Rémi Mégret
IMS
Towards Automatic Honey Bee Flower-Patch Assays with Paint Marking Re-Identification
Nov 13, 2023Abstract:In this paper, we show that paint markings are a feasible approach to automatize the analysis of behavioral assays involving honey bees in the field where marking has to be as lightweight as possible. We contribute a novel dataset for bees re-identification with paint-markings with 4392 images and 27 identities. Contrastive learning with a ResNet backbone and triplet loss led to identity representation features with almost perfect recognition in closed setting where identities are known in advance. Diverse experiments evaluate the capability to generalize to separate IDs, and show the impact of using different body parts for identification, such as using the unmarked abdomen only. In addition, we show the potential to fully automate the visit detection and provide preliminary results of compute time for future real-time deployment in the field on an edge device.
Nested Graph Words for Object Recognition
Apr 23, 2014


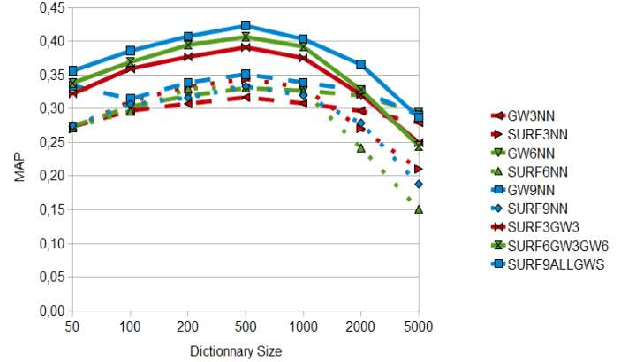
Abstract:In this paper, we propose a new, scalable approach for the task of object based image search or object recognition. Despite the very large literature existing on the scalability issues in CBIR in the sense of retrieval approaches, the scalability of media and scalability of features remain an issue. In our work we tackle the problem of scalability and structural organization of features. The proposed features are nested local graphs built upon sets of SURF feature points with Delaunay triangulation. A Bag-of-Visual-Words (BoVW) framework is applied on these graphs, giving birth to a Bag-of-Graph-Words representation. The nested nature of the descriptors consists in scaling from trivial Delaunay graphs - isolated feature points - by increasing the number of nodes layer by layer up to graphs with maximal number of nodes. For each layer of graphs its proper visual dictionary is built. The experiments conducted on the SIVAL data set reveal that the graph features at different layers exhibit complementary performances on the same content. The nested approach, the combination of all existing layers, yields significant improvement of the object recognition performance compared to single level approaches.
Egocentric vision IT technologies for Alzheimer disease assessment and studies
Mar 13, 2013
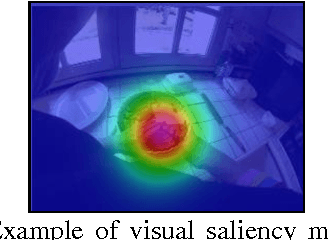

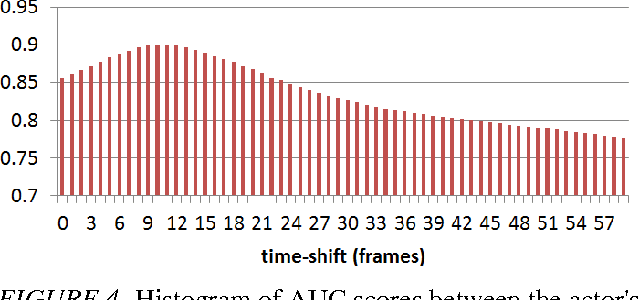
Abstract:Egocentric vision technology consists in capturing the actions of persons from their own visual point of view using wearable camera sensors. We apply this new paradigm to instrumental activities monitoring with the objective of providing new tools for the clinical evaluation of the impact of the disease on persons with dementia. In this paper, we introduce the current state of the development of this technology and focus on two technology modules: automatic location estimation and visual saliency estimation for content interpretation.
Human Daily Activities Indexing in Videos from Wearable Cameras for Monitoring of Patients with Dementia Diseases
Jul 23, 2010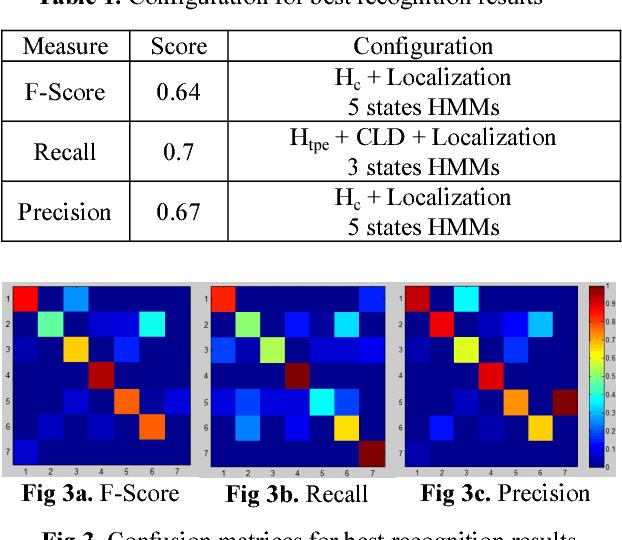

Abstract:Our research focuses on analysing human activities according to a known behaviorist scenario, in case of noisy and high dimensional collected data. The data come from the monitoring of patients with dementia diseases by wearable cameras. We define a structural model of video recordings based on a Hidden Markov Model. New spatio-temporal features, color features and localization features are proposed as observations. First results in recognition of activities are promising.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge