Rajeev Bhatt Ambati
Socratic Students: Teaching Language Models to Learn by Asking Questions
Dec 20, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) excel at static interactions, where they answer user queries by retrieving knowledge encoded in their parameters. However, in many real-world settings, such as educational tutoring or medical assistance, relevant information is not directly available and must be actively acquired through dynamic interactions. An interactive agent would recognize its own uncertainty, ask targeted questions, and retain new knowledge efficiently. Prior work has primarily explored effective ways for a teacher to instruct the student, where the teacher identifies student gaps and provides guidance. In this work, we shift the focus to the student and investigate effective strategies to actively query the teacher in seeking useful information. Across math and coding benchmarks, where baseline student models begin with near-zero performance, we show that student-led approaches consistently yield absolute Pass@k improvements of at least 0.5 over static baselines. To improve question quality, we train students using Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) with guidance from either self or stronger students. We find that this guided training enables smaller models to learn how to ask better questions, further enhancing learning efficiency.
MarginSel : Max-Margin Demonstration Selection for LLMs
Jun 07, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) excel at few-shot learning via in-context learning (ICL). However, the effectiveness of ICL is often sensitive to the selection and ordering of demonstration examples. To address this, we present MarginSel: Max-Margin Demonstration Selection for LLMs, a two-step method that selects hard demonstration examples for the ICL prompt, adapting to each test instance. Our approach achieves 2-7% absolute improvement in F1-score across classification tasks, compared to a random selection of examples. We also provide theoretical insights and empirical evidence showing that MarginSel induces max-margin behavior in LLMs by effectively increasing the margin for hard examples, analogous to support vectors, thereby shifting the decision boundary in a beneficial direction.
Assertion Detection in Multi-Label Clinical Text using Scope Localization
May 19, 2020



Abstract:Multi-label sentences (text) in the clinical domain result from the rich description of scenarios during patient care. The state-of-theart methods for assertion detection mostly address this task in the setting of a single assertion label per sentence (text). In addition, few rules based and deep learning methods perform negation/assertion scope detection on single-label text. It is a significant challenge extending these methods to address multi-label sentences without diminishing performance. Therefore, we developed a convolutional neural network (CNN) architecture to localize multiple labels and their scopes in a single stage end-to-end fashion, and demonstrate that our model performs atleast 12% better than the state-of-the-art on multi-label clinical text.
Read, Highlight and Summarize: A Hierarchical Neural Semantic Encoder-based Approach
Nov 01, 2019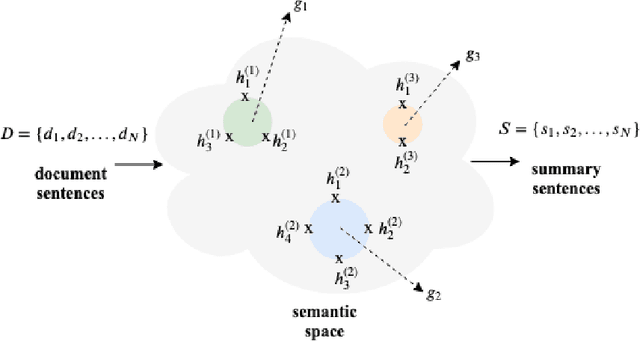
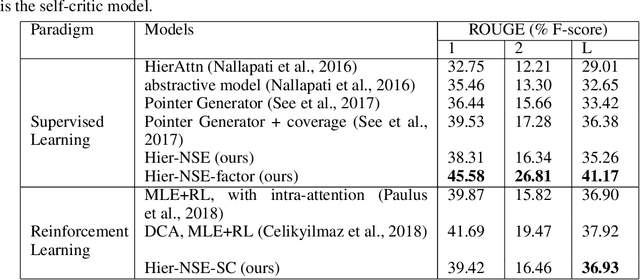
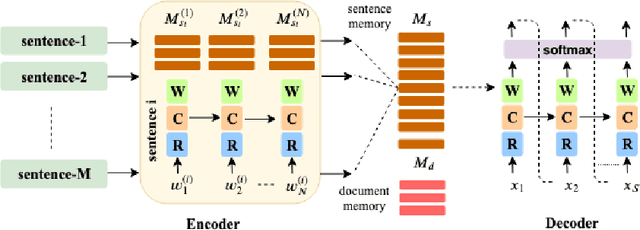
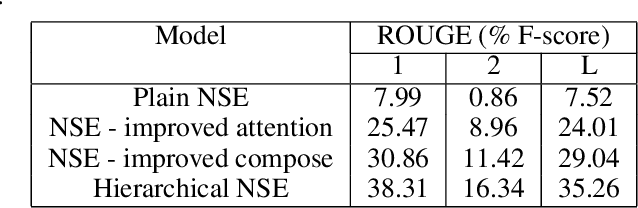
Abstract:Traditional sequence-to-sequence (seq2seq) models and other variations of the attention-mechanism such as hierarchical attention have been applied to the text summarization problem. Though there is a hierarchy in the way humans use language by forming paragraphs from sentences and sentences from words, hierarchical models have usually not worked that much better than their traditional seq2seq counterparts. This effect is mainly because either the hierarchical attention mechanisms are too sparse using hard attention or noisy using soft attention. In this paper, we propose a method based on extracting the highlights of a document; a key concept that is conveyed in a few sentences. In a typical text summarization dataset consisting of documents that are 800 tokens in length (average), capturing long-term dependencies is very important, e.g., the last sentence can be grouped with the first sentence of a document to form a summary. LSTMs (Long Short-Term Memory) proved useful for machine translation. However, they often fail to capture long-term dependencies while modeling long sequences. To address these issues, we have adapted Neural Semantic Encoders (NSE) to text summarization, a class of memory-augmented neural networks by improving its functionalities and proposed a novel hierarchical NSE that outperforms similar previous models significantly. The quality of summarization was improved by augmenting linguistic factors, namely lemma, and Part-of-Speech (PoS) tags, to each word in the dataset for improved vocabulary coverage and generalization. The hierarchical NSE model on factored dataset outperformed the state-of-the-art by nearly 4 ROUGE points. We further designed and used the first GPU-based self-critical Reinforcement Learning model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge