Paul Harvey
Simultaneous Genetic Evolution of Neural Networks for Optimal SFC Embedding
Dec 10, 2025Abstract:The reliance of organisations on computer networks is enabled by network programmability, which is typically achieved through Service Function Chaining. These chains virtualise network functions, link them, and programmatically embed them on networking infrastructure. Optimal embedding of Service Function Chains is an NP-hard problem, with three sub-problems, chain composition, virtual network function embedding, and link embedding, that have to be optimised simultaneously, rather than sequentially, for optimal results. Genetic Algorithms have been employed for this, but existing approaches either do not optimise all three sub-problems or do not optimise all three sub-problems simultaneously. We propose a Genetic Algorithm-based approach called GENESIS, which evolves three sine-function-activated Neural Networks, and funnels their output to a Gaussian distribution and an A* algorithm to optimise all three sub-problems simultaneously. We evaluate GENESIS on an emulator across 48 different data centre scenarios and compare its performance to two state-of-the-art Genetic Algorithms and one greedy algorithm. GENESIS produces an optimal solution for 100% of the scenarios, whereas the second-best method optimises only 71% of the scenarios. Moreover, GENESIS is the fastest among all Genetic Algorithms, averaging 15.84 minutes, compared to an average of 38.62 minutes for the second-best Genetic Algorithm.
OpenRASE: Service Function Chain Emulation
Jul 29, 2025Abstract:Service Function Chains (SFCs) are one of the key enablers in providing programmable computer networks, paving the way for network autonomy. However, this also introduces new challenges, such as resource allocation and optimisation related to their operation, requiring new algorithms to address these challenges. Various tools have been used in the literature to evaluate these algorithms. However, these tools suffer from inaccuracy, low fidelity, unscalability, inflexibility, or additional code requirements. This paper introduces an emulator based on Mininet and Docker for SFCs called OpenRASE. The goal of OpenRASE is to enable the exploration of resource allocation algorithms for SFCs in a dynamic setting, allowing real CPU usage and latency to be measured. We describe the design and implementation of OpenRASE and discuss its characteristics. We also experimentally evaluate two different algorithms to address the SFC resource allocation challenge, including an online Genetic Algorithm, using OpenRASE to show its effectiveness and practicality for dynamic network conditions.
FedFly: Towards Migration in Edge-based Distributed Federated Learning
Nov 02, 2021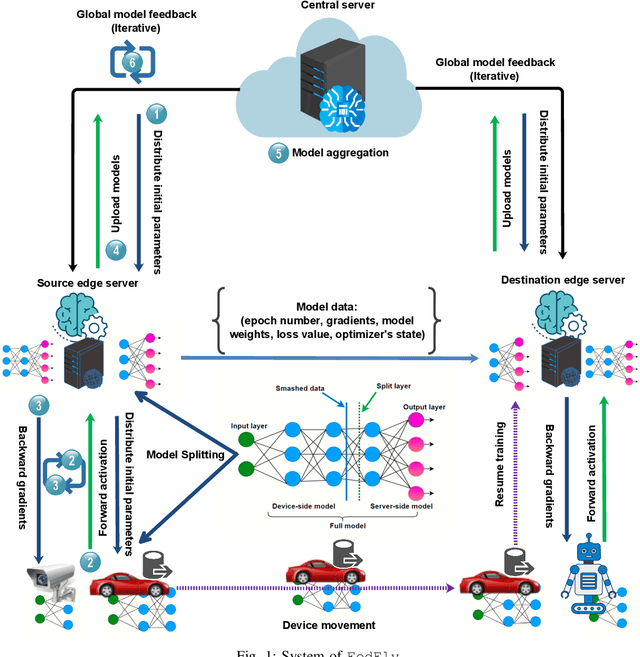
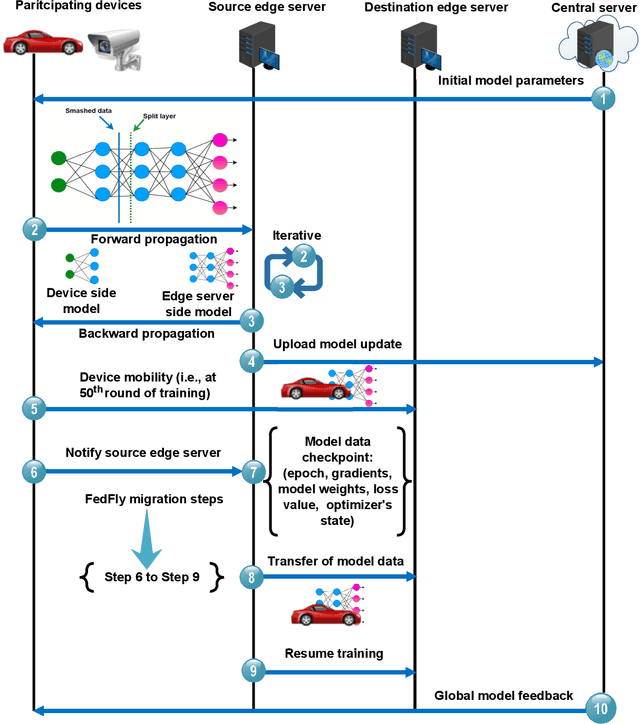
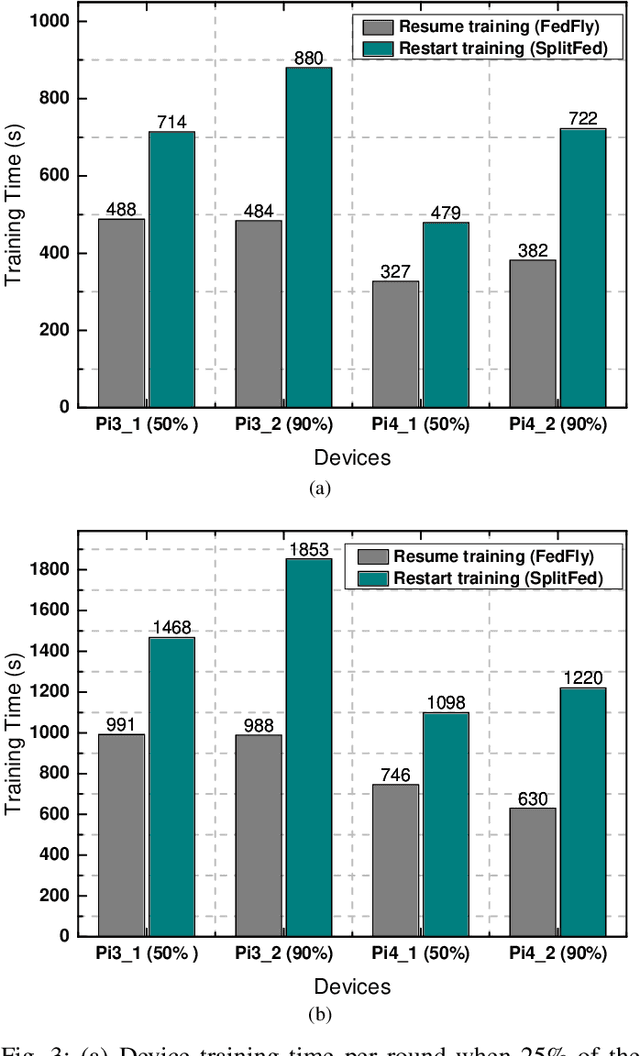
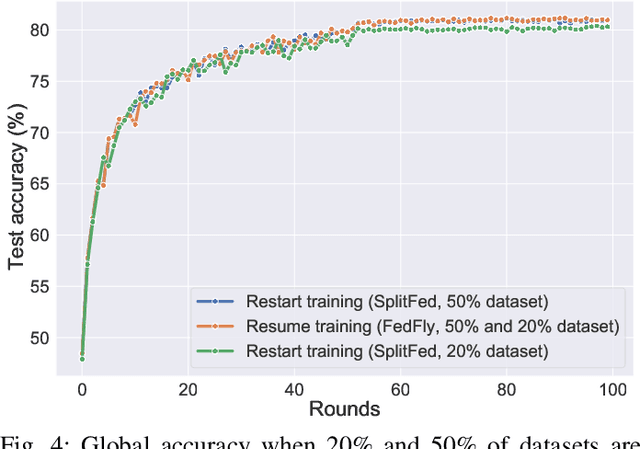
Abstract:Federated learning (FL) is a privacy-preserving distributed machine learning technique that trains models without having direct access to the original data generated on devices. Since devices may be resource constrained, offloading can be used to improve FL performance by transferring computational workload from devices to edge servers. However, due to mobility, devices participating in FL may leave the network during training and need to connect to a different edge server. This is challenging because the offloaded computations from edge server need to be migrated. In line with this assertion, we present FedFly, which is, to the best of our knowledge, the first work to migrate a deep neural network (DNN) when devices move between edge servers during FL training. Our empirical results on the CIFAR-10 dataset, with both balanced and imbalanced data distribution support our claims that FedFly can reduce training time by up to 33% when a device moves after 50% of the training is completed, and by up to 45% when 90% of the training is completed when compared to state-of-the-art offloading approach in FL. FedFly has negligible overhead of 2 seconds and does not compromise accuracy. Finally, we highlight a number of open research issues for further investigation. FedFly can be downloaded from https://github.com/qub-blesson/FedFly
FedAdapt: Adaptive Offloading for IoT Devices in Federated Learning
Jul 09, 2021



Abstract:Applying Federated Learning (FL) on Internet-of-Things devices is necessitated by the large volumes of data they produce and growing concerns of data privacy. However, there are three challenges that need to be addressed to make FL efficient: (i) execute on devices with limited computational capabilities, (ii) account for stragglers due to computational heterogeneity of devices, and (iii) adapt to the changing network bandwidths. This paper presents FedAdapt, an adaptive offloading FL framework to mitigate the aforementioned challenges. FedAdapt accelerates local training in computationally constrained devices by leveraging layer offloading of deep neural networks (DNNs) to servers. Further, FedAdapt adopts reinforcement learning-based optimization and clustering to adaptively identify which layers of the DNN should be offloaded for each individual device on to a server to tackle the challenges of computational heterogeneity and changing network bandwidth. Experimental studies are carried out on a lab-based testbed comprising five IoT devices. By offloading a DNN from the device to the server FedAdapt reduces the training time of a typical IoT device by over half compared to classic FL. The training time of extreme stragglers and the overall training time can be reduced by up to 57%. Furthermore, with changing network bandwidth, FedAdapt is demonstrated to reduce the training time by up to 40% when compared to classic FL, without sacrificing accuracy. FedAdapt can be downloaded from https://github.com/qub-blesson/FedAdapt.
Scission: Context-aware and Performance-driven Edge-based Distributed Deep Neural Networks
Aug 08, 2020



Abstract:Partitioning and distributing deep neural networks (DNNs) across end-devices, edge resources and the cloud has a potential twofold advantage: preserving privacy of the input data, and reducing the ingress bandwidth demand beyond the edge. However, for a given DNN, identifying the optimal partition configuration for distributing the DNN that maximizes performance is a significant challenge since: (i) the combination of potential target hardware resources that maximizes performance and (ii) the sequence of layers of the DNN that should be distributed across the target resources needs to be determined, while accounting for (iii) user-defined objectives/constraints for partitioning. This paper presents Scission, a tool for automated benchmarking of DNNs on a given set of target device, edge and cloud resources for determining optimal partitions that maximize DNN performance. The decision-making approach is context-aware by capitalizing on hardware capabilities of the target resources, their locality, the characteristics of DNN layers, and the network condition. Experimental studies are carried out on 18 DNNs. The decisions made by Scission cannot be manually made by a human given the complexity and the number of dimensions affecting the search space. The results obtained validate that Scission is a valuable tool for achieving performance-driven and context-aware distributed DNNs that leverage the edge. Scission is available for public download at https://github.com/qub-blesson/Scission.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge