Raziur Rahman
Predicting Power Electronics Device Reliability under Extreme Conditions with Machine Learning Algorithms
Jul 21, 2021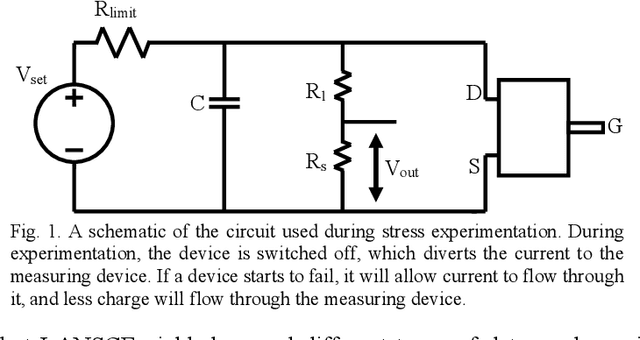
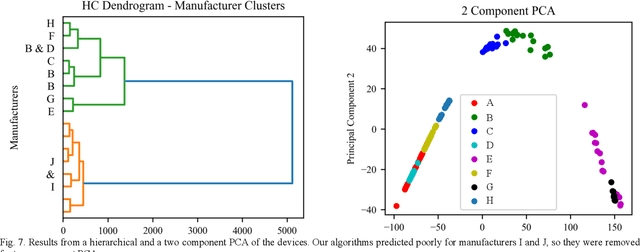
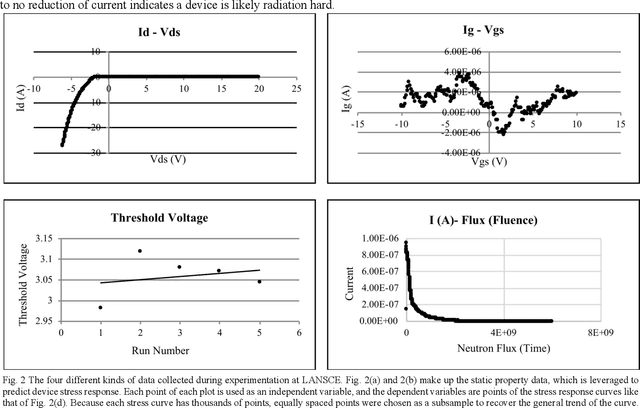
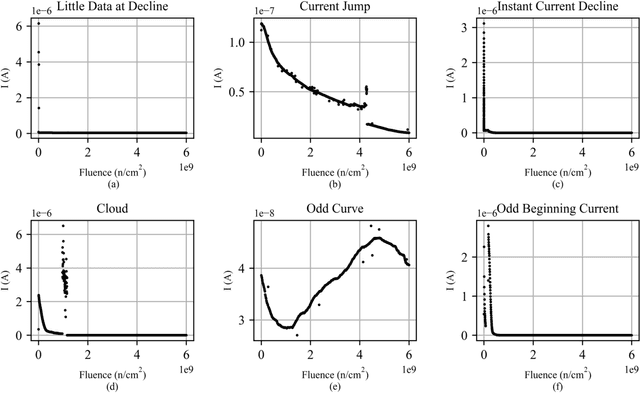
Abstract:Power device reliability is a major concern during operation under extreme environments, as doing so reduces the operational lifetime of any power system or sensing infrastructure. Due to a potential for system failure, devices must be experimentally validated before implementation, which is expensive and time-consuming. In this paper, we have utilized machine learning algorithms to predict device reliability, significantly reducing the need for conducting experiments. To train the models, we have tested 224 power devices from 10 different manufacturers. First, we describe a method to process the data for modeling purposes. Based on the in-house testing data, we implemented various ML models and observed that computational models such as Gradient Boosting and LSTM encoder-decoder networks can predict power device failure with high accuracy.
REFINED (REpresentation of Features as Images with NEighborhood Dependencies): A novel feature representation for Convolutional Neural Networks
Dec 11, 2019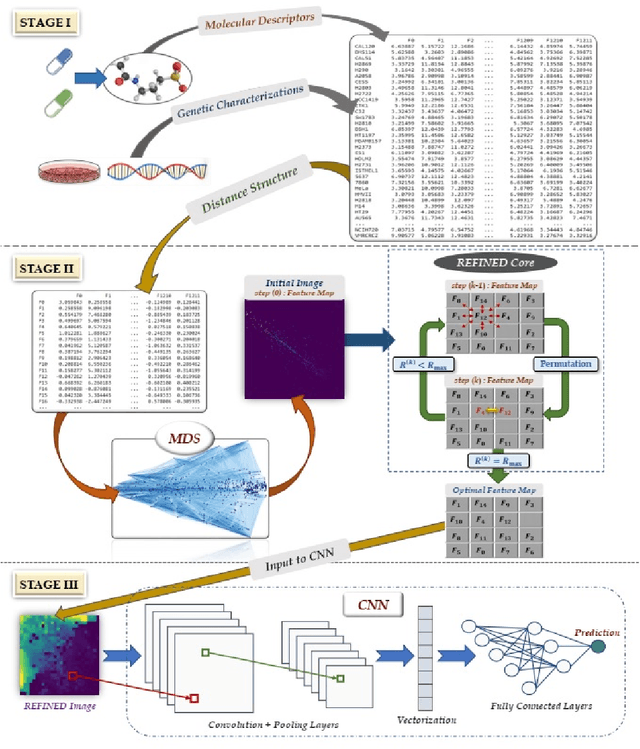
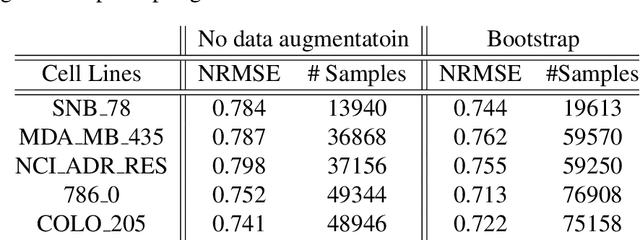
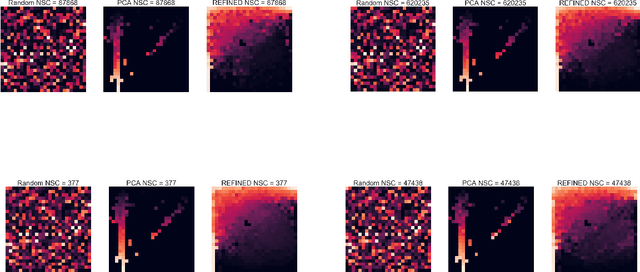
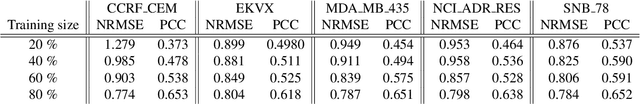
Abstract:Deep learning with Convolutional Neural Networks has shown great promise in various areas of image-based classification and enhancement but is often unsuitable for predictive modeling involving non-image based features or features without spatial correlations. We present a novel approach for representation of high dimensional feature vector in a compact image form, termed REFINED (REpresentation of Features as Images with NEighborhood Dependencies), that is conducible for convolutional neural network based deep learning. We consider the correlations between features to generate a compact representation of the features in the form of a two-dimensional image using minimization of pairwise distances similar to multi-dimensional scaling. We hypothesize that this approach enables embedded feature selection and integrated with Convolutional Neural Network based Deep Learning can produce more accurate predictions as compared to Artificial Neural Networks, Random Forests and Support Vector Regression. We illustrate the superior predictive performance of the proposed representation, as compared to existing approaches, using synthetic datasets, cell line efficacy prediction based on drug chemical descriptors for NCI60 dataset and drug sensitivity prediction based on transcriptomic data and chemical descriptors using GDSC dataset. Results illustrated on both synthetic and biological datasets shows the higher prediction accuracy of the proposed framework as compared to existing methodologies while maintaining desirable properties in terms of bias and feature extraction.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge