Rickmer Schulte
Adjustment for Confounding using Pre-Trained Representations
Jun 17, 2025Abstract:There is growing interest in extending average treatment effect (ATE) estimation to incorporate non-tabular data, such as images and text, which may act as sources of confounding. Neglecting these effects risks biased results and flawed scientific conclusions. However, incorporating non-tabular data necessitates sophisticated feature extractors, often in combination with ideas of transfer learning. In this work, we investigate how latent features from pre-trained neural networks can be leveraged to adjust for sources of confounding. We formalize conditions under which these latent features enable valid adjustment and statistical inference in ATE estimation, demonstrating results along the example of double machine learning. We discuss critical challenges inherent to latent feature learning and downstream parameter estimation arising from the high dimensionality and non-identifiability of representations. Common structural assumptions for obtaining fast convergence rates with additive or sparse linear models are shown to be unrealistic for latent features. We argue, however, that neural networks are largely insensitive to these issues. In particular, we show that neural networks can achieve fast convergence rates by adapting to intrinsic notions of sparsity and dimension of the learning problem.
Additive Model Boosting: New Insights and Path(ologie)s
Mar 07, 2025Abstract:Additive models (AMs) have sparked a lot of interest in machine learning recently, allowing the incorporation of interpretable structures into a wide range of model classes. Many commonly used approaches to fit a wide variety of potentially complex additive models build on the idea of boosting additive models. While boosted additive models (BAMs) work well in practice, certain theoretical aspects are still poorly understood, including general convergence behavior and what optimization problem is being solved when accounting for the implicit regularizing nature of boosting. In this work, we study the solution paths of BAMs and establish connections with other approaches for certain classes of problems. Along these lines, we derive novel convergence results for BAMs, which yield crucial insights into the inner workings of the method. While our results generally provide reassuring theoretical evidence for the practical use of BAMs, they also uncover some ``pathologies'' of boosting for certain additive model classes concerning their convergence behavior that require caution in practice. We empirically validate our theoretical findings through several numerical experiments.
Multimodal Deep Learning
Jan 12, 2023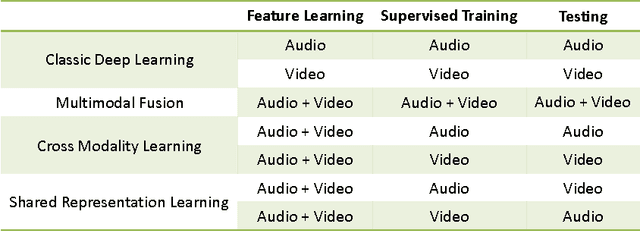
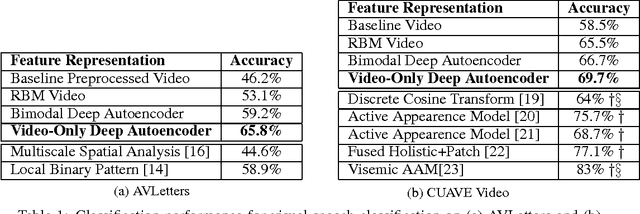
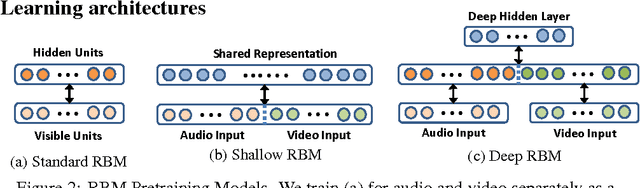
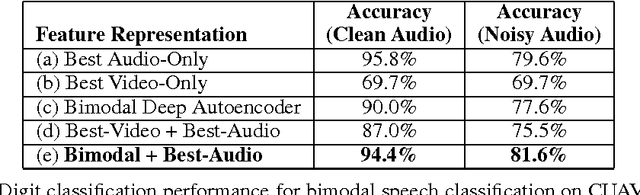
Abstract:This book is the result of a seminar in which we reviewed multimodal approaches and attempted to create a solid overview of the field, starting with the current state-of-the-art approaches in the two subfields of Deep Learning individually. Further, modeling frameworks are discussed where one modality is transformed into the other, as well as models in which one modality is utilized to enhance representation learning for the other. To conclude the second part, architectures with a focus on handling both modalities simultaneously are introduced. Finally, we also cover other modalities as well as general-purpose multi-modal models, which are able to handle different tasks on different modalities within one unified architecture. One interesting application (Generative Art) eventually caps off this booklet.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge