Rabia Latif
A Benchmark Dataset with Larger Context for Non-Factoid Question Answering over Islamic Text
Sep 15, 2024



Abstract:Accessing and comprehending religious texts, particularly the Quran (the sacred scripture of Islam) and Ahadith (the corpus of the sayings or traditions of the Prophet Muhammad), in today's digital era necessitates efficient and accurate Question-Answering (QA) systems. Yet, the scarcity of QA systems tailored specifically to the detailed nature of inquiries about the Quranic Tafsir (explanation, interpretation, context of Quran for clarity) and Ahadith poses significant challenges. To address this gap, we introduce a comprehensive dataset meticulously crafted for QA purposes within the domain of Quranic Tafsir and Ahadith. This dataset comprises a robust collection of over 73,000 question-answer pairs, standing as the largest reported dataset in this specialized domain. Importantly, both questions and answers within the dataset are meticulously enriched with contextual information, serving as invaluable resources for training and evaluating tailored QA systems. However, while this paper highlights the dataset's contributions and establishes a benchmark for evaluating QA performance in the Quran and Ahadith domains, our subsequent human evaluation uncovered critical insights regarding the limitations of existing automatic evaluation techniques. The discrepancy between automatic evaluation metrics, such as ROUGE scores, and human assessments became apparent. The human evaluation indicated significant disparities: the model's verdict consistency with expert scholars ranged between 11% to 20%, while its contextual understanding spanned a broader spectrum of 50% to 90%. These findings underscore the necessity for evaluation techniques that capture the nuances and complexities inherent in understanding religious texts, surpassing the limitations of traditional automatic metrics.
Optimizing Multi-Stuttered Speech Classification: Leveraging Whisper's Encoder for Efficient Parameter Reduction in Automated Assessment
Jun 12, 2024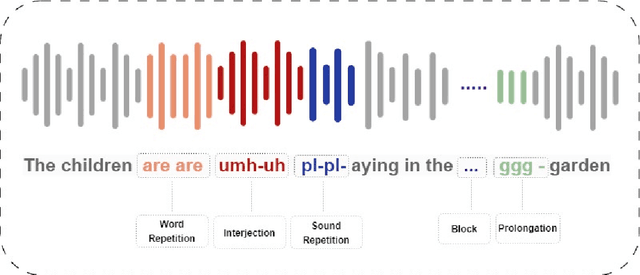



Abstract:The automated classification of stuttered speech has significant implications for timely assessments providing assistance to speech language pathologists. Despite notable advancements in the field, the cases in which multiple disfluencies occur in speech require attention. We have taken a progressive approach to fill this gap by classifying multi-stuttered speech more efficiently. The problem has been addressed by firstly curating a dataset of multi-stuttered disfluencies from SEP-28k audio clips. Secondly, employing Whisper, a state-of-the-art speech recognition model has been leveraged by using its encoder and taking the problem as multi-label classification. Thirdly, using a 6 encoder layer Whisper and experimenting with various layer freezing strategies, a computationally efficient configuration of the model was identified. The proposed configuration achieved micro, macro, and weighted F1- scores of 0.88, 0.85, and 0.87, correspondingly on an external test dataset i.e. Fluency-Bank. In addition, through layer freezing strategies, we were able to achieve the aforementioned results by fine-tuning a single encoder layer, consequently, reducing the model's trainable parameters from 20.27 million to 3.29 million. This research study unveils the contribution of the last encoder layer in the identification of disfluencies in stuttered speech. Consequently, it has led to a computationally efficient approach which makes the model more adaptable for various dialects and languages.
Whisper in Focus: Enhancing Stuttered Speech Classification with Encoder Layer Optimization
Nov 09, 2023



Abstract:In recent years, advancements in the field of speech processing have led to cutting-edge deep learning algorithms with immense potential for real-world applications. The automated identification of stuttered speech is one of such applications that the researchers are addressing by employing deep learning techniques. Recently, researchers have utilized Wav2vec2.0, a speech recognition model to classify disfluency types in stuttered speech. Although Wav2vec2.0 has shown commendable results, its ability to generalize across all disfluency types is limited. In addition, since its base model uses 12 encoder layers, it is considered a resource-intensive model. Our study unravels the capabilities of Whisper for the classification of disfluency types in stuttered speech. We have made notable contributions in three pivotal areas: enhancing the quality of SEP28-k benchmark dataset, exploration of Whisper for classification, and introducing an efficient encoder layer freezing strategy. The optimized Whisper model has achieved the average F1-score of 0.81, which proffers its abilities. This study also unwinds the significance of deeper encoder layers in the identification of disfluency types, as the results demonstrate their greater contribution compared to initial layers. This research represents substantial contributions, shifting the emphasis towards an efficient solution, thereby thriving towards prospective innovation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge