Roland Daynauth
SLMEval: Entropy-Based Calibration for Human-Aligned Evaluation of Large Language Models
May 21, 2025
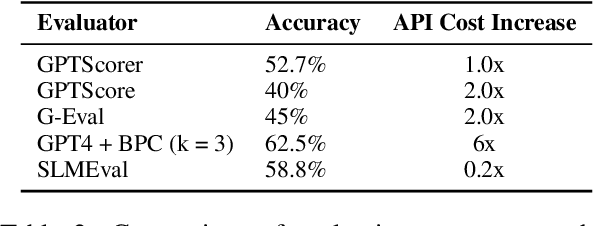
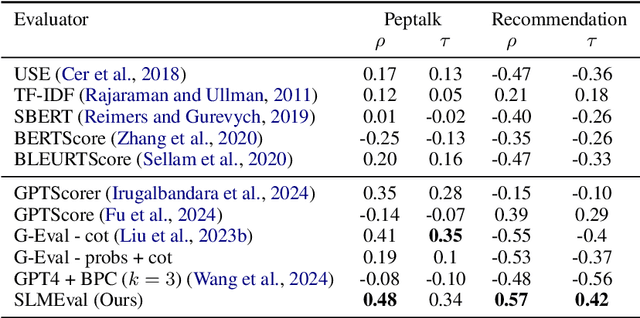
Abstract:The LLM-as-a-Judge paradigm offers a scalable, reference-free approach for evaluating language models. Although several calibration techniques have been proposed to better align these evaluators with human judgment, prior studies focus primarily on narrow, well-structured benchmarks. As a result, it remains unclear whether such calibrations generalize to real-world, open-ended tasks. In this work, we show that SOTA calibrated evaluators often fail in these settings, exhibiting weak or even negative correlation with human judgments. To address this, we propose SLMEval, a novel and efficient calibration method based on entropy maximization over a small amount of human preference data. By estimating a latent distribution over model quality and reweighting evaluator scores accordingly, SLMEval achieves strong correlation with human evaluations across two real-world production use cases and the public benchmark. For example, on one such task, SLMEval achieves a Spearman correlation of 0.57 with human judgments, while G-Eval yields a negative correlation. In addition, SLMEval reduces evaluation costs by 5-30x compared to GPT-4-based calibrated evaluators such as G-eval.
Ranking Unraveled: Recipes for LLM Rankings in Head-to-Head AI Combat
Nov 19, 2024



Abstract:Deciding which large language model (LLM) to use is a complex challenge. Pairwise ranking has emerged as a new method for evaluating human preferences for LLMs. This approach entails humans evaluating pairs of model outputs based on a predefined criterion. By collecting these comparisons, a ranking can be constructed using methods such as Elo. However, applying these algorithms as constructed in the context of LLM evaluation introduces several challenges. In this paper, we explore the effectiveness of ranking systems for head-to-head comparisons of LLMs. We formally define a set of fundamental principles for effective ranking and conduct a series of extensive evaluations on the robustness of several ranking algorithms in the context of LLMs. Our analysis uncovers key insights into the factors that affect ranking accuracy and efficiency, offering guidelines for selecting the most appropriate methods based on specific evaluation contexts and resource constraints.
Guylingo: The Republic of Guyana Creole Corpora
May 06, 2024Abstract:While major languages often enjoy substantial attention and resources, the linguistic diversity across the globe encompasses a multitude of smaller, indigenous, and regional languages that lack the same level of computational support. One such region is the Caribbean. While commonly labeled as "English speaking", the ex-British Caribbean region consists of a myriad of Creole languages thriving alongside English. In this paper, we present Guylingo: a comprehensive corpus designed for advancing NLP research in the domain of Creolese (Guyanese English-lexicon Creole), the most widely spoken language in the culturally rich nation of Guyana. We first outline our framework for gathering and digitizing this diverse corpus, inclusive of colloquial expressions, idioms, and regional variations in a low-resource language. We then demonstrate the challenges of training and evaluating NLP models for machine translation in Creole. Lastly, we discuss the unique opportunities presented by recent NLP advancements for accelerating the formal adoption of Creole languages as official languages in the Caribbean.
A Trade-off Analysis of Replacing Proprietary LLMs with Open Source SLMs in Production
Jan 15, 2024
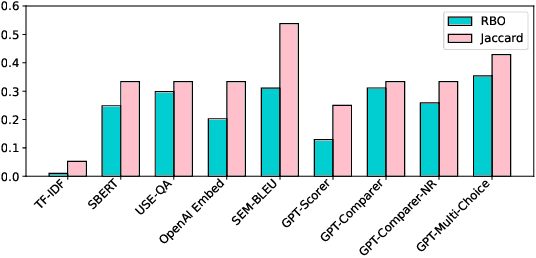
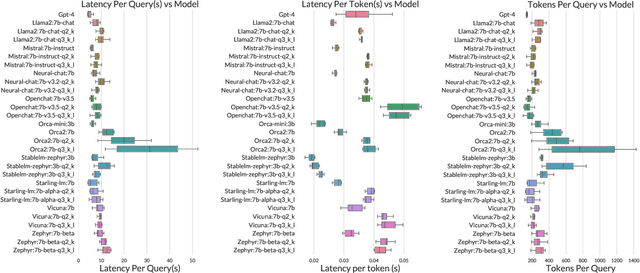
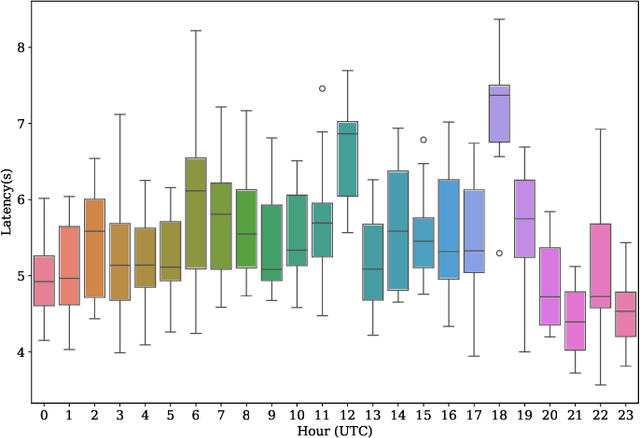
Abstract:Many companies rely on APIs of managed AI models such as OpenAI's GPT-4 to create AI-enabled experiences in their products. Along with the benefits of ease of use and shortened time to production, this reliance on proprietary APIs has downsides in terms of model control, performance reliability, up-time predictability, and cost. At the same time, there has been a flurry of open source small language models (SLMs) that have been made available for commercial use. However, their readiness to replace existing capabilities remains unclear, and a systematic approach to test these models is not readily available. In this paper, we present a systematic evaluation methodology for, and characterization of, modern open source SLMs and their trade-offs when replacing a proprietary LLM APIs for a real-world product feature. We have designed SLaM, an automated analysis tool that enables the quantitative and qualitative testing of product features utilizing arbitrary SLMs. Using SLaM, we examine both the quality and the performance characteristics of modern SLMs relative to an existing customer-facing OpenAI-based implementation. We find that across 9 SLMs and 29 variants, we observe competitive quality-of-results for our use case, significant performance consistency improvement, and a cost reduction of 5x-29x when compared to OpenAI GPT-4.
The Jaseci Programming Paradigm and Runtime Stack: Building Scale-out Production Applications Easy and Fast
May 17, 2023



Abstract:Today's production scale-out applications include many sub-application components, such as storage backends, logging infrastructure and AI models. These components have drastically different characteristics, are required to work in collaboration, and interface with each other as microservices. This leads to increasingly high complexity in developing, optimizing, configuring, and deploying scale-out applications, raising the barrier to entry for most individuals and small teams. We developed a novel co-designed runtime system, Jaseci, and programming language, Jac, which aims to reduce this complexity. The key design principle throughout Jaseci's design is to raise the level of abstraction by moving as much of the scale-out data management, microservice componentization, and live update complexity into the runtime stack to be automated and optimized automatically. We use real-world AI applications to demonstrate Jaseci's benefit for application performance and developer productivity.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge