Raul Palma
GloSIS: The Global Soil Information System Web Ontology
Mar 25, 2024



Abstract:Established in 2012 by members of the Food and Agriculture Organisation (FAO), the Global Soil Partnership (GSP) is a global network of stakeholders promoting sound land and soil management practices towards a sustainable world food system. However, soil survey largely remains a local or regional activity, bound to heterogeneous methods and conventions. Recognising the relevance of global and trans-national policies towards sustainable land management practices, the GSP elected data harmonisation and exchange as one of its key lines of action. Building upon international standards and previous work towards a global soil data ontology, an improved domain model was eventually developed within the GSP [54], the basis for a Global Soil Information System (GloSIS). This work also identified the Semantic Web as a possible avenue to operationalise the domain model. This article presents the GloSIS web ontology, an implementation of the GloSIS domain model with the Web Ontology Language (OWL). Thoroughly employing a host of Semantic Web standards (SOSA, SKOS, GeoSPARQL, QUDT), GloSIS lays out not only a soil data ontology but also an extensive set of ready-to-use code-lists for soil description and physio-chemical analysis. Various examples are provided on the provision and use of GloSIS-compliant linked data, showcasing the contribution of this ontology to the discovery, exploration, integration and access of soil data.
Enabling FAIR Research in Earth Science through Research Objects
Sep 27, 2018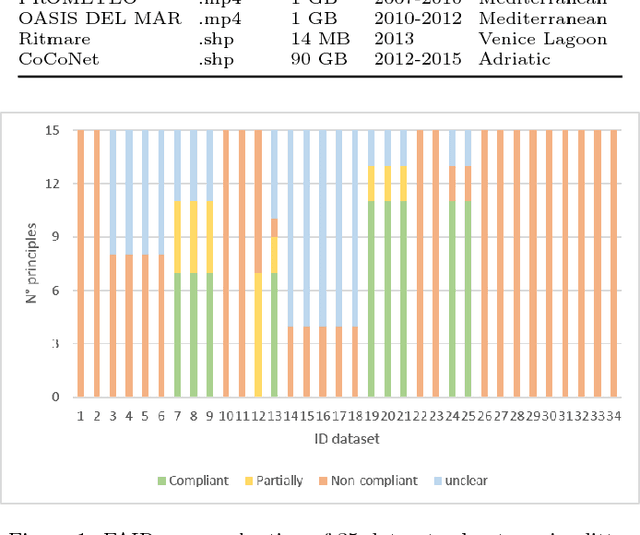
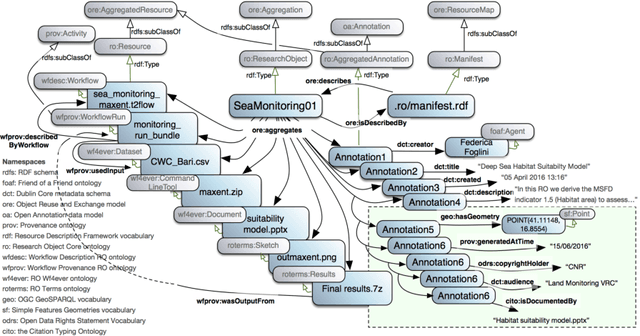
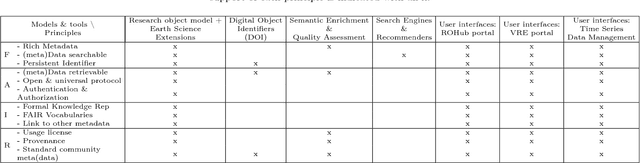
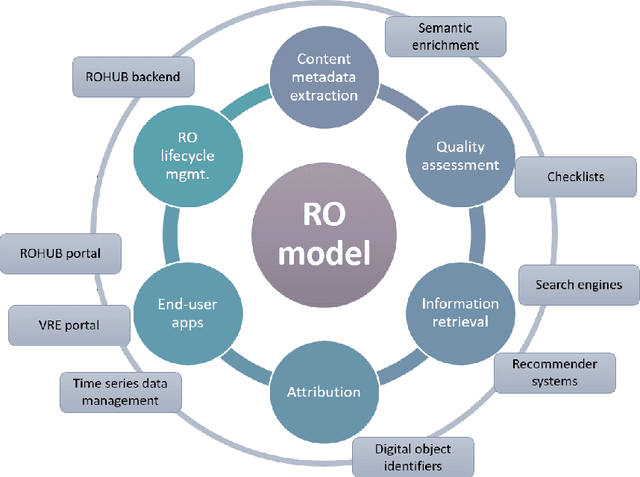
Abstract:Data-intensive science communities are progressively adopting FAIR practices that enhance the visibility of scientific breakthroughs and enable reuse. At the core of this movement, research objects contain and describe scientific information and resources in a way compliant with the FAIR principles and sustain the development of key infrastructure and tools. This paper provides an account of the challenges, experiences and solutions involved in the adoption of FAIR around research objects over several Earth Science disciplines. During this journey, our work has been comprehensive, with outcomes including: an extended research object model adapted to the needs of earth scientists; the provisioning of digital object identifiers (DOI) to enable persistent identification and to give due credit to authors; the generation of content-based, semantically rich, research object metadata through natural language processing, enhancing visibility and reuse through recommendation systems and third-party search engines; and various types of checklists that provide a compact representation of research object quality as a key enabler of scientific reuse. All these results have been integrated in ROHub, a platform that provides research object management functionality to a wealth of applications and interfaces across different scientific communities. To monitor and quantify the community uptake of research objects, we have defined indicators and obtained measures via ROHub that are also discussed herein.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge