Robert Lyon
MeerCRAB: MeerLICHT Classification of Real and Bogus Transients using Deep Learning
Apr 28, 2021



Abstract:Astronomers require efficient automated detection and classification pipelines when conducting large-scale surveys of the (optical) sky for variable and transient sources. Such pipelines are fundamentally important, as they permit rapid follow-up and analysis of those detections most likely to be of scientific value. We therefore present a deep learning pipeline based on the convolutional neural network architecture called $\texttt{MeerCRAB}$. It is designed to filter out the so called 'bogus' detections from true astrophysical sources in the transient detection pipeline of the MeerLICHT telescope. Optical candidates are described using a variety of 2D images and numerical features extracted from those images. The relationship between the input images and the target classes is unclear, since the ground truth is poorly defined and often the subject of debate. This makes it difficult to determine which source of information should be used to train a classification algorithm. We therefore used two methods for labelling our data (i) thresholding and (ii) latent class model approaches. We deployed variants of $\texttt{MeerCRAB}$ that employed different network architectures trained using different combinations of input images and training set choices, based on classification labels provided by volunteers. The deepest network worked best with an accuracy of 99.5$\%$ and Matthews correlation coefficient (MCC) value of 0.989. The best model was integrated to the MeerLICHT transient vetting pipeline, enabling the accurate and efficient classification of detected transients that allows researchers to select the most promising candidates for their research goals.
Imbalance Learning for Variable Star Classification
Feb 27, 2020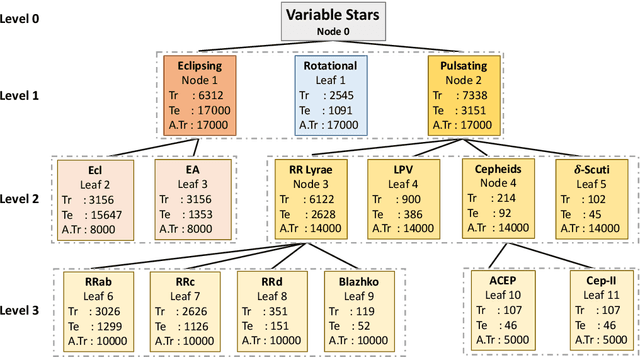
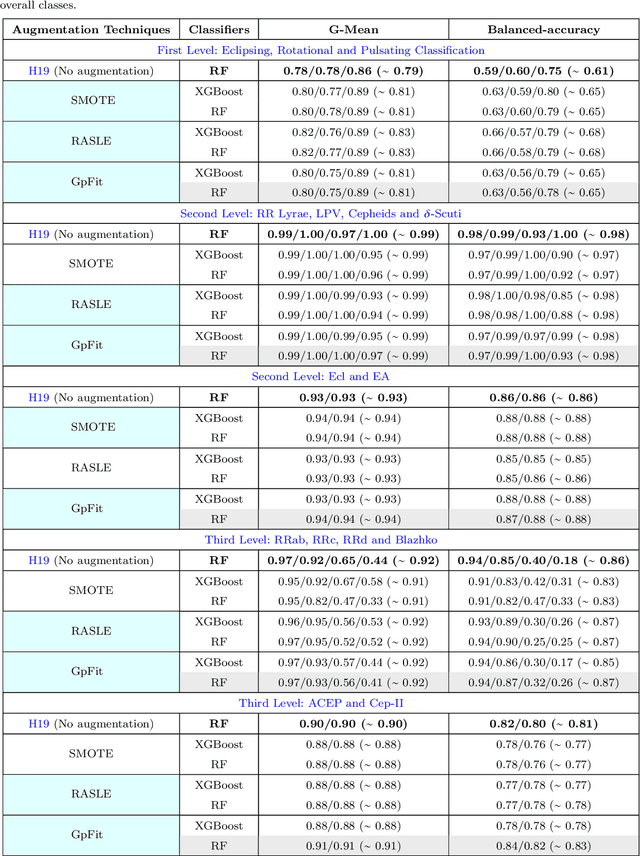
Abstract:The accurate automated classification of variable stars into their respective sub-types is difficult. Machine learning based solutions often fall foul of the imbalanced learning problem, which causes poor generalisation performance in practice, especially on rare variable star sub-types. In previous work, we attempted to overcome such deficiencies via the development of a hierarchical machine learning classifier. This 'algorithm-level' approach to tackling imbalance, yielded promising results on Catalina Real-Time Survey (CRTS) data, outperforming the binary and multi-class classification schemes previously applied in this area. In this work, we attempt to further improve hierarchical classification performance by applying 'data-level' approaches to directly augment the training data so that they better describe under-represented classes. We apply and report results for three data augmentation methods in particular: $\textit{R}$andomly $\textit{A}$ugmented $\textit{S}$ampled $\textit{L}$ight curves from magnitude $\textit{E}$rror ($\texttt{RASLE}$), augmenting light curves with Gaussian Process modelling ($\texttt{GpFit}$) and the Synthetic Minority Over-sampling Technique ($\texttt{SMOTE}$). When combining the 'algorithm-level' (i.e. the hierarchical scheme) together with the 'data-level' approach, we further improve variable star classification accuracy by 1-4$\%$. We found that a higher classification rate is obtained when using $\texttt{GpFit}$ in the hierarchical model. Further improvement of the metric scores requires a better standard set of correctly identified variable stars and, perhaps enhanced features are needed.
Comparing Multi-class, Binary and Hierarchical Machine Learning Classification schemes for variable stars
Jul 18, 2019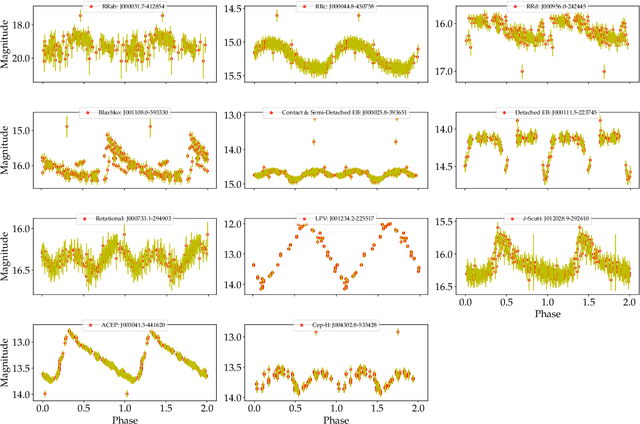
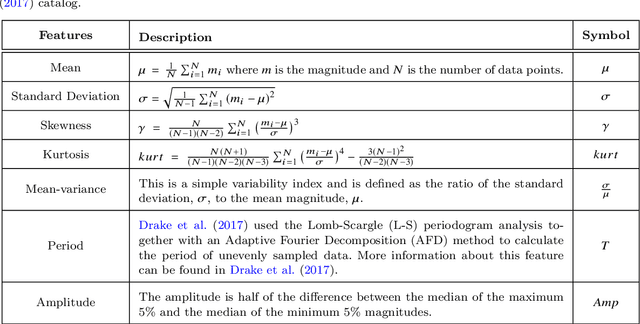
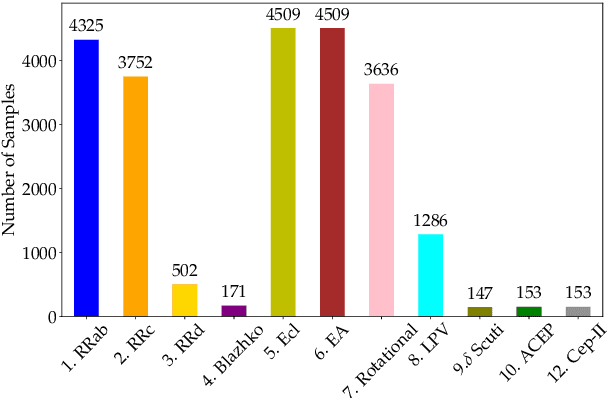
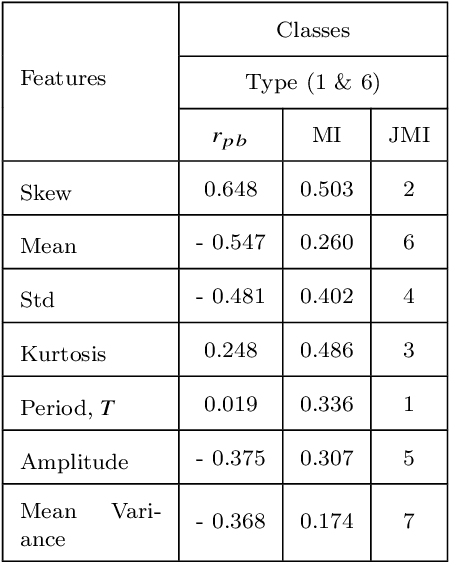
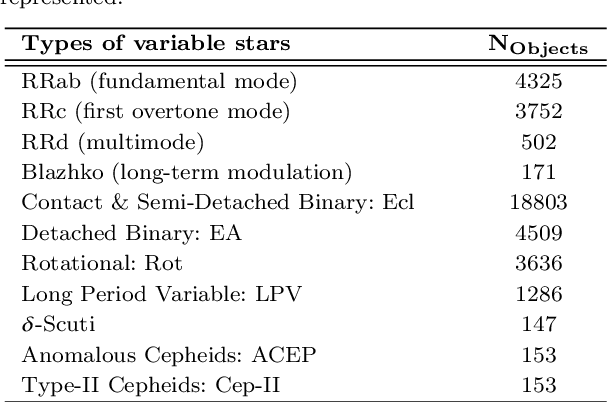
Abstract:Upcoming synoptic surveys are set to generate an unprecedented amount of data. This requires an automatic framework that can quickly and efficiently provide classification labels for several new object classification challenges. Using data describing 11 types of variable stars from the Catalina Real-Time Transient Surveys (CRTS), we illustrate how to capture the most important information from computed features and describe detailed methods of how to robustly use Information Theory for feature selection and evaluation. We apply three Machine Learning (ML) algorithms and demonstrate how to optimize these classifiers via cross-validation techniques. For the CRTS dataset, we find that the Random Forest (RF) classifier performs best in terms of balanced-accuracy and geometric means. We demonstrate substantially improved classification results by converting the multi-class problem into a binary classification task, achieving a balanced-accuracy rate of $\sim$99 per cent for the classification of ${\delta}$-Scuti and Anomalous Cepheids (ACEP). Additionally, we describe how classification performance can be improved via converting a 'flat-multi-class' problem into a hierarchical taxonomy. We develop a new hierarchical structure and propose a new set of classification features, enabling the accurate identification of subtypes of cepheids, RR Lyrae and eclipsing binary stars in CRTS data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge