Paul S. Rosenbloom
Mapping Neural Theories of Consciousness onto the Common Model of Cognition
Jun 13, 2025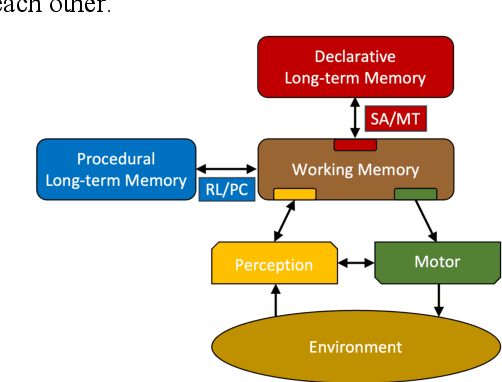
Abstract:A beginning is made at mapping four neural theories of consciousness onto the Common Model of Cognition. This highlights how the four jointly depend on recurrent local modules plus a cognitive cycle operating on a global working memory with complex states, and reveals how an existing integrative view of consciousness from a neural perspective aligns with the Com-mon Model.
A Proposal for Extending the Common Model of Cognition to Emotion
Dec 19, 2024Abstract:Cognition and emotion must be partnered in any complete model of a humanlike mind. This article proposes an extension to the Common Model of Cognition -- a developing consensus concerning what is required in such a mind -- for emotion that includes a linked pair of modules for emotion and metacognitive assessment, plus pervasive connections between these two new modules and the Common Model's existing modules and links.
Thoughts on Architecture
Jun 23, 2023Abstract:The term architecture has evolved considerably from its original Greek roots and its application to buildings and computers to its more recent manifestation for minds. This article considers lessons from this history, in terms of a set of relevant distinctions introduced at each of these stages and a definition of architecture that spans all three, and a reconsideration of three key issues from cognitive architectures for architectures in general and cognitive architectures more particularly.
Rethinking the Physical Symbol Systems Hypothesis
Jun 22, 2023Abstract:It is now more than a half-century since the Physical Symbol Systems Hypothesis (PSSH) was first articulated as an empirical hypothesis. More recent evidence from work with neural networks and cognitive architectures has weakened it, but it has not yet been replaced in any satisfactory manner. Based on a rethinking of the nature of computational symbols -- as atoms or placeholders -- and thus also of the systems in which they participate, a hybrid approach is introduced that responds to these challenges while also helping to bridge the gap between symbolic and neural approaches, resulting in two new hypotheses, one that is to replace the PSSH and other focused more directly on cognitive architectures.
Defining and Explorting the Intelligence Space
Jun 16, 2023



Abstract:Intelligence is a difficult concept to define, despite many attempts at doing so. Rather than trying to settle on a single definition, this article introduces a broad perspective on what intelligence is, by laying out a cascade of definitions that induces both a nested hierarchy of three levels of intelligence and a wider-ranging space that is built around them and approximations to them. Within this intelligence space, regions are identified that correspond to both natural -- most particularly, human -- intelligence and artificial intelligence (AI), along with the crossover notion of humanlike intelligence. These definitions are then exploited in early explorations of four more advanced, and likely more controversial, topics: the singularity, generative AI, ethics, and intellectual property.
Controlling Synthetic Characters in Simulations: A Case for Cognitive Architectures and Sigma
Jan 06, 2021



Abstract:Simulations, along with other similar applications like virtual worlds and video games, require computational models of intelligence that generate realistic and credible behavior for the participating synthetic characters. Cognitive architectures, which are models of the fixed structure underlying intelligent behavior in both natural and artificial systems, provide a conceptually valid common basis, as evidenced by the current efforts towards a standard model of the mind, to generate human-like intelligent behavior for these synthetic characters. Sigma is a cognitive architecture and system that strives to combine what has been learned from four decades of independent work on symbolic cognitive architectures, probabilistic graphical models, and more recently neural models, under its graphical architecture hypothesis. Sigma leverages an extended form of factor graphs towards a uniform grand unification of not only traditional cognitive capabilities but also key non-cognitive aspects, creating unique opportunities for the construction of new kinds of cognitive models that possess a Theory-of-Mind and that are perceptual, autonomous, interactive, affective, and adaptive. In this paper, we will introduce Sigma along with its diverse capabilities and then use three distinct proof-of-concept Sigma models to highlight combinations of these capabilities: (1) Distributional reinforcement learning models in; (2) A pair of adaptive and interactive agent models that demonstrate rule-based, probabilistic, and social reasoning; and (3) A knowledge-free exploration model in which an agent leverages only architectural appraisal variables, namely attention and curiosity, to locate an item while building up a map in a Unity environment.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge