Qinxue Meng
Relational Autoencoder for Feature Extraction
Feb 09, 2018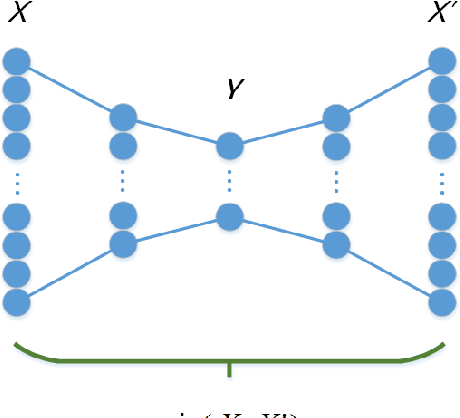
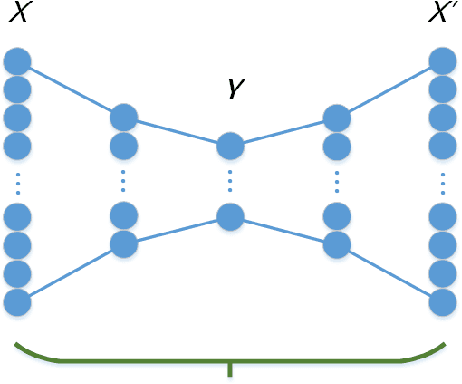
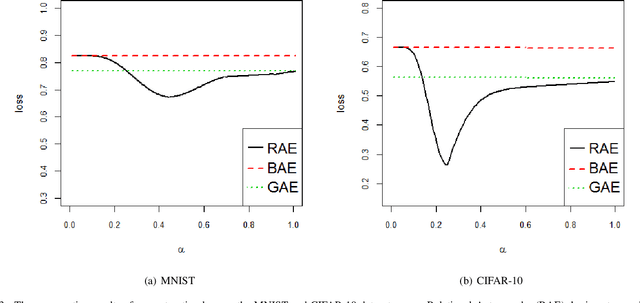
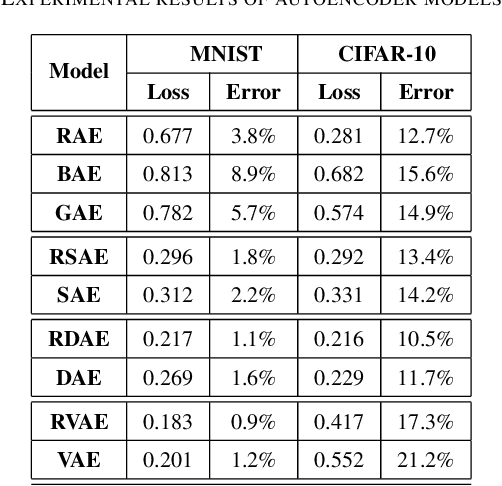
Abstract:Feature extraction becomes increasingly important as data grows high dimensional. Autoencoder as a neural network based feature extraction method achieves great success in generating abstract features of high dimensional data. However, it fails to consider the relationships of data samples which may affect experimental results of using original and new features. In this paper, we propose a Relation Autoencoder model considering both data features and their relationships. We also extend it to work with other major autoencoder models including Sparse Autoencoder, Denoising Autoencoder and Variational Autoencoder. The proposed relational autoencoder models are evaluated on a set of benchmark datasets and the experimental results show that considering data relationships can generate more robust features which achieve lower construction loss and then lower error rate in further classification compared to the other variants of autoencoders.
* IJCNN-2017
Dynamic Island Model based on Spectral Clustering in Genetic Algorithm
Jan 05, 2018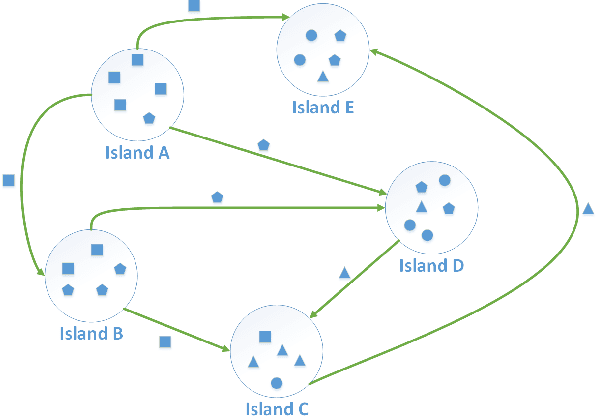
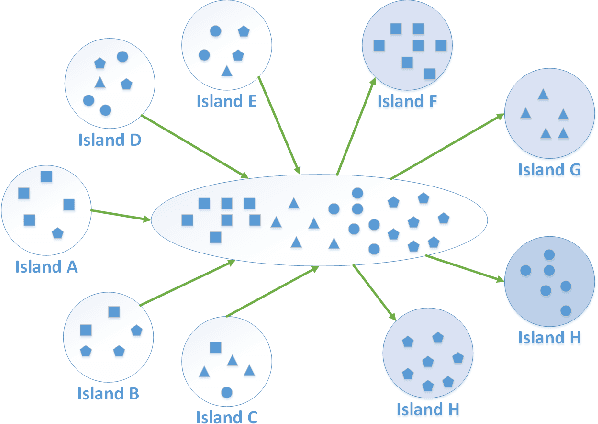
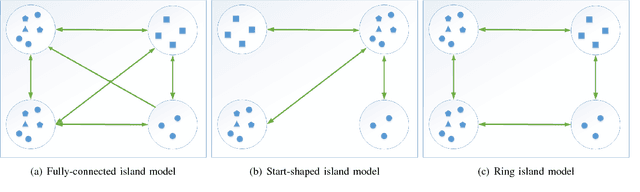
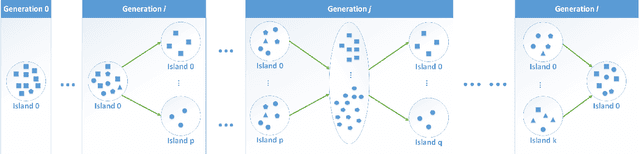
Abstract:How to maintain relative high diversity is important to avoid premature convergence in population-based optimization methods. Island model is widely considered as a major approach to achieve this because of its flexibility and high efficiency. The model maintains a group of sub-populations on different islands and allows sub-populations to interact with each other via predefined migration policies. However, current island model has some drawbacks. One is that after a certain number of generations, different islands may retain quite similar, converged sub-populations thereby losing diversity and decreasing efficiency. Another drawback is that determining the number of islands to maintain is also very challenging. Meanwhile initializing many sub-populations increases the randomness of island model. To address these issues, we proposed a dynamic island model~(DIM-SP) which can force each island to maintain different sub-populations, control the number of islands dynamically and starts with one sub-population. The proposed island model outperforms the other three state-of-the-art island models in three baseline optimization problems including job shop scheduler problem, travelling salesmen problem and quadratic multiple knapsack problem.
* 8 pages
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge