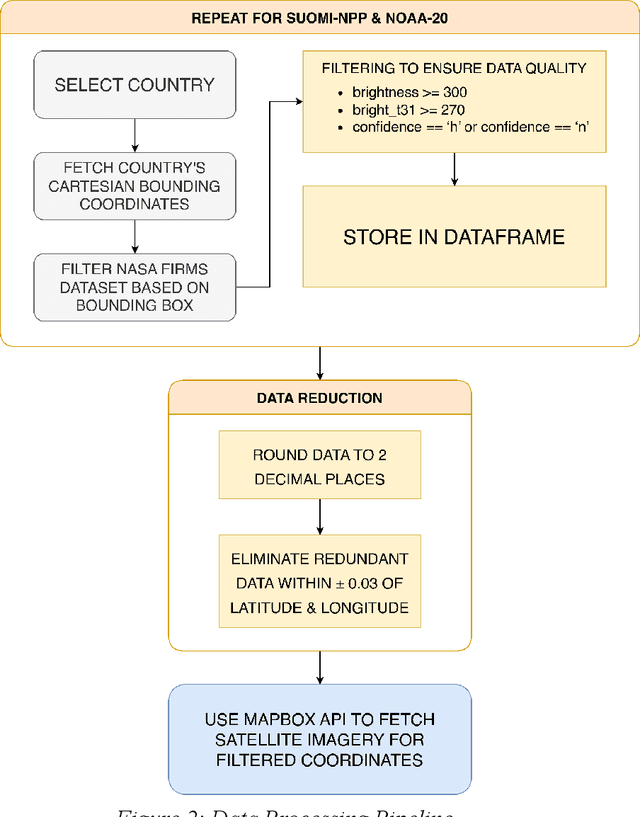

Abstract:Remote sensing has become a crucial part of our daily lives, whether it be from triangulating our location using GPS or providing us with a weather forecast. It has multiple applications in domains such as military, socio-economical, commercial, and even in supporting humanitarian efforts. This work proposes a novel technique for the automated geo-location of Oil & Gas infrastructure with the use of Active Fire Data from the NASA FIRMS data repository & Deep Learning techniques; achieving a top accuracy of 90.68% with the use of ResNet101.
Explanatory Analysis and Rectification of the Pitfalls in COVID-19 Datasets
Nov 10, 2021


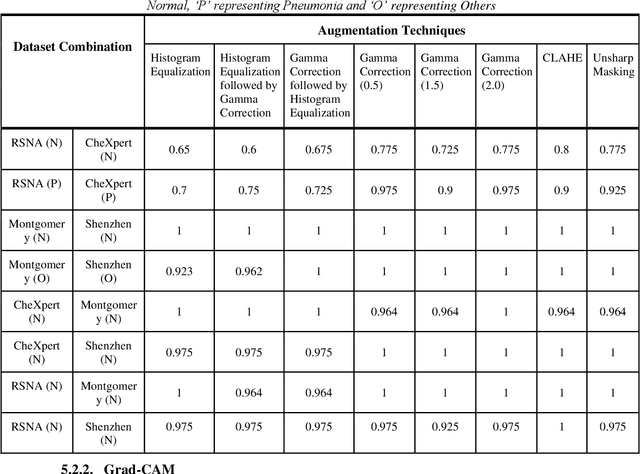
Abstract:Since the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020, millions of people have succumbed to this deadly virus. Many attempts have been made to devise an automated method of testing that could detect the virus. Various researchers around the globe have proposed deep learning based methodologies to detect the COVID-19 using Chest X-Rays. However, questions have been raised on the presence of bias in the publicly available Chest X-Ray datasets which have been used by the majority of the researchers. In this paper, we propose a 2 staged methodology to address this topical issue. Two experiments have been conducted as a part of stage 1 of the methodology to exhibit the presence of bias in the datasets. Subsequently, an image segmentation, super-resolution and CNN based pipeline along with different image augmentation techniques have been proposed in stage 2 of the methodology to reduce the effect of bias. InceptionResNetV2 trained on Chest X-Ray images that were augmented with Histogram Equalization followed by Gamma Correction when passed through the pipeline proposed in stage 2, yielded a top accuracy of 90.47% for 3-class (Normal, Pneumonia, and COVID-19) classification task.
Comparison of Traditional and Hybrid Time Series Models for Forecasting COVID-19 Cases
May 05, 2021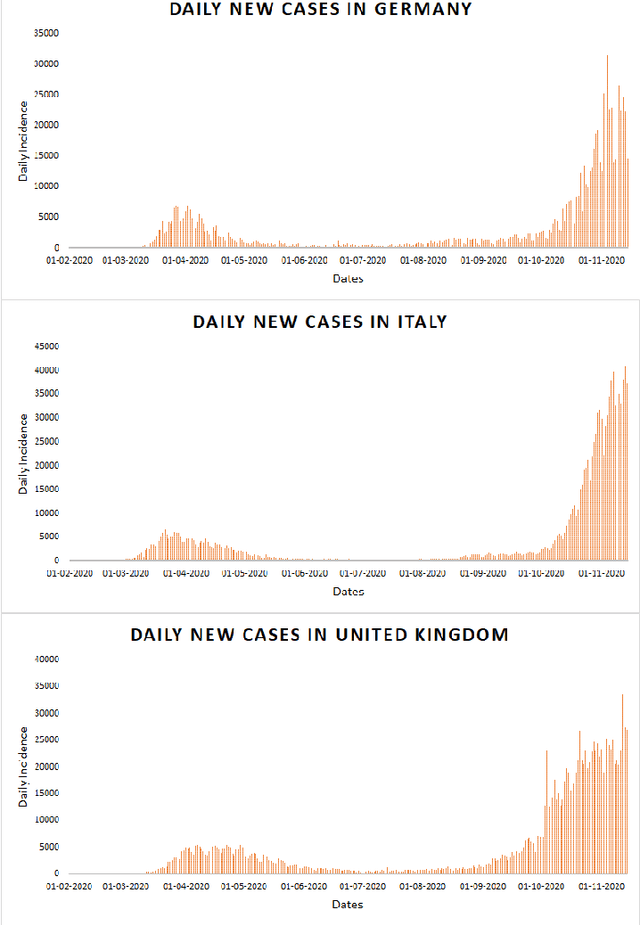
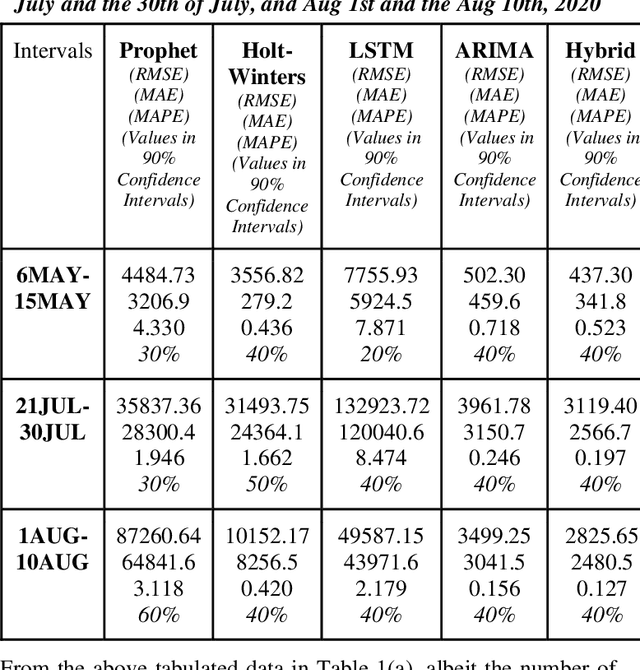
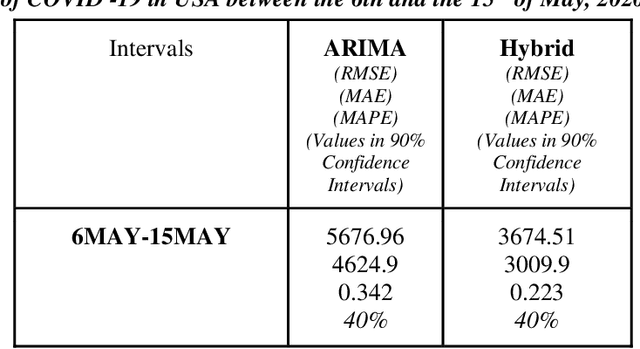

Abstract:Time series forecasting methods play critical role in estimating the spread of an epidemic. The coronavirus outbreak of December 2019 has already infected millions all over the world and continues to spread on. Just when the curve of the outbreak had started to flatten, many countries have again started to witness a rise in cases which is now being referred as the 2nd wave of the pandemic. A thorough analysis of time-series forecasting models is therefore required to equip state authorities and health officials with immediate strategies for future times. This aims of the study are three-fold: (a) To model the overall trend of the spread; (b) To generate a short-term forecast of 10 days in countries with the highest incidence of confirmed cases (USA, India and Brazil); (c) To quantitatively determine the algorithm that is best suited for precise modelling of the linear and non-linear features of the time series. The comparison of forecasting models for the total cumulative cases of each country is carried out by comparing the reported data and the predicted value, and then ranking the algorithms (Prophet, Holt-Winters, LSTM, ARIMA, and ARIMA-NARNN) based on their RMSE, MAE and MAPE values. The hybrid combination of ARIMA and NARNN (Nonlinear Auto-Regression Neural Network) gave the best result among the selected models with a reduced RMSE, which proved to be almost 35.3% better than one of the most prevalent method of time-series prediction (ARIMA). The results demonstrated the efficacy of the hybrid implementation of the ARIMA-NARNN model over other forecasting methods such as Prophet, Holt Winters, LSTM, and the ARIMA model in encapsulating the linear as well as non-linear patterns of the epidemical datasets.
DiaRet: A browser-based application for the grading of Diabetic Retinopathy with Integrated Gradients
Apr 11, 2021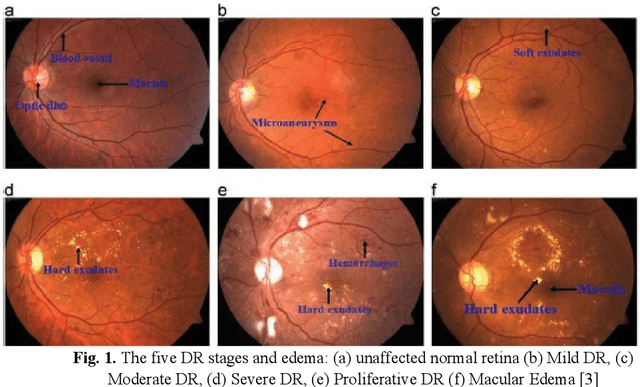
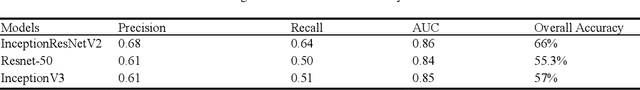
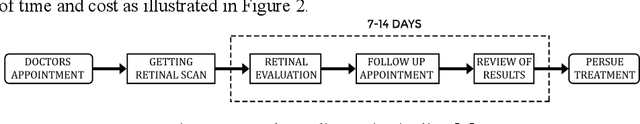
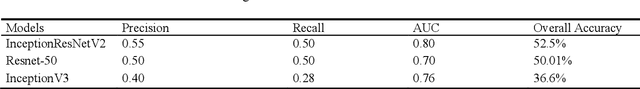
Abstract:Patients with long-standing diabetes often fall prey to Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) resulting in changes in the retina of the human eye, which may lead to loss of vision in extreme cases. The aim of this study is two-fold: (a) create deep learning models that were trained to grade degraded retinal fundus images and (b) to create a browser-based application that will aid in diagnostic procedures by highlighting the key features of the fundus image. In this research work, we have emulated the images plagued by distortions by degrading the images based on multiple different combinations of Light Transmission Disturbance, Image Blurring and insertion of Retinal Artifacts. InceptionV3, ResNet-50 and InceptionResNetV2 were trained and used to classify retinal fundus images based on their severity level and then further used in the creation of a browser-based application, which implements the Integration Gradient (IG) Attribution Mask on the input image and demonstrates the predictions made by the model and the probability associated with each class.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge