Pengyu Ji
Unsupervised Morphological Tree Tokenizer
Jun 21, 2024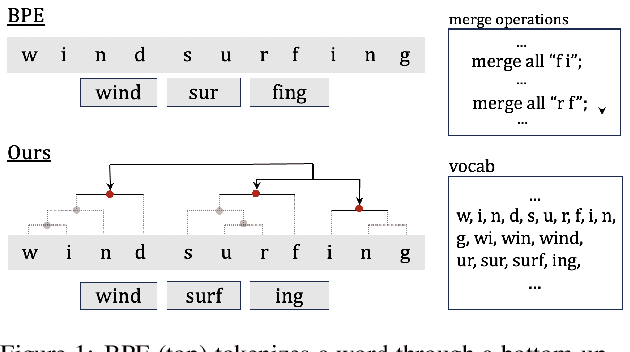
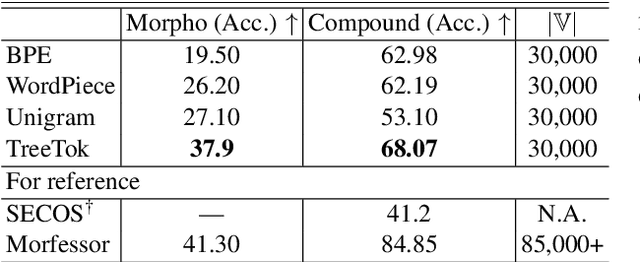
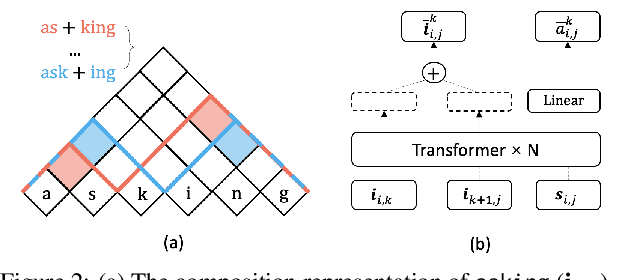
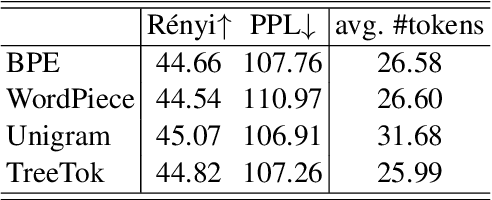
Abstract:As a cornerstone in language modeling, tokenization involves segmenting text inputs into pre-defined atomic units. Conventional statistical tokenizers often disrupt constituent boundaries within words, thereby corrupting semantic information. To address this drawback, we introduce morphological structure guidance to tokenization and propose a deep model to induce character-level structures of words. Specifically, the deep model jointly encodes internal structures and representations of words with a mechanism named $\textit{MorphOverriding}$ to ensure the indecomposability of morphemes. By training the model with self-supervised objectives, our method is capable of inducing character-level structures that align with morphological rules without annotated training data. Based on the induced structures, our algorithm tokenizes words through vocabulary matching in a top-down manner. Empirical results indicate that the proposed method effectively retains complete morphemes and outperforms widely adopted methods such as BPE and WordPiece on both morphological segmentation tasks and language modeling tasks. The code will be released later.
Generative Pretrained Structured Transformers: Unsupervised Syntactic Language Models at Scale
Mar 18, 2024Abstract:A syntactic language model (SLM) incrementally generates a sentence with its syntactic tree in a left-to-right manner. We present Generative Pretrained Structured Transformers (GPST), an unsupervised SLM at scale capable of being pre-trained from scratch on raw texts with high parallelism. GPST circumvents the limitations of previous SLMs such as relying on gold trees and sequential training. It consists of two components, a usual SLM supervised by a uni-directional language modeling loss, and an additional composition model, which induces syntactic parse trees and computes constituent representations, supervised by a bi-directional language modeling loss. We propose a representation surrogate to enable joint parallel training of the two models in a hard-EM fashion. We pre-train GPST on OpenWebText, a corpus with $9$ billion tokens, and demonstrate the superiority of GPST over GPT-2 with a comparable size in numerous tasks covering both language understanding and language generation. Meanwhile, GPST also significantly outperforms existing unsupervised SLMs on left-to-right grammar induction, while holding a substantial acceleration on training.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge