Ramsha Ahmed
Automated segmentation and extraction of posterior eye segment using OCT scans
Sep 21, 2021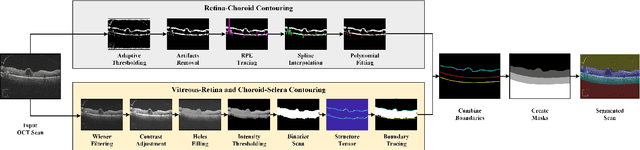
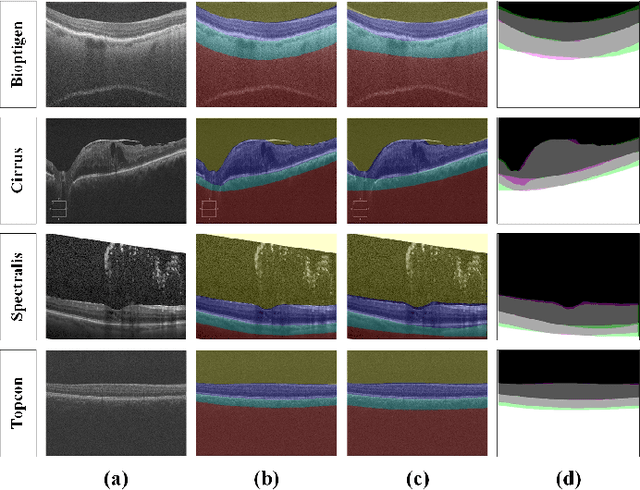
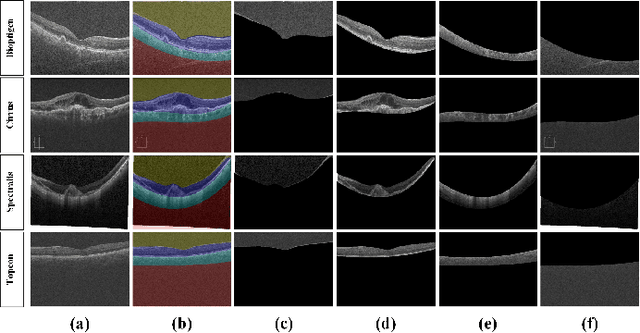
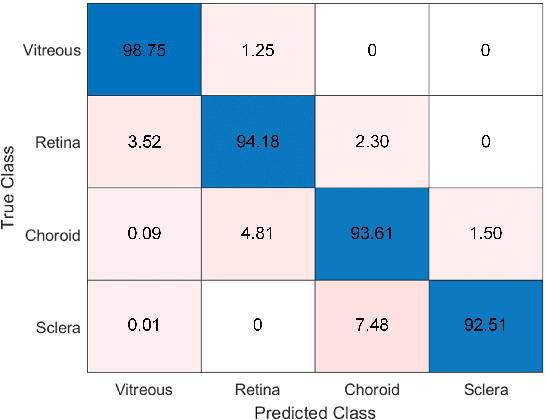
Abstract:This paper proposes an automated method for the segmentation and extraction of the posterior segment of the human eye, including the vitreous, retina, choroid, and sclera compartments, using multi-vendor optical coherence tomography (OCT) scans. The proposed method works in two phases. First extracts the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) layer by applying the adaptive thresholding technique to identify the retina-choroid junction. Then, it exploits the structure tensor guided approach to extract the inner limiting membrane (ILM) and the choroidal stroma (CS) layers, locating the vitreous-retina and choroid-sclera junctions in the candidate OCT scan. Furthermore, these three junction boundaries are utilized to conduct posterior eye compartmentalization effectively for both healthy and disease eye OCT scans. The proposed framework is evaluated over 1000 OCT scans, where it obtained the mean intersection over union (IoU) and mean Dice similarity coefficient (DSC) scores of 0.874 and 0.930, respectively.
SIP-SegNet: A Deep Convolutional Encoder-Decoder Network for Joint Semantic Segmentation and Extraction of Sclera, Iris and Pupil based on Periocular Region Suppression
Feb 15, 2020



Abstract:The current developments in the field of machine vision have opened new vistas towards deploying multimodal biometric recognition systems in various real-world applications. These systems have the ability to deal with the limitations of unimodal biometric systems which are vulnerable to spoofing, noise, non-universality and intra-class variations. In addition, the ocular traits among various biometric traits are preferably used in these recognition systems. Such systems possess high distinctiveness, permanence, and performance while, technologies based on other biometric traits (fingerprints, voice etc.) can be easily compromised. This work presents a novel deep learning framework called SIP-SegNet, which performs the joint semantic segmentation of ocular traits (sclera, iris and pupil) in unconstrained scenarios with greater accuracy. The acquired images under these scenarios exhibit purkinje reflexes, specular reflections, eye gaze, off-angle shots, low resolution, and various occlusions particularly by eyelids and eyelashes. To address these issues, SIP-SegNet begins with denoising the pristine image using denoising convolutional neural network (DnCNN), followed by reflection removal and image enhancement based on contrast limited adaptive histogram equalization (CLAHE). Our proposed framework then extracts the periocular information using adaptive thresholding and employs the fuzzy filtering technique to suppress this information. Finally, the semantic segmentation of sclera, iris and pupil is achieved using the densely connected fully convolutional encoder-decoder network. We used five CASIA datasets to evaluate the performance of SIP-SegNet based on various evaluation metrics. The simulation results validate the optimal segmentation of the proposed SIP-SegNet, with the mean f1 scores of 93.35, 95.11 and 96.69 for the sclera, iris and pupil classes respectively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge