Ruizhong Xu
Integrated Sensing and Communication enabled Multiple Base Stations Cooperative Sensing Towards 6G
Oct 11, 2023Abstract:Driven by the intelligent applications of sixth-generation (6G) mobile communication systems such as smart city and autonomous driving, which connect the physical and cyber space, the integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) brings a revolutionary change to the base stations (BSs) of 6G by integrating radar sensing and communication in the same hardware and wireless resource. However, with the requirements of long-range and accurate sensing in the applications of smart city and autonomous driving, the ISAC enabled single BS still has a limitation in the sensing range and accuracy. With the networked infrastructures of mobile communication systems, multi-BS cooperative sensing is a natural choice satisfying the requirement of long-range and accurate sensing. In this article, the framework of multi-BS cooperative sensing is proposed, breaking through the limitation of single-BS sensing. The enabling technologies, including unified ISAC performance metrics, ISAC signal design and optimization, interference management, cooperative sensing algorithms, are introduced in details. The performance evaluation results are provided to verify the effectiveness of multi-BS cooperative sensing schemes. With ISAC enabled multi-BS cooperative sensing (ISAC-MCS), the intelligent infrastructures connecting physical and cyber space can be established, ushering the era of 6G promoting the intelligence of everything.
* 11 pages 6 figures
Symbol-level Integrated Sensing and Communication enabled Multiple Base Stations Cooperative Sensing
Aug 13, 2023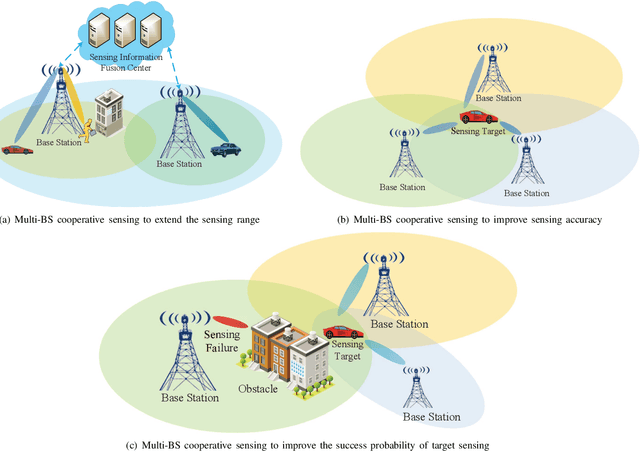
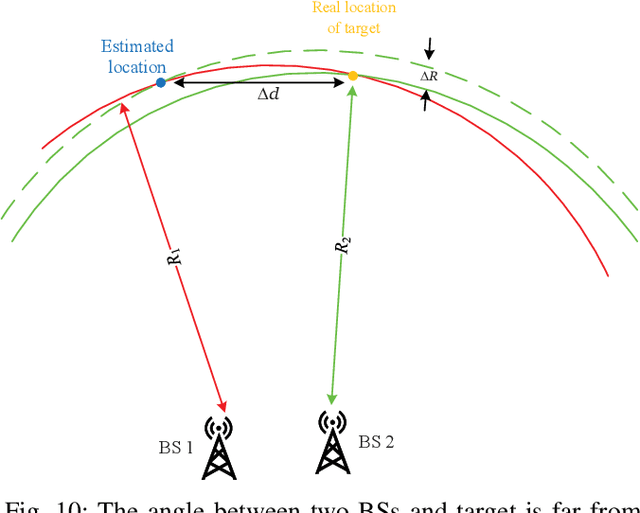
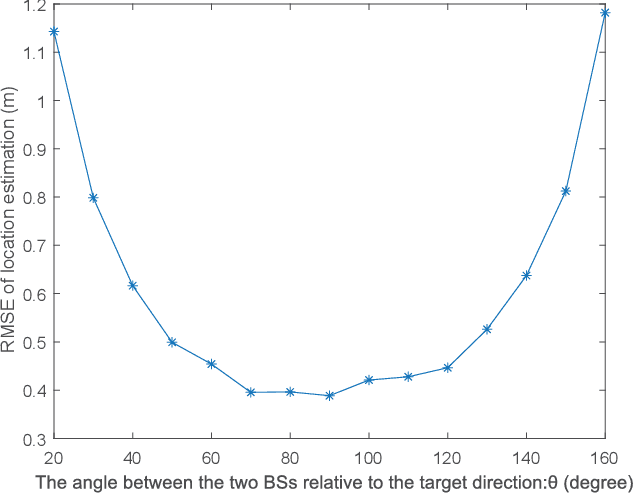
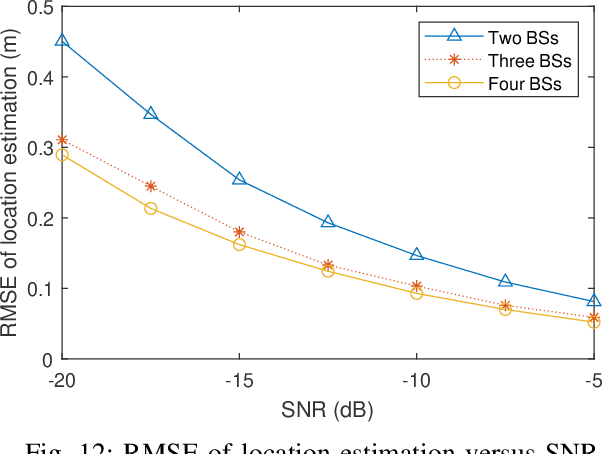
Abstract:With the support of integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) technology, mobile communication system will integrate the function of wireless sensing, thereby facilitating new intelligent applications such as smart city and intelligent transportation. Due to the limited sensing accuracy and sensing range of single base station (BS), multi-BS cooperative sensing can be applied to realize high-accurate, long-range and continuous sensing, exploiting the specific advantages of large-scale networked mobile communication system. This paper proposes a cooperative sensing method suitable to mobile communication systems, which applies symbol-level sensing information fusion to estimate the location and velocity of target. With the demodulation symbols obtained from the echo signals of multiple BSs, the phase features contained in the demodulation symbols are used in the fusion procedure, which realizes cooperative sensing with the synchronization level of mobile communication system. Compared with the signal-level fusion in the area of distributed aperture coherence-synthetic radars, the requirement of synchronization is much lower. When signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) is -5 dB, it is evaluated that symbol-level multi-BS cooperative sensing effectively improves the accuracy of distance and velocity estimation of target. Compared with single-BS sensing, the accuracy of distance and velocity estimation is improved by 40% and 72%, respectively. Compared with data-level multi-BS cooperative sensing based on maximum likelihood (ML) estimation, the accuracy of location and velocity estimation is improved by 12% and 63%, respectively. This work may provide a guideline for the design of multi-BS cooperative sensing system to exploit the widely deployed networked mobile communication system.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge