Pulkit Khandelwal
Development of an isotropic segmentation model for medial temporal lobe subregions on anisotropic MRI atlas using implicit neural representation
Aug 24, 2025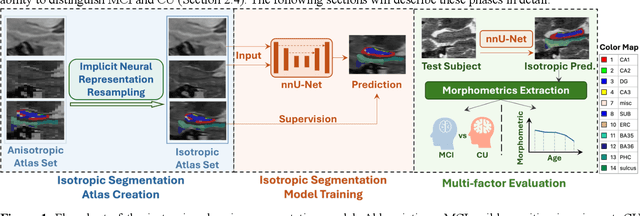
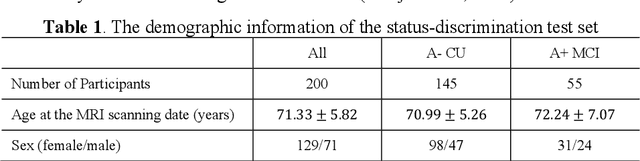
Abstract:Imaging biomarkers in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are important tools for diagnosing and tracking Alzheimer's disease (AD). As medial temporal lobe (MTL) is the earliest region to show AD-related hallmarks, brain atrophy caused by AD can first be observed in the MTL. Accurate segmentation of MTL subregions and extraction of imaging biomarkers from them are important. However, due to imaging limitations, the resolution of T2-weighted (T2w) MRI is anisotropic, which makes it difficult to accurately extract the thickness of cortical subregions in the MTL. In this study, we used an implicit neural representation method to combine the resolution advantages of T1-weighted and T2w MRI to accurately upsample an MTL subregion atlas set from anisotropic space to isotropic space, establishing a multi-modality, high-resolution atlas set. Based on this atlas, we developed an isotropic MTL subregion segmentation model. In an independent test set, the cortical subregion thickness extracted using this isotropic model showed higher significance than an anisotropic method in distinguishing between participants with mild cognitive impairment and cognitively unimpaired (CU) participants. In longitudinal analysis, the biomarkers extracted using isotropic method showed greater stability in CU participants. This study improved the accuracy of AD imaging biomarkers without increasing the amount of atlas annotation work, which may help to more accurately quantify the relationship between AD and brain atrophy and provide more accurate measures for disease tracking.
Nearly isotropic segmentation for medial temporal lobe subregions in multi-modality MRI
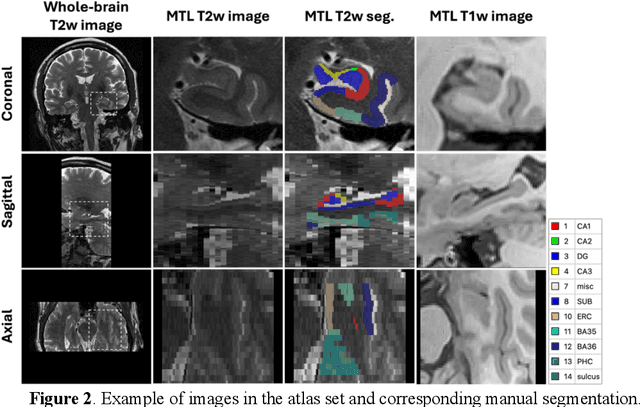
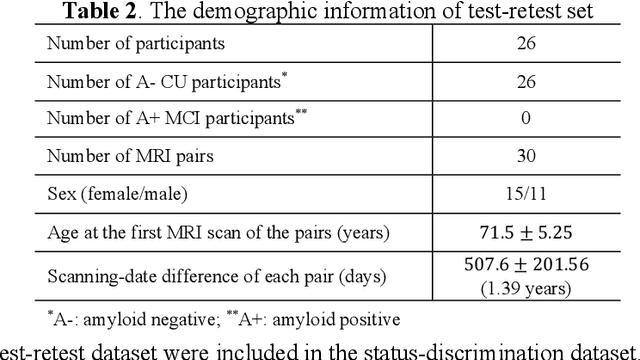
Apr 25, 2025Abstract:Morphometry of medial temporal lobe (MTL) subregions in brain MRI is sensitive biomarker to Alzheimers Disease and other related conditions. While T2-weighted (T2w) MRI with high in-plane resolution is widely used to segment hippocampal subfields due to its higher contrast in hippocampus, its lower out-of-plane resolution reduces the accuracy of subregion thickness measurements. To address this issue, we developed a nearly isotropic segmentation pipeline that incorporates image and label upsampling and high-resolution segmentation in T2w MRI. First, a high-resolution atlas was created based on an existing anisotropic atlas derived from 29 individuals. Both T1-weighted and T2w images in the atlas were upsampled from their original resolution to a nearly isotropic resolution 0.4x0.4x0.52mm3 using a non-local means approach. Manual segmentations within the atlas were also upsampled to match this resolution using a UNet-based neural network, which was trained on a cohort consisting of both high-resolution ex vivo and low-resolution anisotropic in vivo MRI with manual segmentations. Second, a multi-modality deep learning-based segmentation model was trained within this nearly isotropic atlas. Finally, experiments showed the nearly isotropic subregion segmentation improved the accuracy of cortical thickness as an imaging biomarker for neurodegeneration in T2w MRI.
Surface-based parcellation and vertex-wise analysis of ultra high-resolution ex vivo 7 tesla MRI in neurodegenerative diseases
Mar 28, 2024



Abstract:Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the standard modality to understand human brain structure and function in vivo (antemortem). Decades of research in human neuroimaging has led to the widespread development of methods and tools to provide automated volume-based segmentations and surface-based parcellations which help localize brain functions to specialized anatomical regions. Recently ex vivo (postmortem) imaging of the brain has opened-up avenues to study brain structure at sub-millimeter ultra high-resolution revealing details not possible to observe with in vivo MRI. Unfortunately, there has been limited methodological development in ex vivo MRI primarily due to lack of datasets and limited centers with such imaging resources. Therefore, in this work, we present one-of-its-kind dataset of 82 ex vivo T2w whole brain hemispheres MRI at 0.3 mm isotropic resolution spanning Alzheimer's disease and related dementias. We adapted and developed a fast and easy-to-use automated surface-based pipeline to parcellate, for the first time, ultra high-resolution ex vivo brain tissue at the native subject space resolution using the Desikan-Killiany-Tourville (DKT) brain atlas. This allows us to perform vertex-wise analysis in the template space and thereby link morphometry measures with pathology measurements derived from histology. We will open-source our dataset docker container, Jupyter notebooks for ready-to-use out-of-the-box set of tools and command line options to advance ex vivo MRI clinical brain imaging research on the project webpage.
Automated deep learning segmentation of high-resolution 7 T ex vivo MRI for quantitative analysis of structure-pathology correlations in neurodegenerative diseases
Mar 21, 2023



Abstract:Ex vivo MRI of the brain provides remarkable advantages over in vivo MRI for visualizing and characterizing detailed neuroanatomy, and helps to link microscale histology studies with morphometric measurements. However, automated segmentation methods for brain mapping in ex vivo MRI are not well developed, primarily due to limited availability of labeled datasets, and heterogeneity in scanner hardware and acquisition protocols. In this work, we present a high resolution dataset of 37 ex vivo post-mortem human brain tissue specimens scanned on a 7T whole-body MRI scanner. We developed a deep learning pipeline to segment the cortical mantle by benchmarking the performance of nine deep neural architectures. We then segment the four subcortical structures: caudate, putamen, globus pallidus, and thalamus; white matter hyperintensities, and the normal appearing white matter. We show excellent generalizing capabilities across whole brain hemispheres in different specimens, and also on unseen images acquired at different magnetic field strengths and different imaging sequence. We then compute volumetric and localized cortical thickness measurements across key regions, and link them with semi-quantitative neuropathological ratings. Our code, containerized executables, and the processed datasets are publicly available at: https://github.com/Pulkit-Khandelwal/upenn-picsl-brain-ex-vivo.
Improved Segmentation of Deep Sulci in Cortical Gray Matter Using a Deep Learning Framework Incorporating Laplace's Equation
Mar 03, 2023



Abstract:When developing tools for automated cortical segmentation, the ability to produce topologically correct segmentations is important in order to compute geometrically valid morphometry measures. In practice, accurate cortical segmentation is challenged by image artifacts and the highly convoluted anatomy of the cortex itself. To address this, we propose a novel deep learning-based cortical segmentation method in which prior knowledge about the geometry of the cortex is incorporated into the network during the training process. We design a loss function which uses the theory of Laplace's equation applied to the cortex to locally penalize unresolved boundaries between tightly folded sulci. Using an ex vivo MRI dataset of human medial temporal lobe specimens, we demonstrate that our approach outperforms baseline segmentation networks, both quantitatively and qualitatively.
Gray Matter Segmentation in Ultra High Resolution 7 Tesla ex vivo T2w MRI of Human Brain Hemispheres
Oct 14, 2021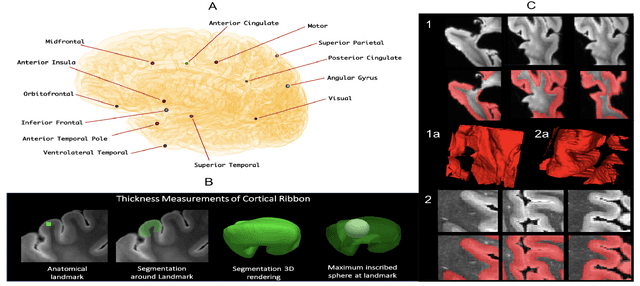
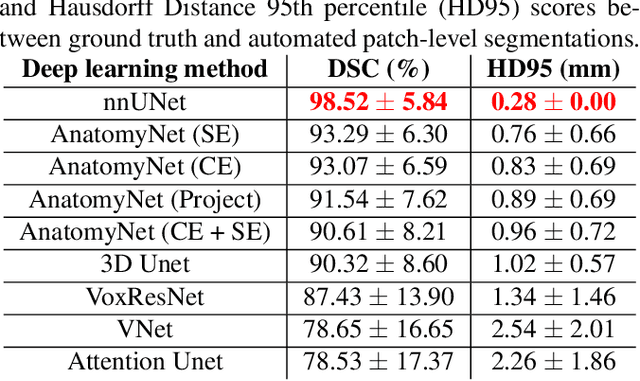
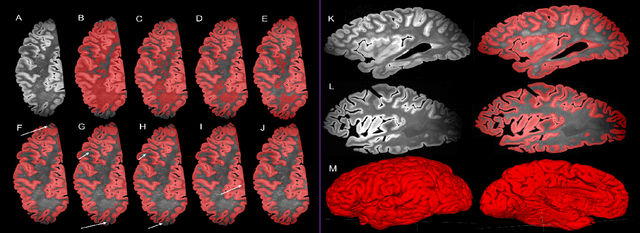
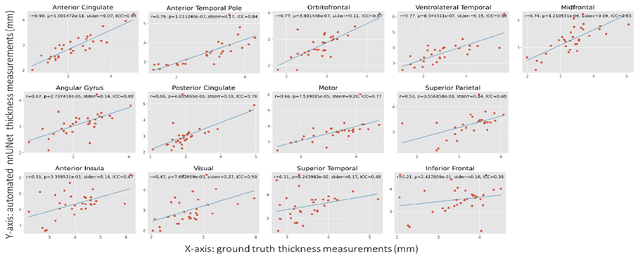
Abstract:Ex vivo MRI of the brain provides remarkable advantages over in vivo MRI for visualizing and characterizing detailed neuroanatomy. However, automated cortical segmentation methods in ex vivo MRI are not well developed, primarily due to limited availability of labeled datasets, and heterogeneity in scanner hardware and acquisition protocols. In this work, we present a high resolution 7 Tesla dataset of 32 ex vivo human brain specimens. We benchmark the cortical mantle segmentation performance of nine neural network architectures, trained and evaluated using manually-segmented 3D patches sampled from specific cortical regions, and show excellent generalizing capabilities across whole brain hemispheres in different specimens, and also on unseen images acquired at different magnetic field strength and imaging sequences. Finally, we provide cortical thickness measurements across key regions in 3D ex vivo human brain images. Our code and processed datasets are publicly available at https://github.com/Pulkit-Khandelwal/picsl-ex-vivo-segmentation.
Domain Generalizer: A Few-shot Meta Learning Framework for Domain Generalization in Medical Imaging
Aug 18, 2020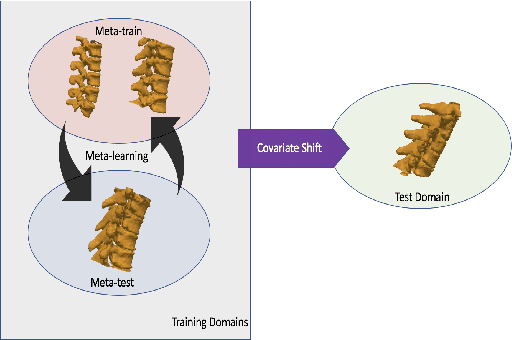
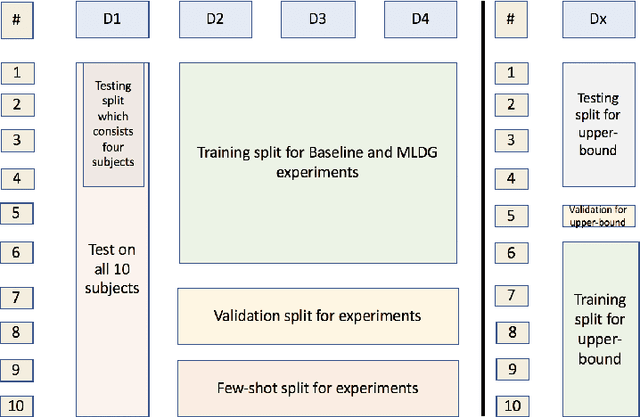
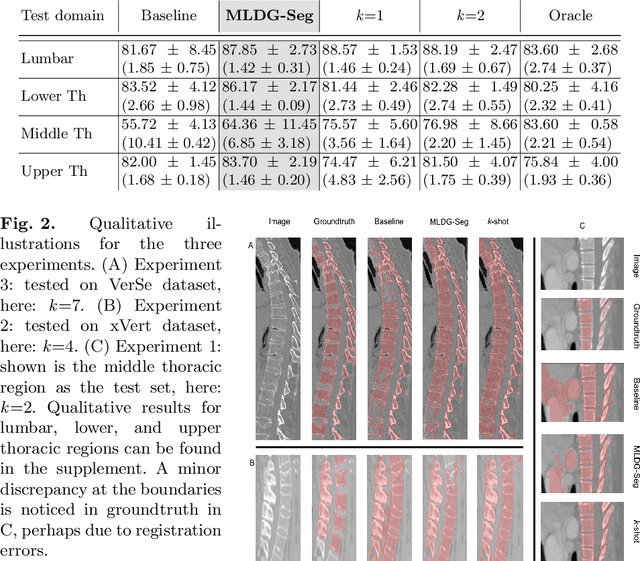
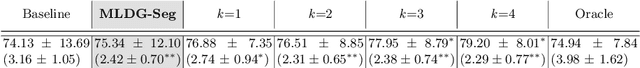
Abstract:Deep learning models perform best when tested on target (test) data domains whose distribution is similar to the set of source (train) domains. However, model generalization can be hindered when there is significant difference in the underlying statistics between the target and source domains. In this work, we adapt a domain generalization method based on a model-agnostic meta-learning framework to biomedical imaging. The method learns a domain-agnostic feature representation to improve generalization of models to the unseen test distribution. The method can be used for any imaging task, as it does not depend on the underlying model architecture. We validate the approach through a computed tomography (CT) vertebrae segmentation task across healthy and pathological cases on three datasets. Next, we employ few-shot learning, i.e. training the generalized model using very few examples from the unseen domain, to quickly adapt the model to new unseen data distribution. Our results suggest that the method could help generalize models across different medical centers, image acquisition protocols, anatomies, different regions in a given scan, healthy and diseased populations across varied imaging modalities.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge