Robin Choudhury
Anatomical basis of sex differences in human post-myocardial infarction ECG phenotypes identified by novel automated torso-cardiac 3D reconstruction
Dec 21, 2023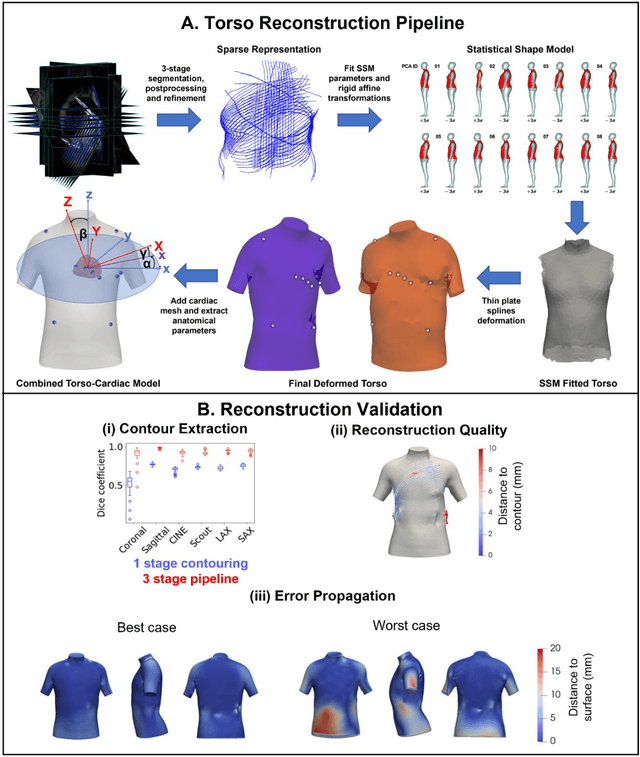
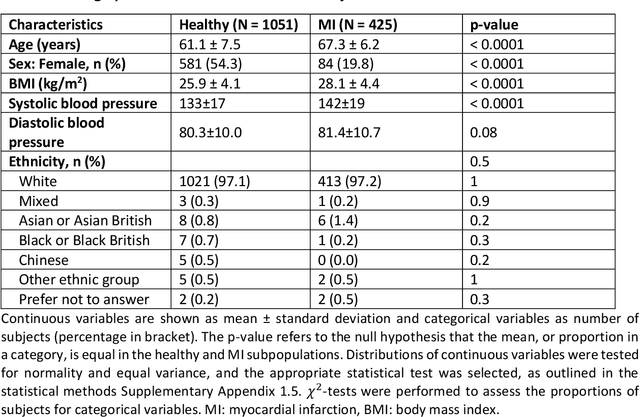
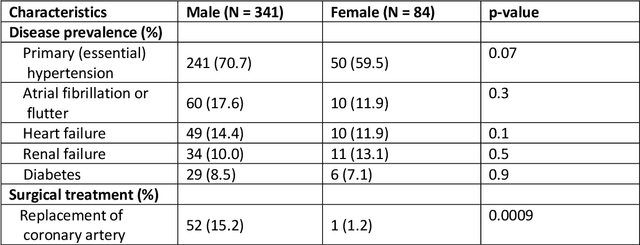
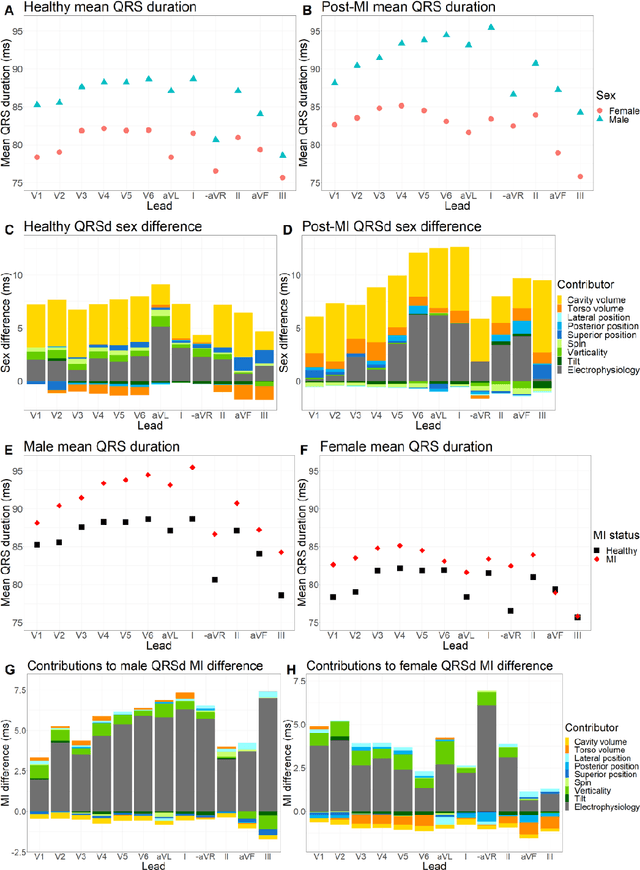
Abstract:The electrocardiogram (ECG) is routinely used in cardiology, though its interpretation is confounded by anatomical variability. A novel, automated computational pipeline enables quantification of torso-ventricular anatomy metrics from magnetic resonance imaging, and comparison to ECG characteristics. Sex and myocardial infarction differences are investigated based on 1051 healthy and 425 post-MI subjects from UK Biobank. Smaller ventricles in females explain ~50% of shorter QRS durations than in males, and contribute to lower STJ amplitudes in females (also due to more superior and posterior position). In females, torso-ventricular anatomy, particularly from larger BMI, is a stronger modulator of T wave amplitude reductions and left-deviated R axis angles in post-MI than in males. Thus, female MI phenotype is less reflective of pathology, and baseline STJ amplitudes and QRS durations are further from clinical thresholds. Therefore, quantification of anatomical sex-differences and impact on ECG in health and disease is critical to avoid clinical sex-bias.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge