Po Yuan Mao
HOMOE: A Memory-Based and Composition-Aware Framework for Zero-Shot Learning with Hopfield Network and Soft Mixture of Experts
Nov 23, 2023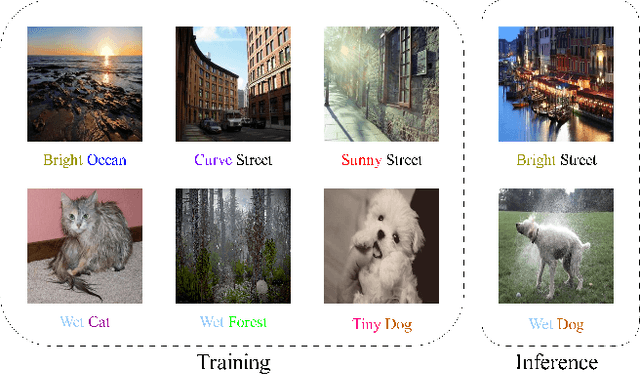
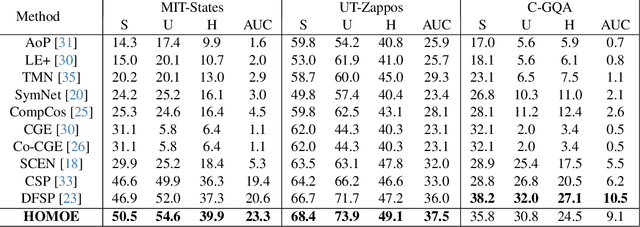
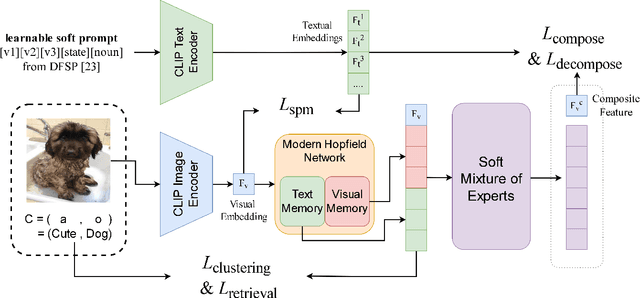
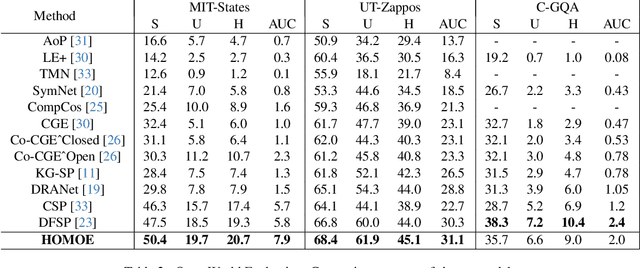
Abstract:Compositional Zero-Shot Learning (CZSL) has emerged as an essential paradigm in machine learning, aiming to overcome the constraints of traditional zero-shot learning by incorporating compositional thinking into its methodology. Conventional zero-shot learning has difficulty managing unfamiliar combinations of seen and unseen classes because it depends on pre-defined class embeddings. In contrast, Compositional Zero-Shot Learning uses the inherent hierarchies and structural connections among classes, creating new class representations by combining attributes, components, or other semantic elements. In our paper, we propose a novel framework that for the first time combines the Modern Hopfield Network with a Mixture of Experts (HOMOE) to classify the compositions of previously unseen objects. Specifically, the Modern Hopfield Network creates a memory that stores label prototypes and identifies relevant labels for a given input image. Following this, the Mixture of Expert models integrates the image with the fitting prototype to produce the final composition classification. Our approach achieves SOTA performance on several benchmarks, including MIT-States and UT-Zappos. We also examine how each component contributes to improved generalization.
The Challenges of Image Generation Models in Generating Multi-Component Images
Nov 22, 2023



Abstract:Recent advances in text-to-image generators have led to substantial capabilities in image generation. However, the complexity of prompts acts as a bottleneck in the quality of images generated. A particular under-explored facet is the ability of generative models to create high-quality images comprising multiple components given as a prior. In this paper, we propose and validate a metric called Components Inclusion Score (CIS) to evaluate the extent to which a model can correctly generate multiple components. Our results reveal that the evaluated models struggle to incorporate all the visual elements from prompts with multiple components (8.53% drop in CIS per component for all evaluated models). We also identify a significant decline in the quality of the images and context awareness within an image as the number of components increased (15.91% decrease in inception Score and 9.62% increase in Frechet Inception Distance). To remedy this issue, we fine-tuned Stable Diffusion V2 on a custom-created test dataset with multiple components, outperforming its vanilla counterpart. To conclude, these findings reveal a critical limitation in existing text-to-image generators, shedding light on the challenge of generating multiple components within a single image using a complex prompt.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge