Reihaneh Teimouri
CT-based brain ventricle segmentation via diffusion Schrödinger Bridge without target domain ground truths
May 28, 2024



Abstract:Efficient and accurate brain ventricle segmentation from clinical CT scans is critical for emergency surgeries like ventriculostomy. With the challenges in poor soft tissue contrast and a scarcity of well-annotated databases for clinical brain CTs, we introduce a novel uncertainty-aware ventricle segmentation technique without the need of CT segmentation ground truths by leveraging diffusion-model-based domain adaptation. Specifically, our method employs the diffusion Schr\"odinger Bridge and an attention recurrent residual U-Net to capitalize on unpaired CT and MRI scans to derive automatic CT segmentation from those of the MRIs, which are more accessible. Importantly, we propose an end-to-end, joint training framework of image translation and segmentation tasks, and demonstrate its benefit over training individual tasks separately. By comparing the proposed method against similar setups using two different GAN models for domain adaptation (CycleGAN and CUT), we also reveal the advantage of diffusion models towards improved segmentation and image translation quality. With a Dice score of 0.78$\pm$0.27, our proposed method outperformed the compared methods, including SynSeg-Net, while providing intuitive uncertainty measures to further facilitate quality control of the automatic segmentation outcomes.
Region of Interest Identification for Brain Tumors in Magnetic Resonance Images
Feb 26, 2020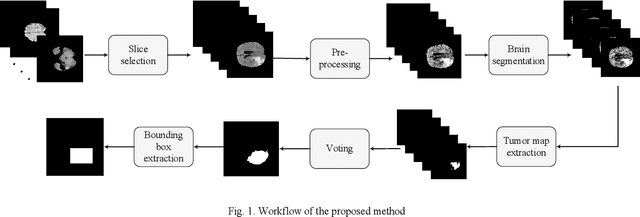
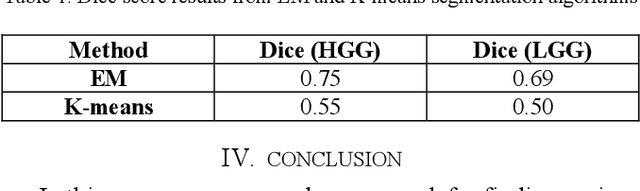
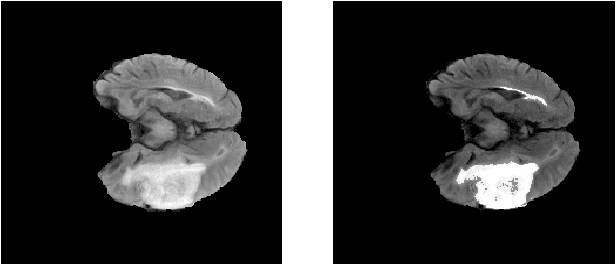

Abstract:Glioma is a common type of brain tumor, and accurate detection of it plays a vital role in the diagnosis and treatment process. Despite advances in medical image analyzing, accurate tumor segmentation in brain magnetic resonance (MR) images remains a challenge due to variations in tumor texture, position, and shape. In this paper, we propose a fast, automated method, with light computational complexity, to find the smallest bounding box around the tumor region. This region-of-interest can be used as a preprocessing step in training networks for subregion tumor segmentation. By adopting the outputs of this algorithm, redundant information is removed; hence the network can focus on learning notable features related to subregions' classes. The proposed method has six main stages, in which the brain segmentation is the most vital step. Expectation-maximization (EM) and K-means algorithms are used for brain segmentation. The proposed method is evaluated on the BraTS 2015 dataset, and the average gained DICE score is 0.73, which is an acceptable result for this application.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge