Qazaleh Mirsharif
Crowd Sourcing based Active Learning Approach for Parking Sign Recognition
Dec 03, 2018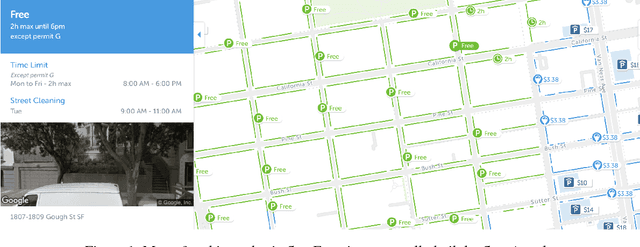
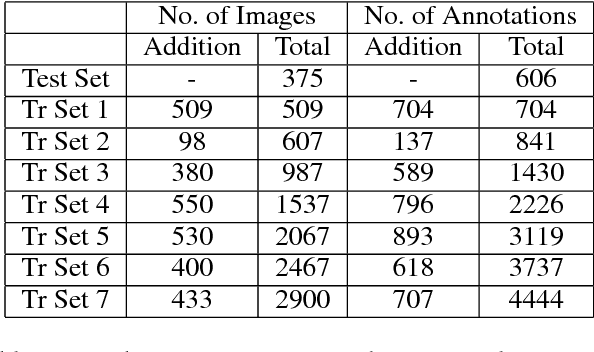

Abstract:Deep learning models have been used extensively to solve real-world problems in recent years. The performance of such models relies heavily on large amounts of labeled data for training. While the advances of data collection technology have enabled the acquisition of a massive volume of data, labeling the data remains an expensive and time-consuming task. Active learning techniques are being progressively adopted to accelerate the development of machine learning solutions by allowing the model to query the data they learn from. In this paper, we introduce a real-world problem, the recognition of parking signs, and present a framework that combines active learning techniques with a transfer learning approach and crowd-sourcing tools to create and train a machine learning solution to the problem. We discuss how such a framework contributes to building an accurate model in a cost-effective and fast way to solve the parking sign recognition problem in spite of the unevenness of the data associated with the fact that street-level images (such as parking signs) vary in shape, color, orientation and scale, and often appear on top of different types of background.
A Semi-Automated Method for Object Segmentation in Infant's Egocentric Videos to Study Object Perception
Feb 08, 2016
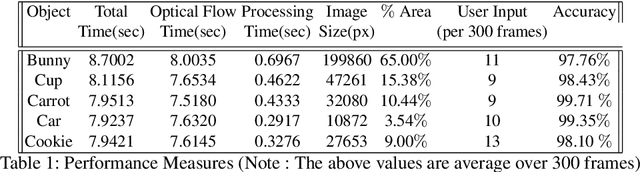
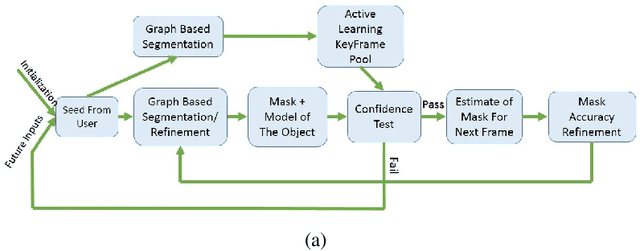
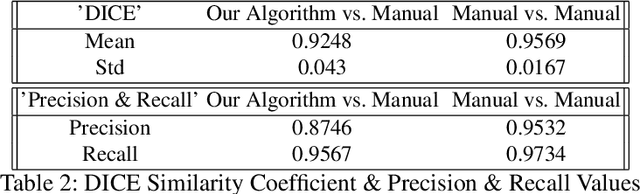
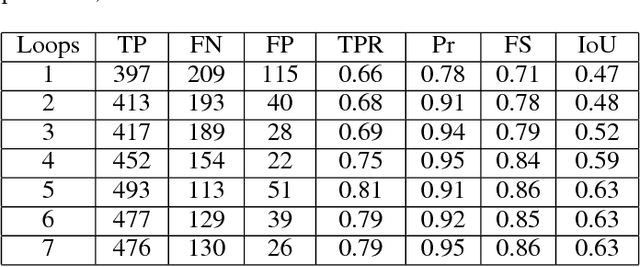
Abstract:Object segmentation in infant's egocentric videos is a fundamental step in studying how children perceive objects in early stages of development. From the computer vision perspective, object segmentation in such videos pose quite a few challenges because the child's view is unfocused, often with large head movements, effecting in sudden changes in the child's point of view which leads to frequent change in object properties such as size, shape and illumination. In this paper, we develop a semi-automated, domain specific, method to address these concerns and facilitate the object annotation process for cognitive scientists allowing them to select and monitor the object under segmentation. The method starts with an annotation from the user of the desired object and employs graph cut segmentation and optical flow computation to predict the object mask for subsequent video frames automatically. To maintain accuracy, we use domain specific heuristic rules to re-initialize the program with new user input whenever object properties change dramatically. The evaluations demonstrate the high speed and accuracy of the presented method for object segmentation in voluminous egocentric videos. We apply the proposed method to investigate potential patterns in object distribution in child's view at progressive ages.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge