Peter Krause
Landscape-Aware Automated Algorithm Configuration using Multi-output Mixed Regression and Classification
Sep 02, 2024Abstract:In landscape-aware algorithm selection problem, the effectiveness of feature-based predictive models strongly depends on the representativeness of training data for practical applications. In this work, we investigate the potential of randomly generated functions (RGF) for the model training, which cover a much more diverse set of optimization problem classes compared to the widely-used black-box optimization benchmarking (BBOB) suite. Correspondingly, we focus on automated algorithm configuration (AAC), that is, selecting the best suited algorithm and fine-tuning its hyperparameters based on the landscape features of problem instances. Precisely, we analyze the performance of dense neural network (NN) models in handling the multi-output mixed regression and classification tasks using different training data sets, such as RGF and many-affine BBOB (MA-BBOB) functions. Based on our results on the BBOB functions in 5d and 20d, near optimal configurations can be identified using the proposed approach, which can most of the time outperform the off-the-shelf default configuration considered by practitioners with limited knowledge about AAC. Furthermore, the predicted configurations are competitive against the single best solver in many cases. Overall, configurations with better performance can be best identified by using NN models trained on a combination of RGF and MA-BBOB functions.
DoE2Vec: Deep-learning Based Features for Exploratory Landscape Analysis
Mar 31, 2023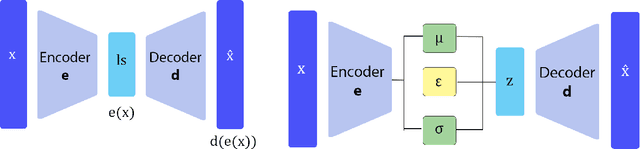
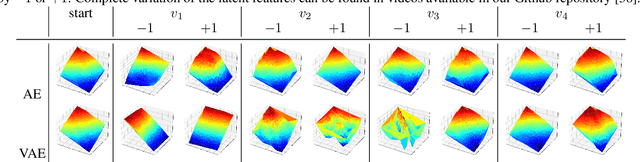
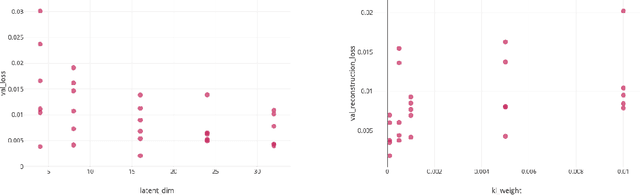
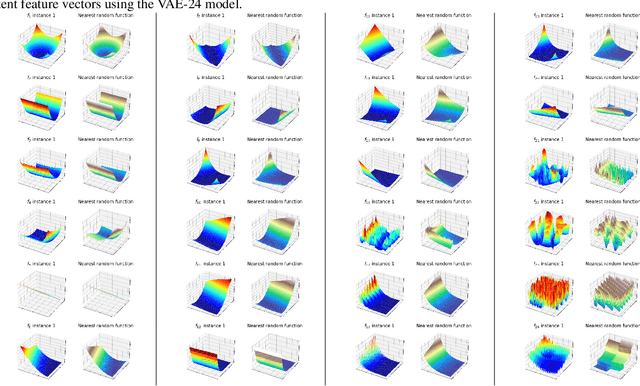
Abstract:We propose DoE2Vec, a variational autoencoder (VAE)-based methodology to learn optimization landscape characteristics for downstream meta-learning tasks, e.g., automated selection of optimization algorithms. Principally, using large training data sets generated with a random function generator, DoE2Vec self-learns an informative latent representation for any design of experiments (DoE). Unlike the classical exploratory landscape analysis (ELA) method, our approach does not require any feature engineering and is easily applicable for high dimensional search spaces. For validation, we inspect the quality of latent reconstructions and analyze the latent representations using different experiments. The latent representations not only show promising potentials in identifying similar (cheap-to-evaluate) surrogate functions, but also can significantly boost performances when being used complementary to the classical ELA features in classification tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge