Prabu David
A Linguistic Comparison between Human and ChatGPT-Generated Conversations
Feb 02, 2024Abstract:This study explores linguistic differences between human and LLM-generated dialogues, using 19.5K dialogues generated by ChatGPT-3.5 as a companion to the EmpathicDialogues dataset. The research employs Linguistic Inquiry and Word Count (LIWC) analysis, comparing ChatGPT-generated conversations with human conversations across 118 linguistic categories. Results show greater variability and authenticity in human dialogues, but ChatGPT excels in categories such as social processes, analytical style, cognition, attentional focus, and positive emotional tone, reinforcing recent findings of LLMs being "more human than human." However, no significant difference was found in positive or negative affect between ChatGPT and human dialogues. Classifier analysis of dialogue embeddings indicates implicit coding of the valence of affect despite no explicit mention of affect in the conversations. The research also contributes a novel, companion ChatGPT-generated dataset of conversations between two independent chatbots, which were designed to replicate a corpus of human conversations available for open access and used widely in AI research on language modeling. Our findings increase understanding of ChatGPT's linguistic capabilities and inform ongoing efforts to distinguish between human and LLM-generated text, which is critical in detecting AI-generated fakes, misinformation, and disinformation.
A multilevel framework for AI governance
Jul 13, 2023

Abstract:To realize the potential benefits and mitigate potential risks of AI, it is necessary to develop a framework of governance that conforms to ethics and fundamental human values. Although several organizations have issued guidelines and ethical frameworks for trustworthy AI, without a mediating governance structure, these ethical principles will not translate into practice. In this paper, we propose a multilevel governance approach that involves three groups of interdependent stakeholders: governments, corporations, and citizens. We examine their interrelationships through dimensions of trust, such as competence, integrity, and benevolence. The levels of governance combined with the dimensions of trust in AI provide practical insights that can be used to further enhance user experiences and inform public policy related to AI.
Trust in AI and Its Role in the Acceptance of AI Technologies
Mar 23, 2022



Abstract:As AI-enhanced technologies become common in a variety of domains, there is an increasing need to define and examine the trust that users have in such technologies. Given the progress in the development of AI, a correspondingly sophisticated understanding of trust in the technology is required. This paper addresses this need by explaining the role of trust on the intention to use AI technologies. Study 1 examined the role of trust in the use of AI voice assistants based on survey responses from college students. A path analysis confirmed that trust had a significant effect on the intention to use AI, which operated through perceived usefulness and participants' attitude toward voice assistants. In study 2, using data from a representative sample of the U.S. population, different dimensions of trust were examined using exploratory factor analysis, which yielded two dimensions: human-like trust and functionality trust. The results of the path analyses from Study 1 were replicated in Study 2, confirming the indirect effect of trust and the effects of perceived usefulness, ease of use, and attitude on intention to use. Further, both dimensions of trust shared a similar pattern of effects within the model, with functionality-related trust exhibiting a greater total impact on usage intention than human-like trust. Overall, the role of trust in the acceptance of AI technologies was significant across both studies. This research contributes to the advancement and application of the TAM in AI-related applications and offers a multidimensional measure of trust that can be utilized in the future study of trustworthy AI.
DeepTalk: Vocal Style Encoding for Speaker Recognition and Speech Synthesis
Dec 09, 2020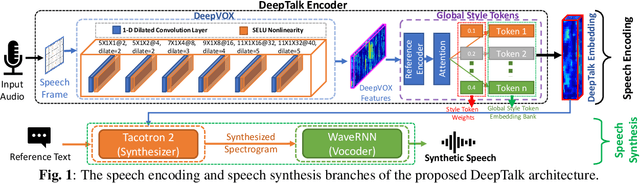
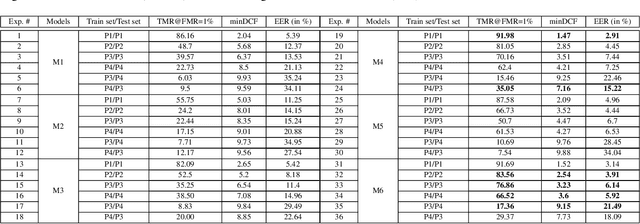
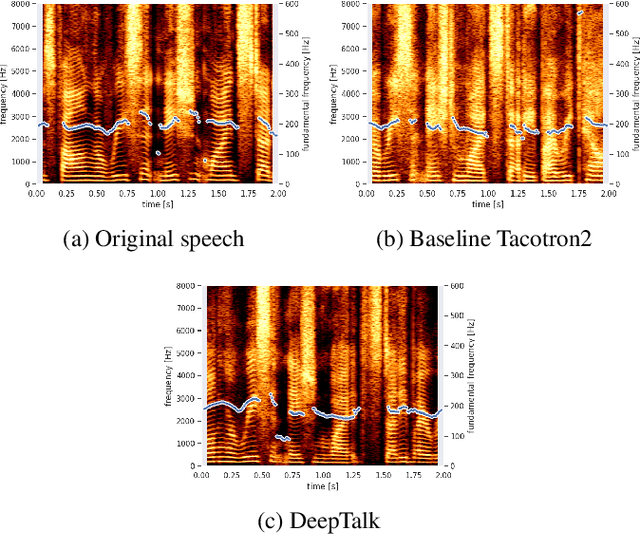
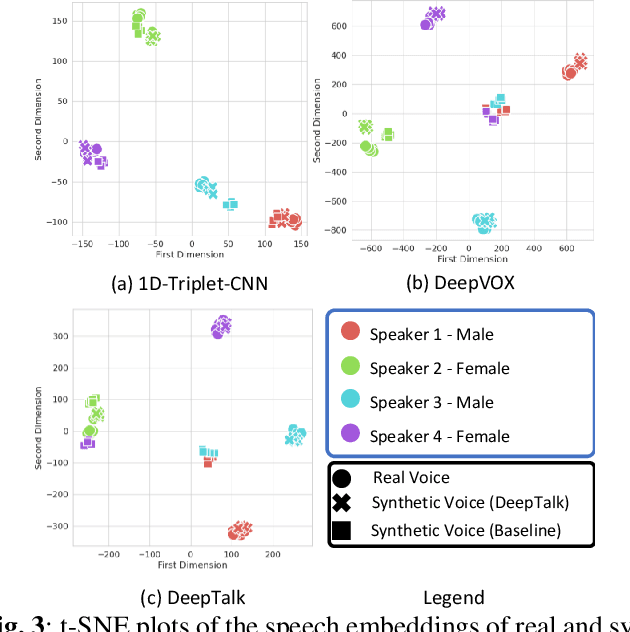
Abstract:Automatic speaker recognition algorithms typically use physiological speech characteristics encoded in the short term spectral features for characterizing speech audio. Such algorithms do not capitalize on the complementary and discriminative speaker-dependent characteristics present in the behavioral speech features. In this work, we propose a prosody encoding network called DeepTalk for extracting vocal style features directly from raw audio data. The DeepTalk method outperforms several state-of-the-art physiological speech characteristics-based speaker recognition systems across multiple challenging datasets. The speaker recognition performance is further improved by combining DeepTalk with a state-of-the-art physiological speech feature-based speaker recognition system. We also integrate the DeepTalk method into a current state-of-the-art speech synthesizer to generate synthetic speech. A detailed analysis of the synthetic speech shows that the DeepTalk captures F0 contours essential for vocal style modeling. Furthermore, DeepTalk-based synthetic speech is shown to be almost indistinguishable from real speech in the context of speaker recognition.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge