Sakshyam Panda
Principled Data-Driven Decision Support for Cyber-Forensic Investigations
Nov 23, 2022
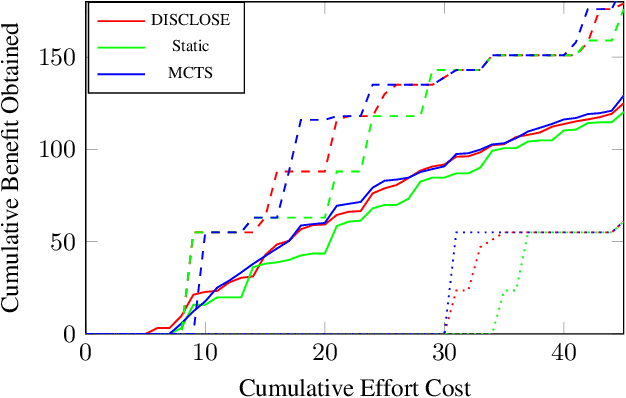
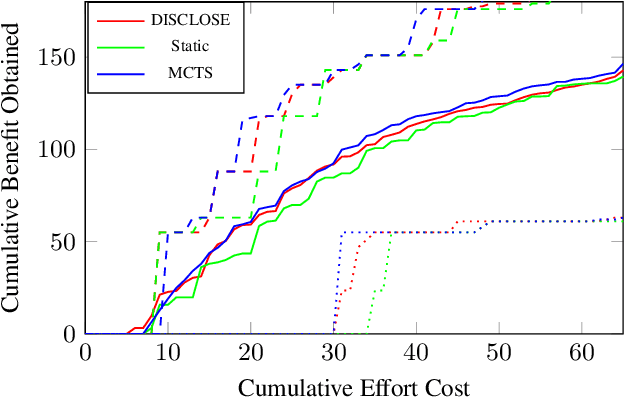
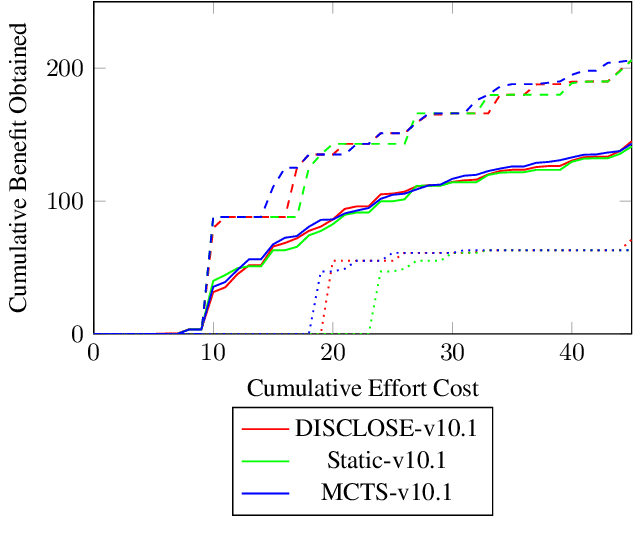
Abstract:In the wake of a cybersecurity incident, it is crucial to promptly discover how the threat actors breached security in order to assess the impact of the incident and to develop and deploy countermeasures that can protect against further attacks. To this end, defenders can launch a cyber-forensic investigation, which discovers the techniques that the threat actors used in the incident. A fundamental challenge in such an investigation is prioritizing the investigation of particular techniques since the investigation of each technique requires time and effort, but forensic analysts cannot know which ones were actually used before investigating them. To ensure prompt discovery, it is imperative to provide decision support that can help forensic analysts with this prioritization. A recent study demonstrated that data-driven decision support, based on a dataset of prior incidents, can provide state-of-the-art prioritization. However, this data-driven approach, called DISCLOSE, is based on a heuristic that utilizes only a subset of the available information and does not approximate optimal decisions. To improve upon this heuristic, we introduce a principled approach for data-driven decision support for cyber-forensic investigations. We formulate the decision-support problem using a Markov decision process, whose states represent the states of a forensic investigation. To solve the decision problem, we propose a Monte Carlo tree search based method, which relies on a k-NN regression over prior incidents to estimate state-transition probabilities. We evaluate our proposed approach on multiple versions of the MITRE ATT&CK dataset, which is a knowledge base of adversarial techniques and tactics based on real-world cyber incidents, and demonstrate that our approach outperforms DISCLOSE in terms of techniques discovered per effort spent.
HoneyCar: A Framework to Configure HoneypotVulnerabilities on the Internet of Vehicles
Nov 03, 2021
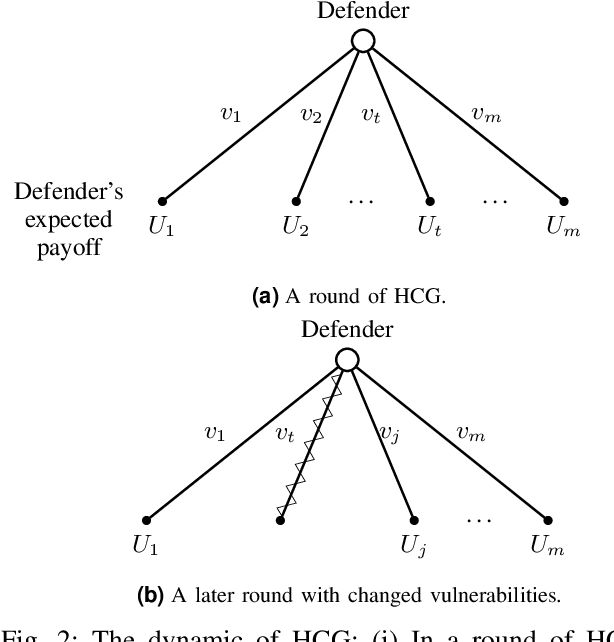
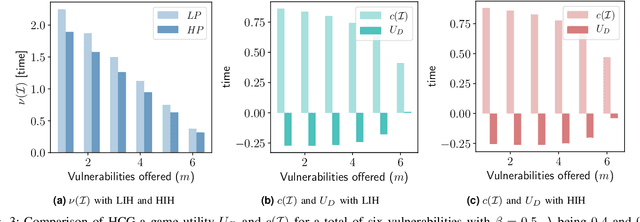
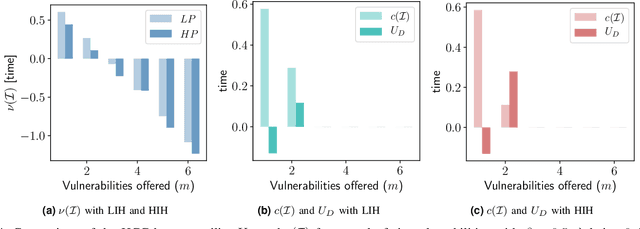
Abstract:The Internet of Vehicles (IoV), whereby interconnected vehicles communicate with each other and with road infrastructure on a common network, has promising socio-economic benefits but also poses new cyber-physical threats. Data on vehicular attackers can be realistically gathered through cyber threat intelligence using systems like honeypots. Admittedly, configuring honeypots introduces a trade-off between the level of honeypot-attacker interactions and any incurred overheads and costs for implementing and monitoring these honeypots. We argue that effective deception can be achieved through strategically configuring the honeypots to represent components of the IoV and engage attackers to collect cyber threat intelligence. In this paper, we present HoneyCar, a novel decision support framework for honeypot deception in IoV. HoneyCar builds upon a repository of known vulnerabilities of the autonomous and connected vehicles found in the Common Vulnerabilities and Exposure (CVE) data within the National Vulnerability Database (NVD) to compute optimal honeypot configuration strategies. By taking a game-theoretic approach, we model the adversarial interaction as a repeated imperfect-information zero-sum game in which the IoV network administrator chooses a set of vulnerabilities to offer in a honeypot and a strategic attacker chooses a vulnerability of the IoV to exploit under uncertainty. Our investigation is substantiated by examining two different versions of the game, with and without the re-configuration cost to empower the network administrator to determine optimal honeypot configurations. We evaluate HoneyCar in a realistic use case to support decision makers with determining optimal honeypot configuration strategies for strategic deployment in IoV.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge