Pierre Gançarski
Towards Measuring Domain Shift in Histopathological Stain Translation in an Unsupervised Manner
May 09, 2022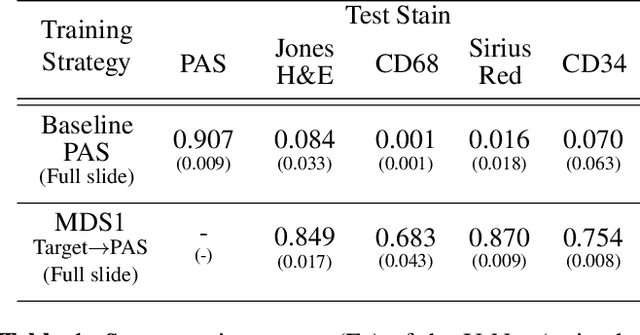
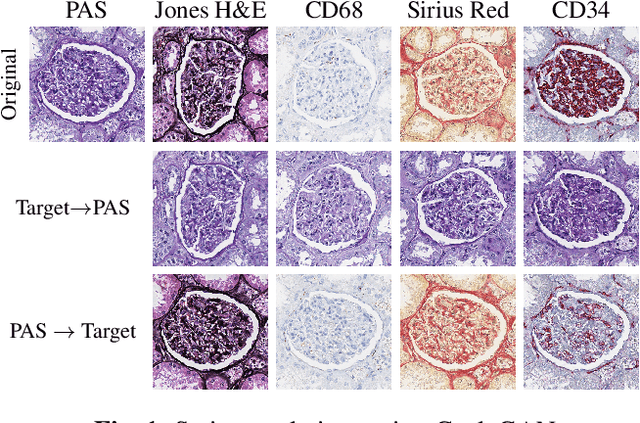
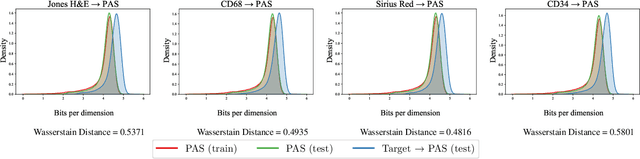

Abstract:Domain shift in digital histopathology can occur when different stains or scanners are used, during stain translation, etc. A deep neural network trained on source data may not generalise well to data that has undergone some domain shift. An important step towards being robust to domain shift is the ability to detect and measure it. This article demonstrates that the PixelCNN and domain shift metric can be used to detect and quantify domain shift in digital histopathology, and they demonstrate a strong correlation with generalisation performance. These findings pave the way for a mechanism to infer the average performance of a model (trained on source data) on unseen and unlabelled target data.
* 5 pages, 3 figures, 2 tables
An Empirical Study into Annotator Agreement, Ground Truth Estimation, and Algorithm Evaluation
Apr 26, 2016



Abstract:Although agreement between annotators has been studied in the past from a statistical viewpoint, little work has attempted to quantify the extent to which this phenomenon affects the evaluation of computer vision (CV) object detection algorithms. Many researchers utilise ground truth (GT) in experiments and more often than not this GT is derived from one annotator's opinion. How does the difference in opinion affect an algorithm's evaluation? Four examples of typical CV problems are chosen, and a methodology is applied to each to quantify the inter-annotator variance and to offer insight into the mechanisms behind agreement and the use of GT. It is found that when detecting linear objects annotator agreement is very low. The agreement in object position, linear or otherwise, can be partially explained through basic image properties. Automatic object detectors are compared to annotator agreement and it is found that a clear relationship exists. Several methods for calculating GTs from a number of annotations are applied and the resulting differences in the performance of the object detectors are quantified. It is found that the rank of a detector is highly dependent upon the method used to form the GT. It is also found that although the STAPLE and LSML GT estimation methods appear to represent the mean of the performance measured using the individual annotations, when there are few annotations, or there is a large variance in them, these estimates tend to degrade. Furthermore, one of the most commonly adopted annotation combination methods--consensus voting--accentuates more obvious features, which results in an overestimation of the algorithm's performance. Finally, it is concluded that in some datasets it may not be possible to state with any confidence that one algorithm outperforms another when evaluating upon one GT and a method for calculating confidence bounds is discussed.
* 16 pages
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge