Qiqi Li
Segment Discovery: Enhancing E-commerce Targeting
Sep 20, 2024Abstract:Modern e-commerce services frequently target customers with incentives or interventions to engage them in their products such as games, shopping, video streaming, etc. This customer engagement increases acquisition of more customers and retention of existing ones, leading to more business for the company while improving customer experience. Often, customers are either randomly targeted or targeted based on the propensity of desirable behavior. However, such policies can be suboptimal as they do not target the set of customers who would benefit the most from the intervention and they may also not take account of any constraints. In this paper, we propose a policy framework based on uplift modeling and constrained optimization that identifies customers to target for a use-case specific intervention so as to maximize the value to the business, while taking account of any given constraints. We demonstrate improvement over state-of-the-art targeting approaches using two large-scale experimental studies and a production implementation.
Image Deconvolution with Deep Image and Kernel Priors
Oct 18, 2019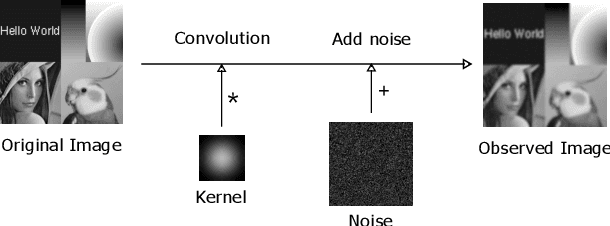
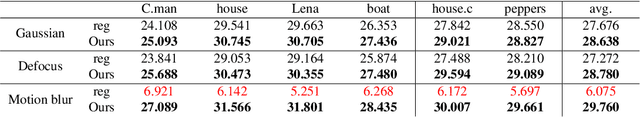

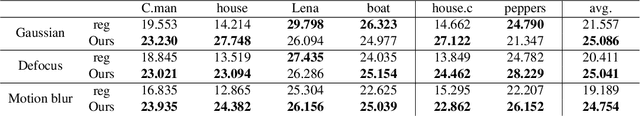
Abstract:Image deconvolution is the process of recovering convolutional degraded images, which is always a hard inverse problem because of its mathematically ill-posed property. On the success of the recently proposed deep image prior (DIP), we build an image deconvolution model with deep image and kernel priors (DIKP). DIP is a learning-free representation which uses neural net structures to express image prior information, and it showed great success in many energy-based models, e.g. denoising, super-resolution, inpainting. Instead, our DIKP model uses such priors in image deconvolution to model not only images but also kernels, combining the ideas of traditional learning-free deconvolution methods with neural nets. In this paper, we show that DIKP improve the performance of learning-free image deconvolution, and we experimentally demonstrate this on the standard benchmark of six standard test images in terms of PSNR and visual effects.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge