Raúl Rojas
Dancing Honey bee Robot Elicits Dance-Following and Recruits Foragers
Mar 19, 2018



Abstract:The honey bee dance communication system is one of the most popular examples of animal communication. Forager bees communicate the flight vector towards food, water, or resin sources to nestmates by performing a stereotypical motion pattern on the comb surface in the darkness of the hive. Bees that actively follow the circles of the dancer, so called dance-followers, may decode the message and fly according to the indicated vector that refers to the sun compass and their visual odometer. We investigated the dance communication system with a honeybee robot that reproduced the waggle dance pattern for a flight vector chosen by the experimenter. The dancing robot, called RoboBee, generated multiple cues contained in the biological dance pattern and elicited natural dance-following behavior in live bees. By tracking the flight trajectory of departing bees after following the dancing robot via harmonic radar we confirmed that bees used information obtained from the robotic dance to adjust their flight path. This is the first report on successful dance following and subsequent flight performance of bees recruited by a biomimetic robot.
Automatic detection and decoding of honey bee waggle dances
Dec 05, 2017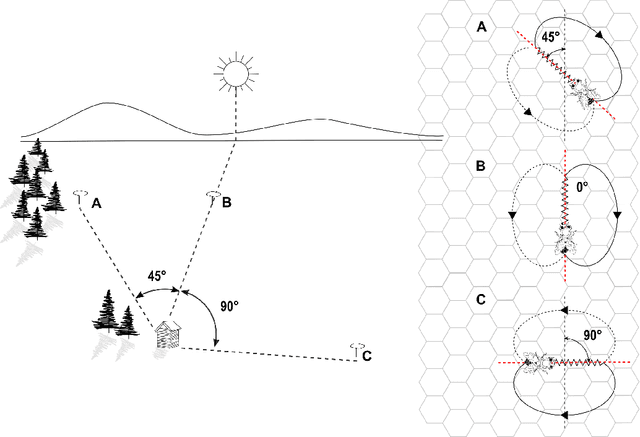
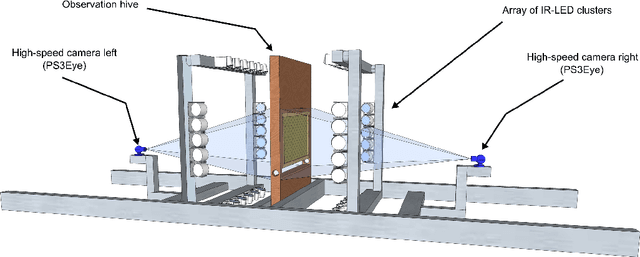
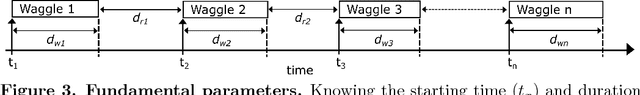
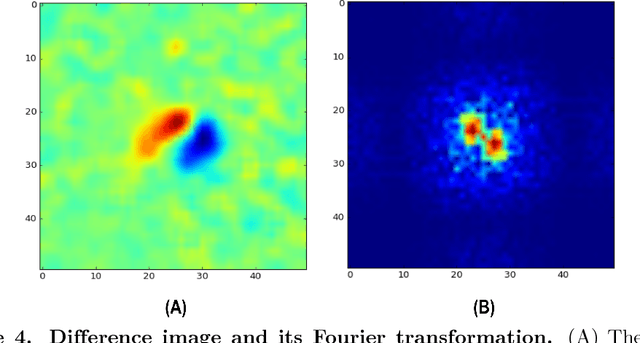
Abstract:The waggle dance is one of the most popular examples of animal communication. Forager bees direct their nestmates to profitable resources via a complex motor display. Essentially, the dance encodes the polar coordinates to the resource in the field. Unemployed foragers follow the dancer's movements and then search for the advertised spots in the field. Throughout the last decades, biologists have employed different techniques to measure key characteristics of the waggle dance and decode the information it conveys. Early techniques involved the use of protractors and stopwatches to measure the dance orientation and duration directly from the observation hive. Recent approaches employ digital video recordings and manual measurements on screen. However, manual approaches are very time-consuming. Most studies, therefore, regard only small numbers of animals in short periods of time. We have developed a system capable of automatically detecting, decoding and mapping communication dances in real-time. In this paper, we describe our recording setup, the image processing steps performed for dance detection and decoding and an algorithm to map dances to the field. The proposed system performs with a detection accuracy of 90.07\%. The decoded waggle orientation has an average error of -2.92{\deg} ($\pm$ 7.37{\deg} ), well within the range of human error. To evaluate and exemplify the system's performance, a group of bees was trained to an artificial feeder, and all dances in the colony were automatically detected, decoded and mapped. The system presented here is the first of this kind made publicly available, including source code and hardware specifications. We hope this will foster quantitative analyses of the honey bee waggle dance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge