Ram Dyuthi Sristi
Contextual Feature Selection with Conditional Stochastic Gates
Dec 21, 2023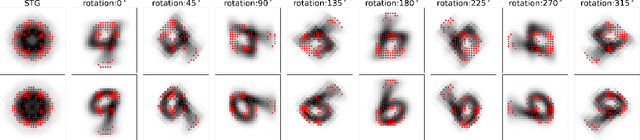
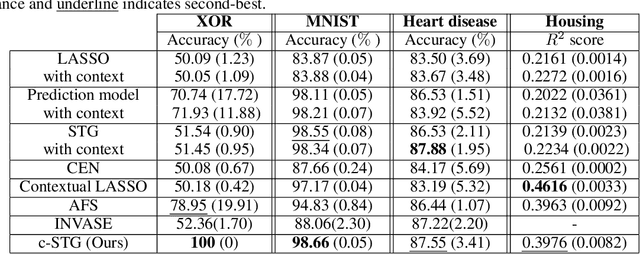
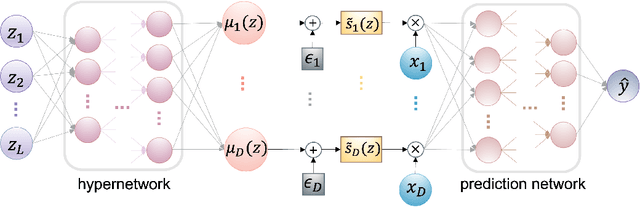
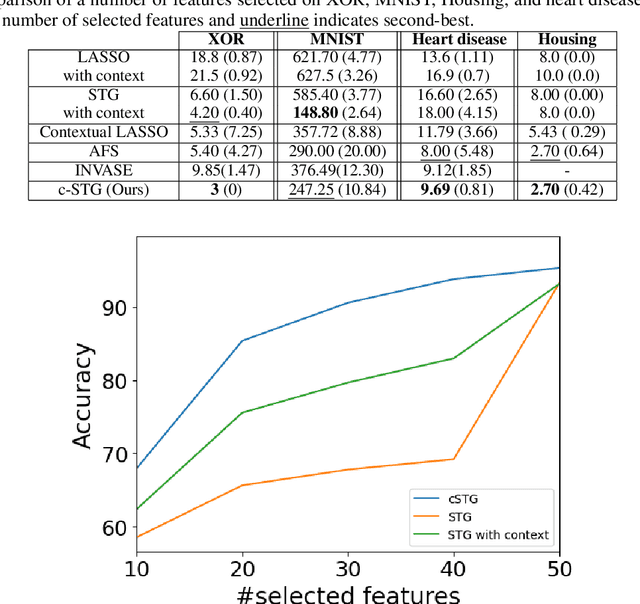
Abstract:We study the problem of contextual feature selection, where the goal is to learn a predictive function while identifying subsets of informative features conditioned on specific contexts. Towards this goal, we generalize the recently proposed stochastic gates (STG) Yamada et al. [2020] by modeling the probabilistic gates as conditional Bernoulli variables whose parameters are predicted based on the contextual variables. Our new scheme, termed conditional-STG (c-STG), comprises two networks: a hypernetwork that establishes the mapping between contextual variables and probabilistic feature selection parameters and a prediction network that maps the selected feature to the response variable. Training the two networks simultaneously ensures the comprehensive incorporation of context and feature selection within a unified model. We provide a theoretical analysis to examine several properties of the proposed framework. Importantly, our model leads to improved flexibility and adaptability of feature selection and, therefore, can better capture the nuances and variations in the data. We apply c-STG to simulated and real-world datasets, including healthcare, housing, and neuroscience, and demonstrate that it effectively selects contextually meaningful features, thereby enhancing predictive performance and interpretability.
DiSC: Differential Spectral Clustering of Features
Nov 10, 2022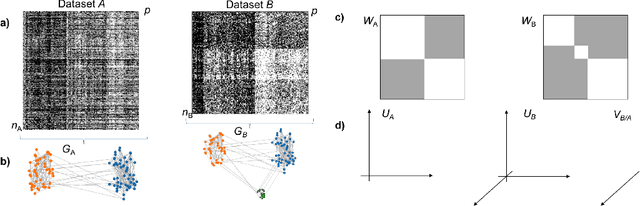
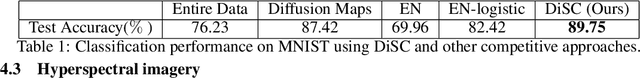
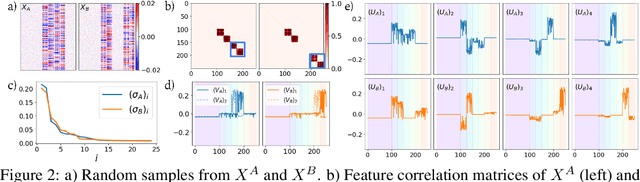
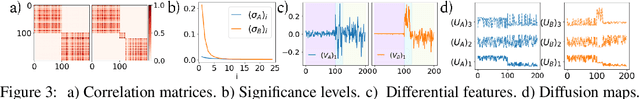
Abstract:Selecting subsets of features that differentiate between two conditions is a key task in a broad range of scientific domains. In many applications, the features of interest form clusters with similar effects on the data at hand. To recover such clusters we develop DiSC, a data-driven approach for detecting groups of features that differentiate between conditions. For each condition, we construct a graph whose nodes correspond to the features and whose weights are functions of the similarity between them for that condition. We then apply a spectral approach to compute subsets of nodes whose connectivity differs significantly between the condition-specific feature graphs. On the theoretical front, we analyze our approach with a toy example based on the stochastic block model. We evaluate DiSC on a variety of datasets, including MNIST, hyperspectral imaging, simulated scRNA-seq and task fMRI, and demonstrate that DiSC uncovers features that better differentiate between conditions compared to competing methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge