Preux Philippe
INRIA Lille - Nord Europe, LIFL
gym-DSSAT: a crop model turned into a Reinforcement Learning environment
Jul 07, 2022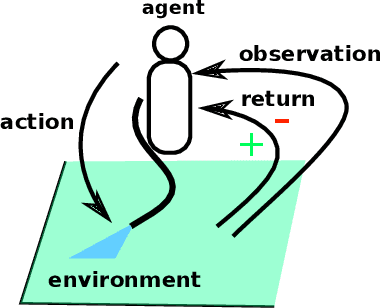
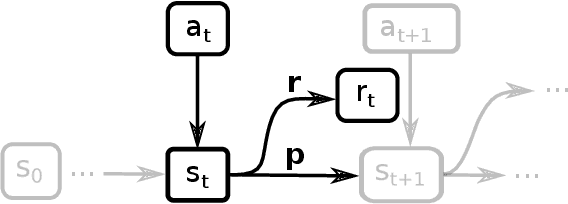
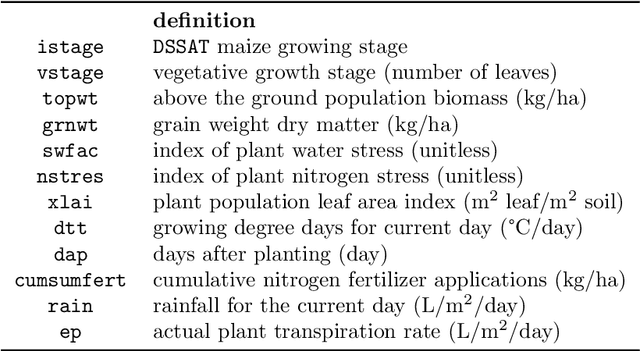
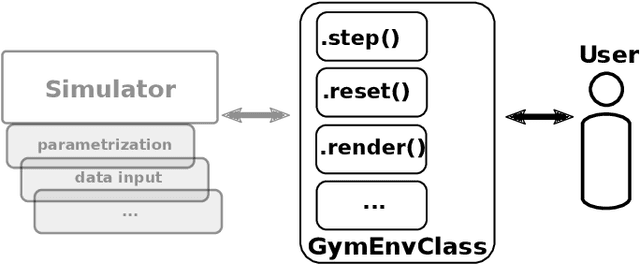
Abstract:Addressing a real world sequential decision problem with Reinforcement Learning (RL) usually starts with the use of a simulated environment that mimics real conditions. We present a novel open source RL environment for realistic crop management tasks. gym-DSSAT is a gym interface to the Decision Support System for Agrotechnology Transfer (DSSAT), a high fidelity crop simulator. DSSAT has been developped over the last 30 years and is widely recognized by agronomists. gym-DSSAT comes with predefined simulations based on real world maize experiments. The environment is as easy to use as any gym environment. We provide performance baselines using basic RL algorithms. We also briefly outline how the monolithic DSSAT simulator written in Fortran has been turned into a Python RL environment. Our methodology is generic and may be applied to similar simulators. We report on very preliminary experimental results which suggest that RL can help researchers to improve sustainability of fertilization and irrigation practices.
Bandits Warm-up Cold Recommender Systems
Jul 10, 2014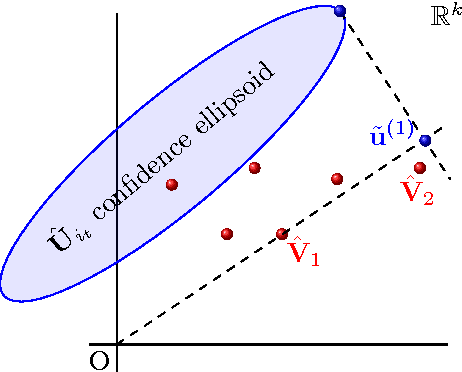
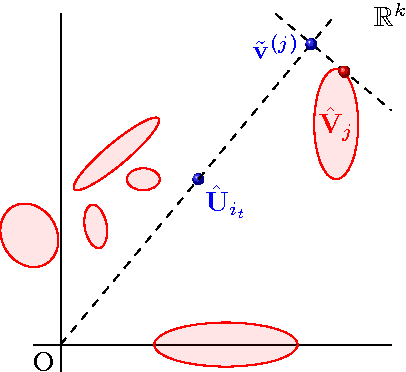
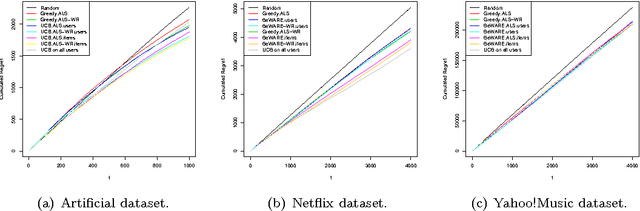
Abstract:We address the cold start problem in recommendation systems assuming no contextual information is available neither about users, nor items. We consider the case in which we only have access to a set of ratings of items by users. Most of the existing works consider a batch setting, and use cross-validation to tune parameters. The classical method consists in minimizing the root mean square error over a training subset of the ratings which provides a factorization of the matrix of ratings, interpreted as a latent representation of items and users. Our contribution in this paper is 5-fold. First, we explicit the issues raised by this kind of batch setting for users or items with very few ratings. Then, we propose an online setting closer to the actual use of recommender systems; this setting is inspired by the bandit framework. The proposed methodology can be used to turn any recommender system dataset (such as Netflix, MovieLens,...) into a sequential dataset. Then, we explicit a strong and insightful link between contextual bandit algorithms and matrix factorization; this leads us to a new algorithm that tackles the exploration/exploitation dilemma associated to the cold start problem in a strikingly new perspective. Finally, experimental evidence confirm that our algorithm is effective in dealing with the cold start problem on publicly available datasets. Overall, the goal of this paper is to bridge the gap between recommender systems based on matrix factorizations and those based on contextual bandits.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge