Sakthivel Rajendran
BioALBERT: A Simple and Effective Pre-trained Language Model for Biomedical Named Entity Recognition
Sep 19, 2020
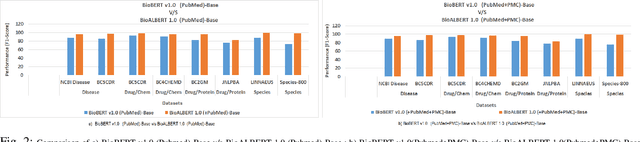
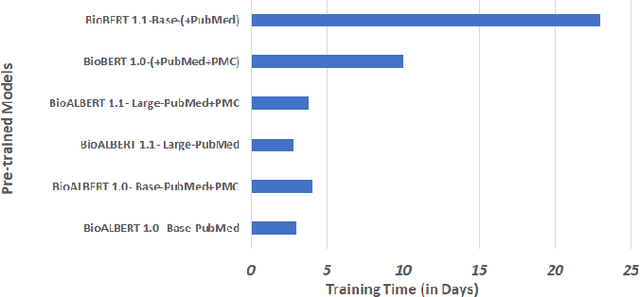

Abstract:In recent years, with the growing amount of biomedical documents, coupled with advancement in natural language processing algorithms, the research on biomedical named entity recognition (BioNER) has increased exponentially. However, BioNER research is challenging as NER in the biomedical domain are: (i) often restricted due to limited amount of training data, (ii) an entity can refer to multiple types and concepts depending on its context and, (iii) heavy reliance on acronyms that are sub-domain specific. Existing BioNER approaches often neglect these issues and directly adopt the state-of-the-art (SOTA) models trained in general corpora which often yields unsatisfactory results. We propose biomedical ALBERT (A Lite Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers for Biomedical Text Mining) bioALBERT, an effective domain-specific language model trained on large-scale biomedical corpora designed to capture biomedical context-dependent NER. We adopted a self-supervised loss used in ALBERT that focuses on modelling inter-sentence coherence to better learn context-dependent representations and incorporated parameter reduction techniques to lower memory consumption and increase the training speed in BioNER. In our experiments, BioALBERT outperformed comparative SOTA BioNER models on eight biomedical NER benchmark datasets with four different entity types. We trained four different variants of BioALBERT models which are available for the research community to be used in future research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge