Saksham Sharma
AI for Sustainable Data Protection and Fair Algorithmic Management in Environmental Regulation
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Integration of AI into environmental regulation represents a significant advancement in data management. It offers promising results in both data protection plus algorithmic fairness. This research addresses the critical need for sustainable data protection in the era of ever evolving cyber threats. Traditional encryption methods face limitations in handling the dynamic nature of environmental data. This necessitates the exploration of advanced cryptographic techniques. The objective of this study is to evaluate how AI can enhance these techniques to ensure robust data protection while facilitating fair algorithmic management. The methodology involves a comprehensive review of current advancements in AI-enhanced homomorphic encryption (HE) and multi-party computation (MPC). It is coupled with an analysis of how these techniques can be applied to environmental data regulation. Key findings indicate that AI-driven dynamic key management, adaptive encryption schemes, and optimized computational efficiency in HE, alongside AI-enhanced protocol optimization and fault mitigation in MPC, significantly improve the security of environmental data processing. These findings highlight a crucial research gap in the intersection of AI, cyber laws, and environmental regulation, particularly in terms of addressing algorithmic bias, transparency, and accountability. The implications of this research underscore the need for stricter cyber laws. Also, the development of comprehensive regulations to safeguard sensitive environmental data. Future efforts should focus on refining AI systems to balance security with privacy and ensuring that regulatory frameworks can adapt to technological advancements. This study provides a foundation for future research aimed at achieving secure sustainable environmental data management through AI innovations.
* Presented at National Conference on Navigating The Intersection of Artificial Intelligence and Law: Ethical and Legal Horizons, 29 September 2024, pp. 91-106
IRisPath: Enhancing Off-Road Navigation with Robust IR-RGB Fusion for Improved Day and Night Traversability
Dec 04, 2024
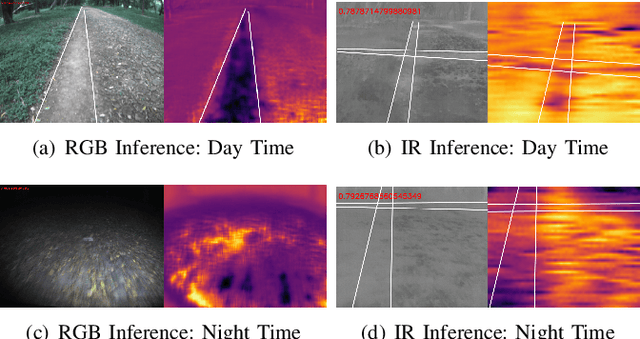
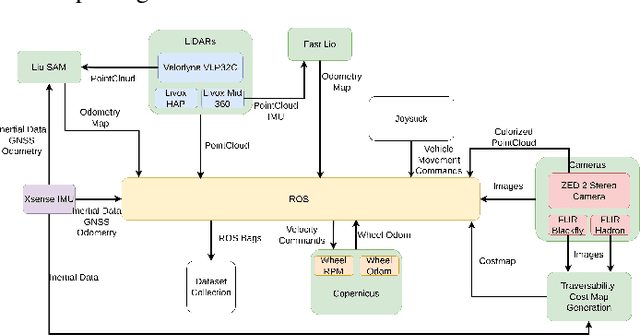
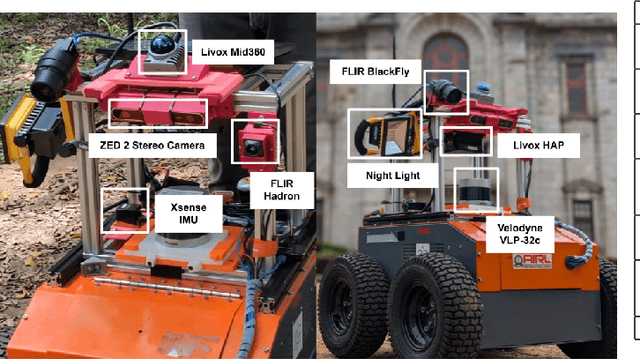
Abstract:Autonomous off-road navigation is required for applications in agriculture, construction, search and rescue and defence. Traditional on-road autonomous methods struggle with dynamic terrains, leading to poor vehicle control on off-road. Recent deep-learning models have used perception sensors along with kinesthetic feedback for navigation on such terrains. However, this approach has out-of-domain uncertainty. Factors like change in weather and time of day impacts the performance of the model. We propose a multi modal fusion network FuseIsPath capable of using LWIR and RGB images to provide robustness against dynamic weather and light conditions. To aid further works in this domain, we also open-source a day-night dataset with LWIR and RGB images along with pseudo-labels for traversability. In order to co-register the two images we developed a novel method for targetless extrinsic calibration of LWIR, LiDAR and RGB cameras with translation accuracy of 1.7cm and rotation accuracy of 0.827degree.
TipsC: Tips and Corrections for programming MOOCs
Apr 02, 2018



Abstract:With the widespread adoption of MOOCs in academic institutions, it has become imperative to come up with better techniques to solve the tutoring and grading problems posed by programming courses. Programming being the new 'writing', it becomes a challenge to ensure that a large section of the society is exposed to programming. Due to the gradient in learning abilities of students, the course instructor must ensure that everyone can cope up with the material, and receive adequate help in completing assignments while learning along the way. We introduce TipsC for this task. By analyzing a large number of correct submissions, TipsC can search for correct codes resembling a given incorrect solution. Without revealing the actual code, TipsC then suggests changes in the incorrect code to help the student fix logical runtime errors. In addition, this also serves as a cluster visualization tool for the instructor, revealing different patterns in user submissions. We evaluated the effectiveness of TipsC's clustering algorithm on data collected from previous offerings of an introductory programming course conducted at IIT Kanpur where the grades were given by human TAs. The results show the weighted average variance of marks for clusters when similar submissions are grouped together is 47% less compared to the case when all programs are grouped together.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge