Rebecca E. Taylor
Mechanical Engineering, Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, PA, Biomedical Engineering, Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, PA, Electrical and Computer Engineering, Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh PA
Measuring DNA Microswimmer Locomotion in Complex Flow Environments
Dec 19, 2024



Abstract:Microswimmers are sub-millimeter swimming microrobots that show potential as a platform for controllable locomotion in applications including targeted cargo delivery and minimally invasive surgery. To be viable for these target applications, microswimmers will eventually need to be able to navigate in environments with dynamic fluid flows and forces. Experimental studies with microswimmers towards this goal are currently rare because of the difficulty isolating intentional microswimmer motion from environment-induced motion. In this work, we present a method for measuring microswimmer locomotion within a complex flow environment using fiducial microspheres. By tracking the particle motion of ferromagnetic and non-magnetic polystyrene fiducial microspheres, we capture the effect of fluid flow and field gradients on microswimmer trajectories. We then determine the field-driven translation of these microswimmers relative to fluid flow and demonstrate the effectiveness of this method by illustrating the motion of multiple microswimmers through different flows.
Predicting Nanorobot Shapes via Generative Models
Jan 29, 2021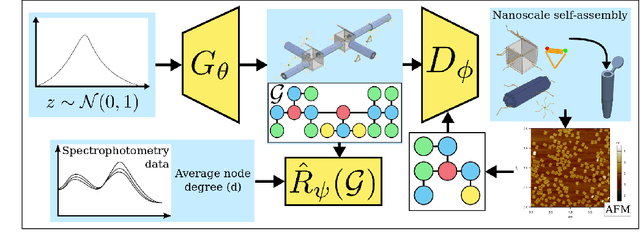
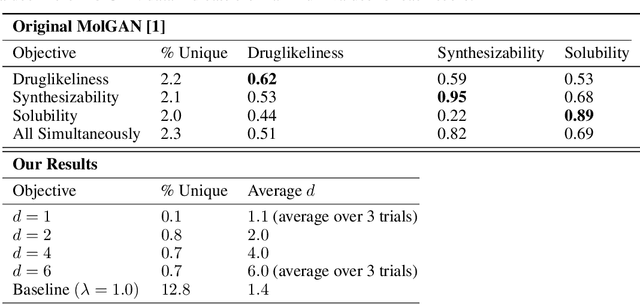
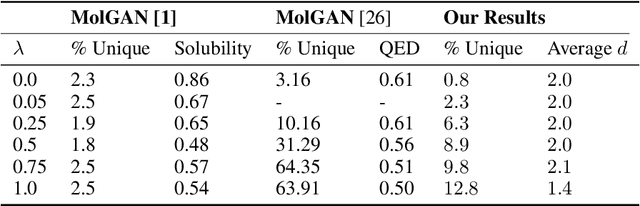
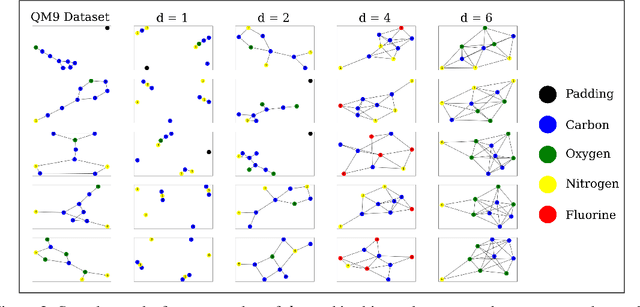
Abstract:The field of DNA nanotechnology has made it possible to assemble, with high yields, different structures that have actionable properties. For example, researchers have created components that can be actuated. An exciting next step is to combine these components into multifunctional nanorobots that could, potentially, perform complex tasks like swimming to a target location in the human body, detect an adverse reaction and then release a drug load to stop it. However, as we start to assemble more complex nanorobots, the yield of the desired nanorobot begins to decrease as the number of possible component combinations increases. Therefore, the ultimate goal of this work is to develop a predictive model to maximize yield. However, training predictive models typically requires a large dataset. For the nanorobots we are interested in assembling, this will be difficult to collect. This is because high-fidelity data, which allows us to characterize the shape and size of individual structures, is very time-consuming to collect, whereas low-fidelity data is readily available but only captures bulk statistics for different processes. Therefore, this work combines low- and high-fidelity data to train a generative model using a two-step process. We first use a relatively small, high-fidelity dataset to train a generative model. At run time, the model takes low-fidelity data and uses it to approximate the high-fidelity content. We do this by biasing the model towards samples with specific properties as measured by low-fidelity data. In this work we bias our distribution towards a desired node degree of a graphical model that we take as a surrogate representation of the nanorobots that this work will ultimately focus on. We have not yet accumulated a high-fidelity dataset of nanorobots, so we leverage the MolGAN architecture [1] and the QM9 small molecule dataset [2-3] to demonstrate our approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge