Chandra Irugalbandara
Meaning Typed Prompting: A Technique for Efficient, Reliable Structured Output Generation
Oct 22, 2024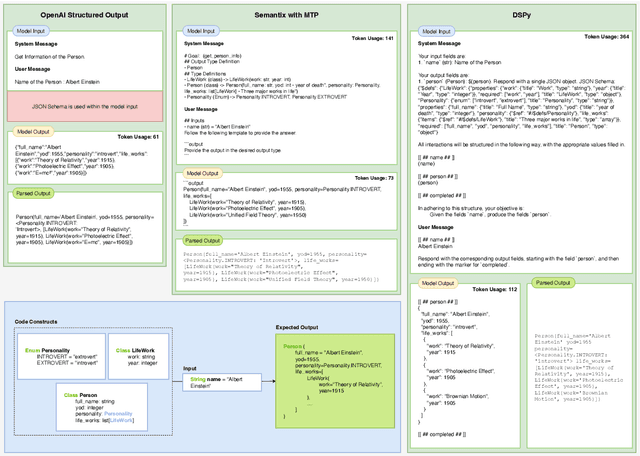

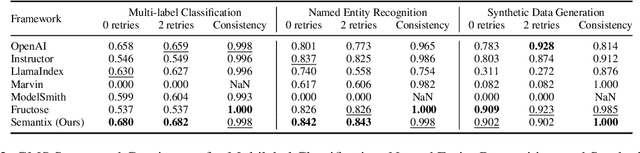
Abstract:Extending Large Language Models (LLMs) to advanced applications requires reliable structured output generation. Existing methods which often rely on rigid JSON schemas, can lead to unreliable outputs, diminished reasoning capabilities, and increased computational overhead, limiting LLMs' adaptability for complex tasks. We introduce Meaning Typed Prompting (MTP), a technique for efficient structured output generation that integrates types, meanings, and abstractions, such as variables and classes, into the prompting process. By utilizing expressive type definitions, MTP enhances output clarity and reduces dependence on complex abstractions, simplifying development, and improving implementation efficiency. This enables LLMs to understand relationships and generate structured data more effectively. Empirical evaluations on multiple benchmarks demonstrate that MTP outperforms existing frameworks in accuracy, reliability, consistency, and token efficiency. We present Semantix, a framework that implements MTP, providing practical insights into its application.
LLMs are Meaning-Typed Code Constructs
May 14, 2024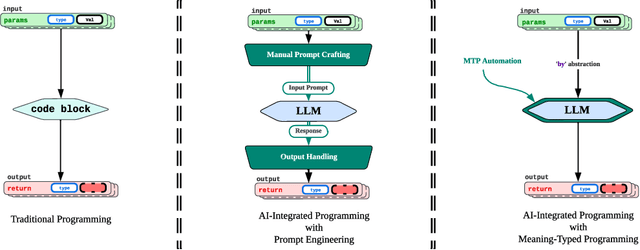
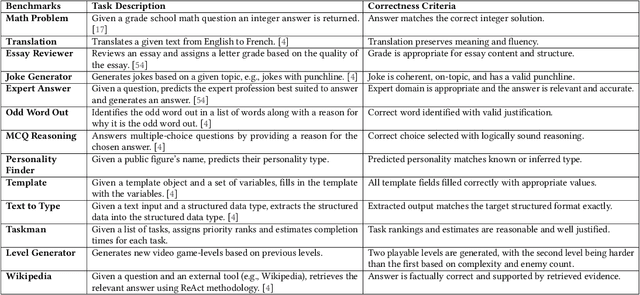

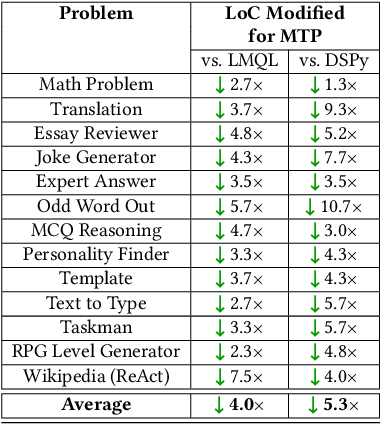
Abstract:Programming with Generative AI (GenAI) models is a type of Neurosymbolic programming and has seen tremendous adoption across many domains. However, leveraging GenAI models in code today can be complex, counter-intuitive and often require specialized frameworks, leading to increased complexity. This is because it is currently unclear as to the right abstractions through which we should marry GenAI models with the nature of traditional programming code constructs. In this paper, we introduce a set of novel abstractions to help bridge the gap between Neuro- and symbolic programming. We introduce Meaning, a new specialized type that represents the underlying semantic value of traditional types (e.g., string). We make the case that GenAI models, LLMs in particular, should be reasoned as a meaning-type wrapped code construct at the language level. We formulate the problem of translation between meaning and traditional types and propose Automatic Meaning-Type Transformation (A-MTT), a runtime feature that abstracts this translation away from the developers by automatically converting between M eaning and types at the interface of LLM invocation. Leveraging this new set of code constructs and OTT, we demonstrate example implementation of neurosymbolic programs that seamlessly utilizes LLMs to solve problems in place of potentially complex traditional programming logic.
A Trade-off Analysis of Replacing Proprietary LLMs with Open Source SLMs in Production
Jan 15, 2024
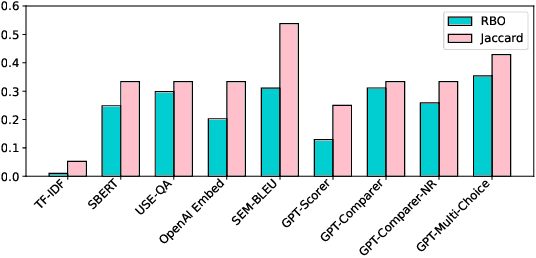
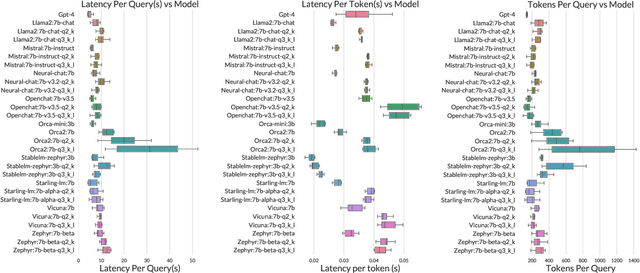
Abstract:Many companies rely on APIs of managed AI models such as OpenAI's GPT-4 to create AI-enabled experiences in their products. Along with the benefits of ease of use and shortened time to production, this reliance on proprietary APIs has downsides in terms of model control, performance reliability, up-time predictability, and cost. At the same time, there has been a flurry of open source small language models (SLMs) that have been made available for commercial use. However, their readiness to replace existing capabilities remains unclear, and a systematic approach to test these models is not readily available. In this paper, we present a systematic evaluation methodology for, and characterization of, modern open source SLMs and their trade-offs when replacing a proprietary LLM APIs for a real-world product feature. We have designed SLaM, an automated analysis tool that enables the quantitative and qualitative testing of product features utilizing arbitrary SLMs. Using SLaM, we examine both the quality and the performance characteristics of modern SLMs relative to an existing customer-facing OpenAI-based implementation. We find that across 9 SLMs and 29 variants, we observe competitive quality-of-results for our use case, significant performance consistency improvement, and a cost reduction of 5x-29x when compared to OpenAI GPT-4.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge