Ruijian Xu
Learning an Effective Context-Response Matching Model with Self-Supervised Tasks for Retrieval-based Dialogues
Sep 14, 2020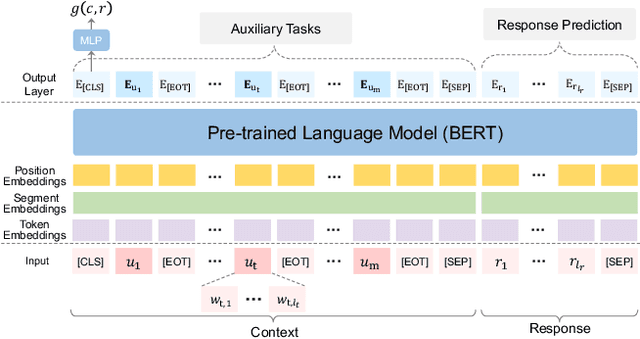
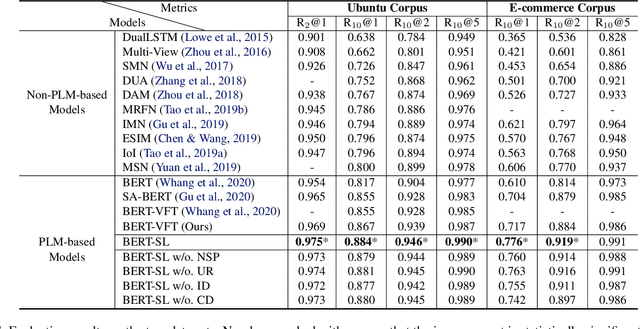
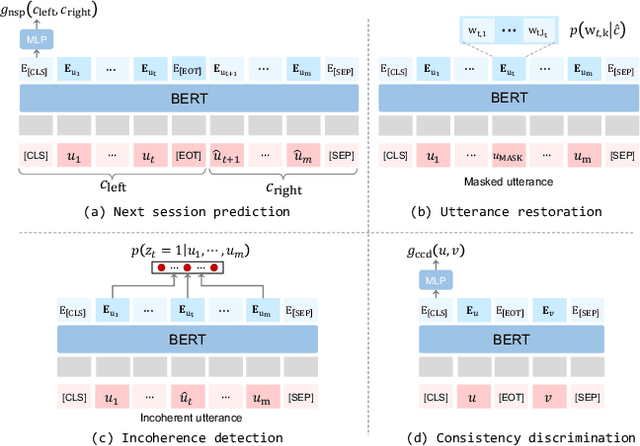
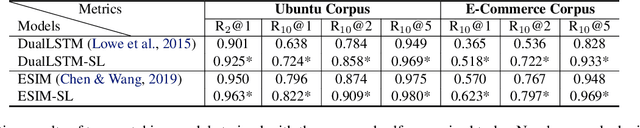
Abstract:Building an intelligent dialogue system with the ability to select a proper response according to a multi-turn context is a great challenging task. Existing studies focus on building a context-response matching model with various neural architectures or PLMs and typically learning with a single response prediction task. These approaches overlook many potential training signals contained in dialogue data, which might be beneficial for context understanding and produce better features for response prediction. Besides, the response retrieved from existing dialogue systems supervised by the conventional way still faces some critical challenges, including incoherence and inconsistency. To address these issues, in this paper, we propose learning a context-response matching model with auxiliary self-supervised tasks designed for the dialogue data based on pre-trained language models. Specifically, we introduce four self-supervised tasks including next session prediction, utterance restoration, incoherence detection and consistency discrimination, and jointly train the PLM-based response selection model with these auxiliary tasks in a multi-task manner. By this means, the auxiliary tasks can guide the learning of the matching model to achieve a better local optimum and select a more proper response. Experiment results on two benchmarks indicate that the proposed auxiliary self-supervised tasks bring significant improvement for multi-turn response selection in retrieval-based dialogues, and our model achieves new state-of-the-art results on both datasets.
Chat More If You Like: Dynamic Cue Words Planning to Flow Longer Conversations
Nov 19, 2018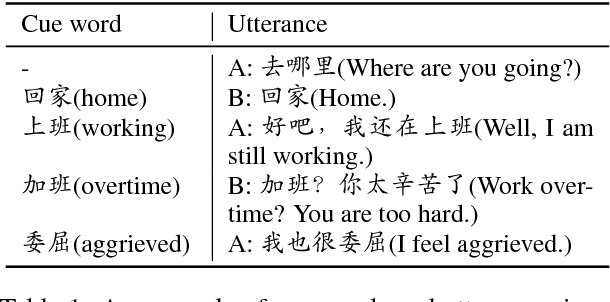
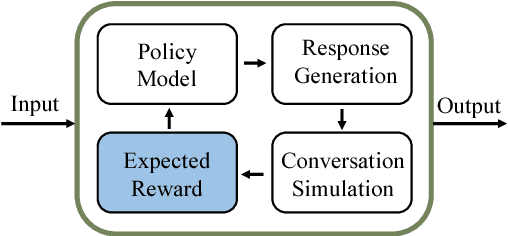
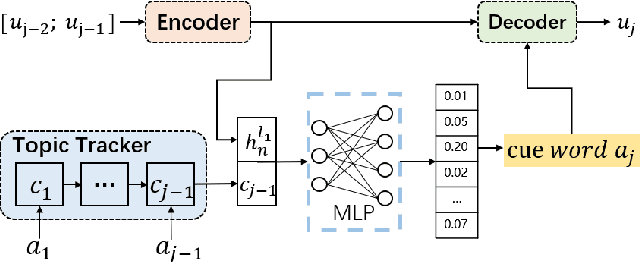

Abstract:To build an open-domain multi-turn conversation system is one of the most interesting and challenging tasks in Artificial Intelligence. Many research efforts have been dedicated to building such dialogue systems, yet few shed light on modeling the conversation flow in an ongoing dialogue. Besides, it is common for people to talk about highly relevant aspects during a conversation. And the topics are coherent and drift naturally, which demonstrates the necessity of dialogue flow modeling. To this end, we present the multi-turn cue-words driven conversation system with reinforcement learning method (RLCw), which strives to select an adaptive cue word with the greatest future credit, and therefore improve the quality of generated responses. We introduce a new reward to measure the quality of cue words in terms of effectiveness and relevance. To further optimize the model for long-term conversations, a reinforcement approach is adopted in this paper. Experiments on real-life dataset demonstrate that our model consistently outperforms a set of competitive baselines in terms of simulated turns, diversity and human evaluation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge