Amrit Raj
OGInfra: Geolocating Oil & Gas Infrastructure using Remote Sensing based Active Fire Data
Oct 30, 2022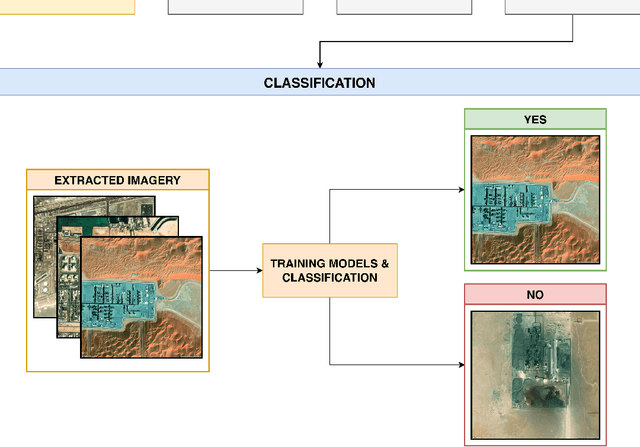
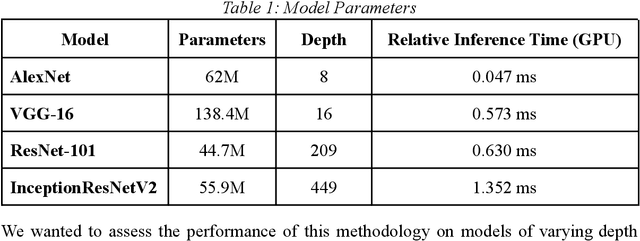
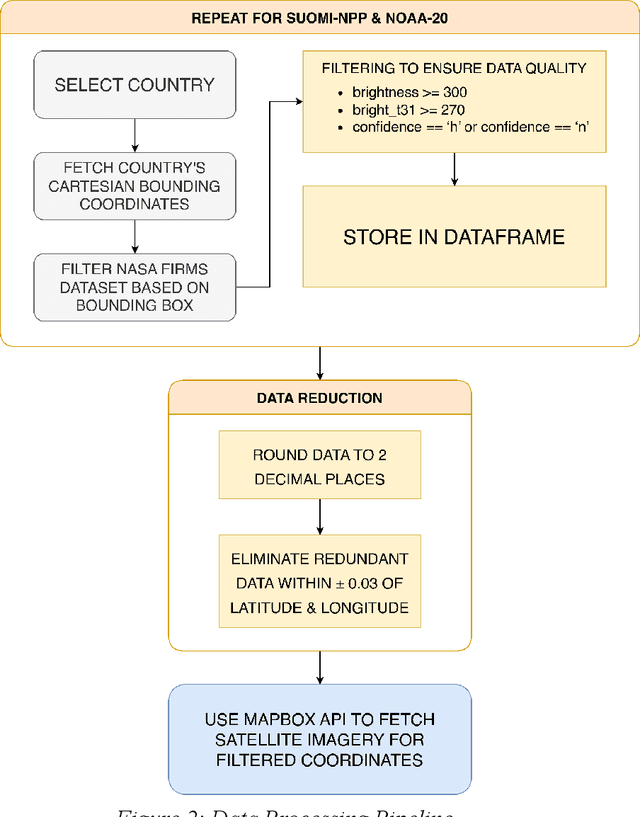

Abstract:Remote sensing has become a crucial part of our daily lives, whether it be from triangulating our location using GPS or providing us with a weather forecast. It has multiple applications in domains such as military, socio-economical, commercial, and even in supporting humanitarian efforts. This work proposes a novel technique for the automated geo-location of Oil & Gas infrastructure with the use of Active Fire Data from the NASA FIRMS data repository & Deep Learning techniques; achieving a top accuracy of 90.68% with the use of ResNet101.
Explanatory Analysis and Rectification of the Pitfalls in COVID-19 Datasets
Nov 10, 2021


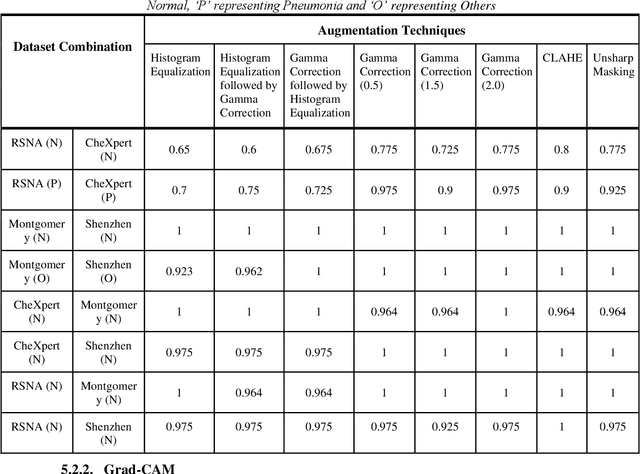
Abstract:Since the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020, millions of people have succumbed to this deadly virus. Many attempts have been made to devise an automated method of testing that could detect the virus. Various researchers around the globe have proposed deep learning based methodologies to detect the COVID-19 using Chest X-Rays. However, questions have been raised on the presence of bias in the publicly available Chest X-Ray datasets which have been used by the majority of the researchers. In this paper, we propose a 2 staged methodology to address this topical issue. Two experiments have been conducted as a part of stage 1 of the methodology to exhibit the presence of bias in the datasets. Subsequently, an image segmentation, super-resolution and CNN based pipeline along with different image augmentation techniques have been proposed in stage 2 of the methodology to reduce the effect of bias. InceptionResNetV2 trained on Chest X-Ray images that were augmented with Histogram Equalization followed by Gamma Correction when passed through the pipeline proposed in stage 2, yielded a top accuracy of 90.47% for 3-class (Normal, Pneumonia, and COVID-19) classification task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge