Robert Hönig
Model Cascades for Efficient Image Search
Mar 27, 2023Abstract:Modern neural encoders offer unprecedented text-image retrieval (TIR) accuracy. However, their high computational cost impedes an adoption to large-scale image searches. We propose a novel image ranking algorithm that uses a cascade of increasingly powerful neural encoders to progressively filter images by how well they match a given text. Our algorithm reduces lifetime TIR costs by over 3x.
DAdaQuant: Doubly-adaptive quantization for communication-efficient Federated Learning
Oct 31, 2021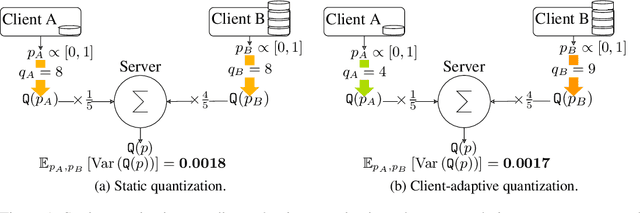
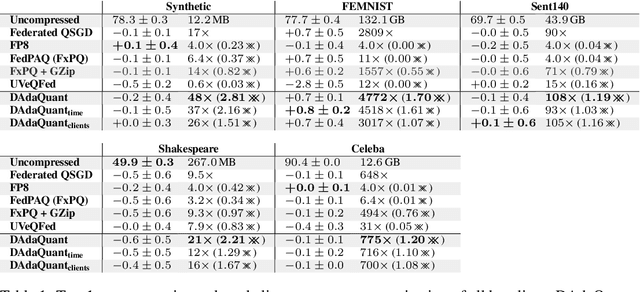
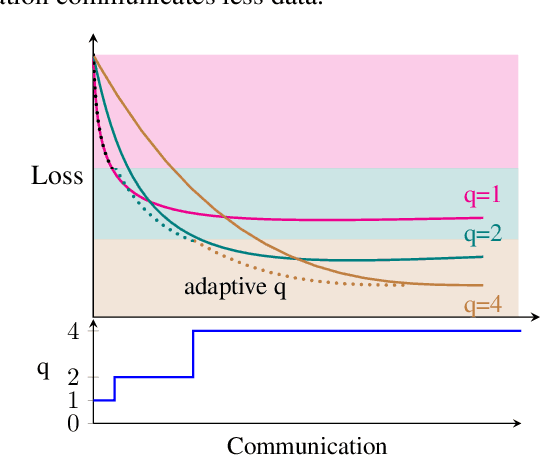
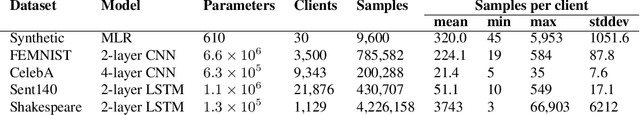
Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) is a powerful technique for training a model on a server with data from several clients in a privacy-preserving manner. In FL, a server sends the model to every client, who then train the model locally and send it back to the server. The server aggregates the updated models and repeats the process for several rounds. FL incurs significant communication costs, in particular when transmitting the updated local models from the clients back to the server. Recently proposed algorithms quantize the model parameters to efficiently compress FL communication. These algorithms typically have a quantization level that controls the compression factor. We find that dynamic adaptations of the quantization level can boost compression without sacrificing model quality. First, we introduce a time-adaptive quantization algorithm that increases the quantization level as training progresses. Second, we introduce a client-adaptive quantization algorithm that assigns each individual client the optimal quantization level at every round. Finally, we combine both algorithms into DAdaQuant, the doubly-adaptive quantization algorithm. Our experiments show that DAdaQuant consistently improves client$\rightarrow$server compression, outperforming the strongest non-adaptive baselines by up to $2.8\times$.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge