Pritee Khanna
Secure and Privacy Preserving Proxy Biometrics Identities
Dec 21, 2022



Abstract:With large-scale adaption to biometric based applications, security and privacy of biometrics is utmost important especially when operating in unsupervised online mode. This work proposes a novel approach for generating new artificial fingerprints also called proxy fingerprints that are natural looking, non-invertible, revocable and privacy preserving. These proxy biometrics can be generated from original ones only with the help of a user-specific key. Instead of using the original fingerprint, these proxy templates can be used anywhere with same convenience. The manuscripts walks through an interesting way in which proxy fingerprints of different types can be generated and how they can be combined with use-specific keys to provide revocability and cancelability in case of compromise. Using the proposed approach a proxy dataset is generated from samples belonging to Anguli fingerprint database. Matching experiments were performed on the new set which is 5 times larger than the original, and it was found that their performance is at par with 0 FAR and 0 FRR in the stolen key, safe key scenarios. Other parameters on revocability and diversity are also analyzed for protection performance.
Explainable vision transformer enabled convolutional neural network for plant disease identification: PlantXViT
Jul 16, 2022
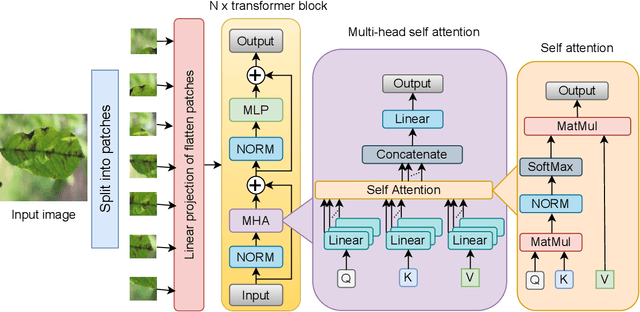


Abstract:Plant diseases are the primary cause of crop losses globally, with an impact on the world economy. To deal with these issues, smart agriculture solutions are evolving that combine the Internet of Things and machine learning for early disease detection and control. Many such systems use vision-based machine learning methods for real-time disease detection and diagnosis. With the advancement in deep learning techniques, new methods have emerged that employ convolutional neural networks for plant disease detection and identification. Another trend in vision-based deep learning is the use of vision transformers, which have proved to be powerful models for classification and other problems. However, vision transformers have rarely been investigated for plant pathology applications. In this study, a Vision Transformer enabled Convolutional Neural Network model called "PlantXViT" is proposed for plant disease identification. The proposed model combines the capabilities of traditional convolutional neural networks with the Vision Transformers to efficiently identify a large number of plant diseases for several crops. The proposed model has a lightweight structure with only 0.8 million trainable parameters, which makes it suitable for IoT-based smart agriculture services. The performance of PlantXViT is evaluated on five publicly available datasets. The proposed PlantXViT network performs better than five state-of-the-art methods on all five datasets. The average accuracy for recognising plant diseases is shown to exceed 93.55%, 92.59%, and 98.33% on Apple, Maize, and Rice datasets, respectively, even under challenging background conditions. The efficiency in terms of explainability of the proposed model is evaluated using gradient-weighted class activation maps and Local Interpretable Model Agnostic Explanation.
Discriminative Kernel Convolution Network for Multi-Label Ophthalmic Disease Detection on Imbalanced Fundus Image Dataset
Jul 16, 2022



Abstract:It is feasible to recognize the presence and seriousness of eye disease by investigating the progressions in retinal biological structure. Fundus examination is a diagnostic procedure to examine the biological structure and anomaly of the eye. Ophthalmic diseases like glaucoma, diabetic retinopathy, and cataract are the main reason for visual impairment around the world. Ocular Disease Intelligent Recognition (ODIR-5K) is a benchmark structured fundus image dataset utilized by researchers for multi-label multi-disease classification of fundus images. This work presents a discriminative kernel convolution network (DKCNet), which explores discriminative region-wise features without adding extra computational cost. DKCNet is composed of an attention block followed by a squeeze and excitation (SE) block. The attention block takes features from the backbone network and generates discriminative feature attention maps. The SE block takes the discriminative feature maps and improves channel interdependencies. Better performance of DKCNet is observed with InceptionResnet backbone network for multi-label classification of ODIR-5K fundus images with 96.08 AUC, 94.28 F1-score and 0.81 kappa score. The proposed method splits the common target label for an eye pair based on the diagnostic keyword. Based on these labels oversampling and undersampling is done to resolve class imbalance. To check the biasness of proposed model towards training data, the model trained on ODIR dataset is tested on three publicly available benchmark datasets. It is found to give good performance on completely unseen fundus images also.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge