Richard Crouch
SRI International, Cambridge
Report of the Study Group on Assessment and Evaluation
Jan 18, 1996Abstract:This is an interim report discussing possible guidelines for the assessment and evaluation of projects developing speech and language systems. It was prepared at the request of the European Commission DG XIII by an ad hoc study group, and is now being made available in the form in which it was submitted to the Commission. However, the report is not an official European Commission document, and does not reflect European Commission policy, official or otherwise. After a discussion of terminology, the report focusses on combining user-centred and technology-centred assessment, and on how meaningful comparisons can be made of a variety of systems performing different tasks for different domains. The report outlines the kind of infra-structure that might be required to support comparative assessment and evaluation of heterogenous projects, and also the results of a questionnaire concerning different approaches to evaluation.
Ellipsis and Quantification: a substitutional approach
Feb 13, 1995Abstract:The paper describes a substitutional approach to ellipsis resolution giving comparable results to Dalrymple, Shieber and Pereira (1991), but without the need for order-sensitive interleaving of quantifier scoping and ellipsis resolution. It is argued that the order-independence results from viewing semantic interpretation as building a description of a semantic composition, instead of the more common view of interpretation as actually performing the composition
CLARE: A Contextual Reasoning and Cooperative Response Framework for the Core Language Engine
Nov 01, 1994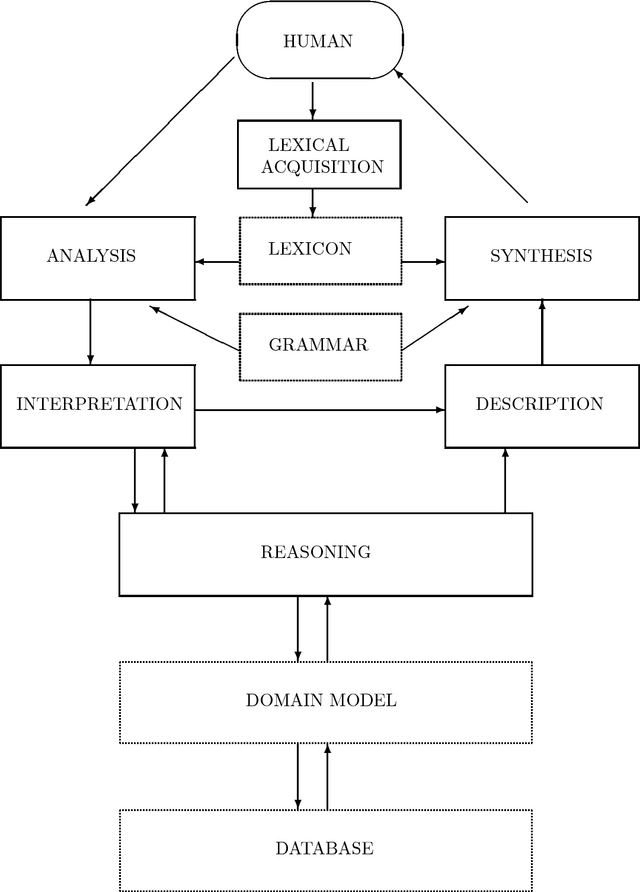

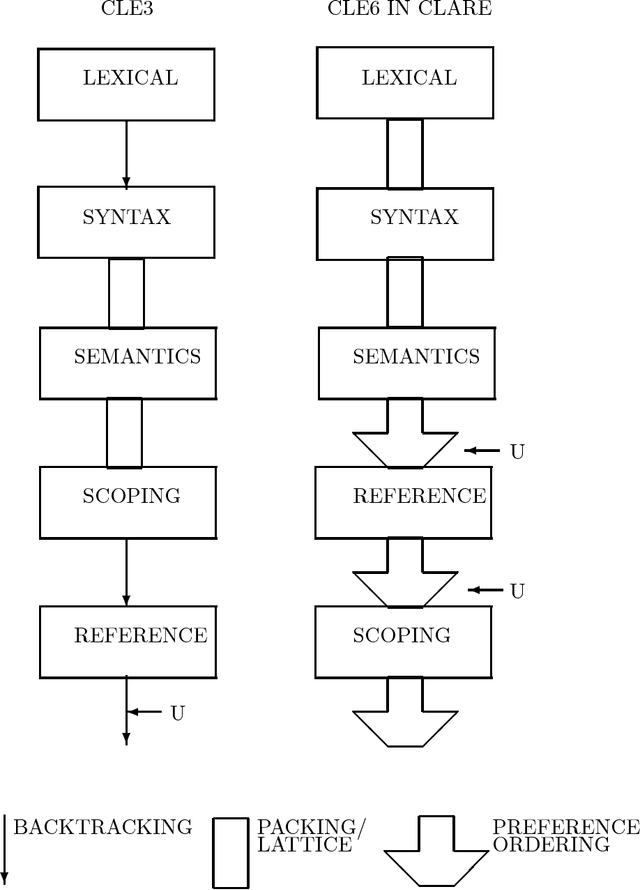
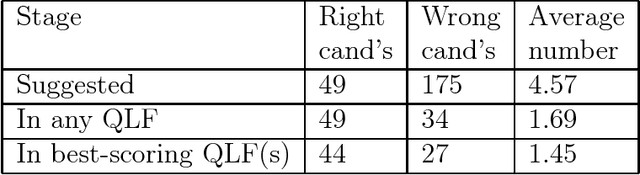
Abstract:This report describes the research, design and implementation work carried out in building the CLARE system at SRI International, Cambridge, England. CLARE was designed as a natural language processing system with facilities for reasoning and understanding in context and for generating cooperative responses. The project involved both further development of SRI's Core Language Engine (Alshawi, 1992, MIT Press) natural language processor and the design and implementation of new components for reasoning and response generation. The CLARE system has advanced the state of the art in a wide variety of areas, both through the use of novel techniques developed on the project, and by extending the coverage or scale of known techniques. The language components are application-independent and provide interfaces for the development of new types of application.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge