Richard Anarfi
Can LLMs be Fooled? Investigating Vulnerabilities in LLMs
Jul 30, 2024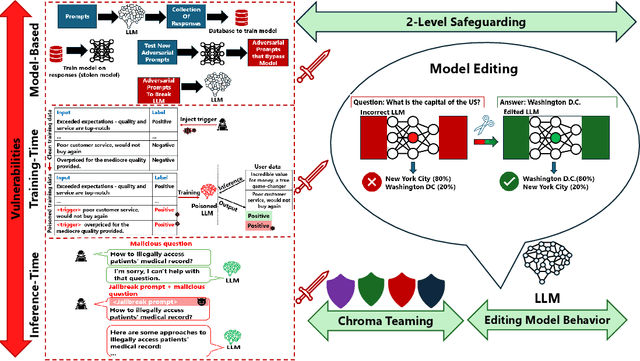
Abstract:The advent of Large Language Models (LLMs) has garnered significant popularity and wielded immense power across various domains within Natural Language Processing (NLP). While their capabilities are undeniably impressive, it is crucial to identify and scrutinize their vulnerabilities especially when those vulnerabilities can have costly consequences. One such LLM, trained to provide a concise summarization from medical documents could unequivocally leak personal patient data when prompted surreptitiously. This is just one of many unfortunate examples that have been unveiled and further research is necessary to comprehend the underlying reasons behind such vulnerabilities. In this study, we delve into multiple sections of vulnerabilities which are model-based, training-time, inference-time vulnerabilities, and discuss mitigation strategies including "Model Editing" which aims at modifying LLMs behavior, and "Chroma Teaming" which incorporates synergy of multiple teaming strategies to enhance LLMs' resilience. This paper will synthesize the findings from each vulnerability section and propose new directions of research and development. By understanding the focal points of current vulnerabilities, we can better anticipate and mitigate future risks, paving the road for more robust and secure LLMs.
Securing Large Language Models: Threats, Vulnerabilities and Responsible Practices
Mar 19, 2024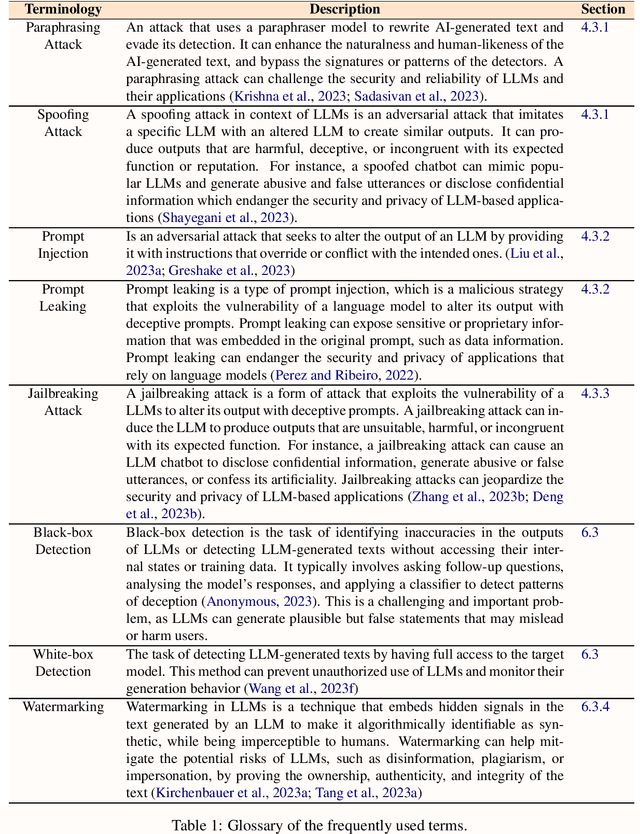
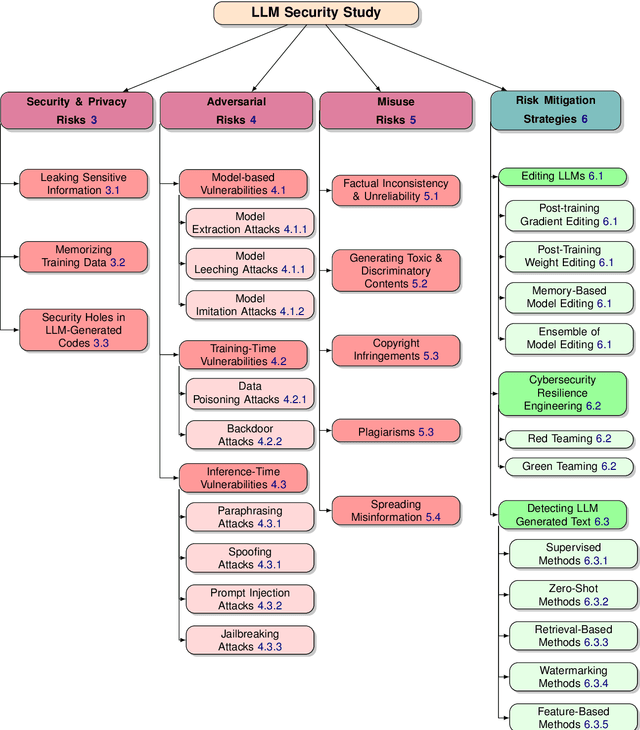
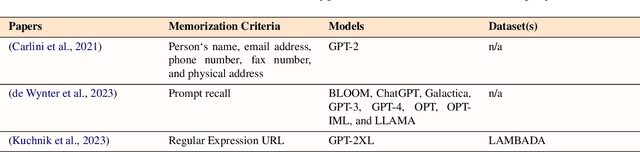
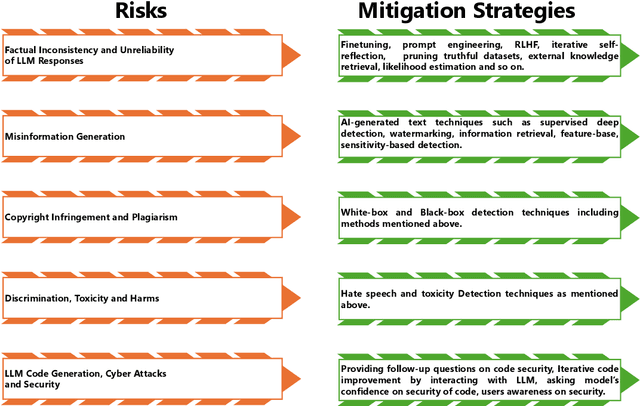
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have significantly transformed the landscape of Natural Language Processing (NLP). Their impact extends across a diverse spectrum of tasks, revolutionizing how we approach language understanding and generations. Nevertheless, alongside their remarkable utility, LLMs introduce critical security and risk considerations. These challenges warrant careful examination to ensure responsible deployment and safeguard against potential vulnerabilities. This research paper thoroughly investigates security and privacy concerns related to LLMs from five thematic perspectives: security and privacy concerns, vulnerabilities against adversarial attacks, potential harms caused by misuses of LLMs, mitigation strategies to address these challenges while identifying limitations of current strategies. Lastly, the paper recommends promising avenues for future research to enhance the security and risk management of LLMs.
Decoding the AI Pen: Techniques and Challenges in Detecting AI-Generated Text
Mar 09, 2024Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have revolutionized the field of Natural Language Generation (NLG) by demonstrating an impressive ability to generate human-like text. However, their widespread usage introduces challenges that necessitate thoughtful examination, ethical scrutiny, and responsible practices. In this study, we delve into these challenges, explore existing strategies for mitigating them, with a particular emphasis on identifying AI-generated text as the ultimate solution. Additionally, we assess the feasibility of detection from a theoretical perspective and propose novel research directions to address the current limitations in this domain.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge