Paul A Raschky
Object Recognition for Economic Development from Daytime Satellite Imagery
Sep 11, 2020
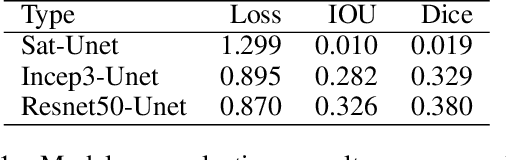
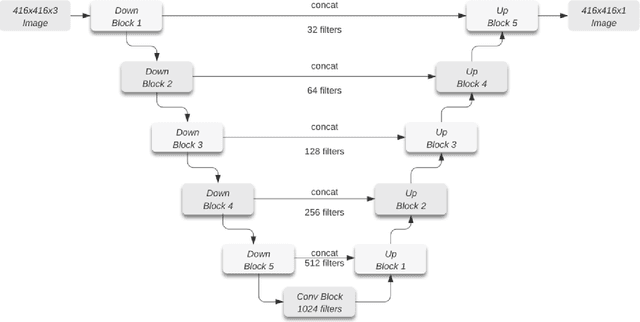
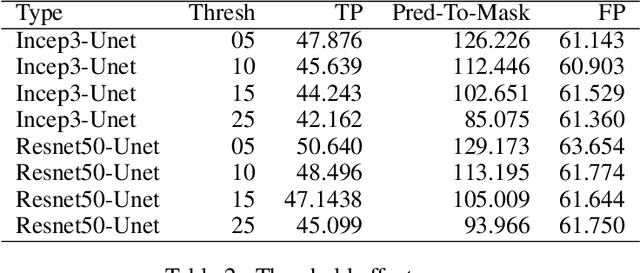
Abstract:Reliable data about the stock of physical capital and infrastructure in developing countries is typically very scarce. This is particular a problem for data at the subnational level where existing data is often outdated, not consistently measured or coverage is incomplete. Traditional data collection methods are time and labor-intensive costly, which often prohibits developing countries from collecting this type of data. This paper proposes a novel method to extract infrastructure features from high-resolution satellite images. We collected high-resolution satellite images for 5 million 1km $\times$ 1km grid cells covering 21 African countries. We contribute to the growing body of literature in this area by training our machine learning algorithm on ground-truth data. We show that our approach strongly improves the predictive accuracy. Our methodology can build the foundation to then predict subnational indicators of economic development for areas where this data is either missing or unreliable.
The Internet as Quantitative Social Science Platform: Insights from a Trillion Observations
Jan 19, 2017



Abstract:With the large-scale penetration of the internet, for the first time, humanity has become linked by a single, open, communications platform. Harnessing this fact, we report insights arising from a unified internet activity and location dataset of an unparalleled scope and accuracy drawn from over a trillion (1.5$\times 10^{12}$) observations of end-user internet connections, with temporal resolution of just 15min over 2006-2012. We first apply this dataset to the expansion of the internet itself over 1,647 urban agglomerations globally. We find that unique IP per capita counts reach saturation at approximately one IP per three people, and take, on average, 16.1 years to achieve; eclipsing the estimated 100- and 60- year saturation times for steam-power and electrification respectively. Next, we use intra-diurnal internet activity features to up-scale traditional over-night sleep observations, producing the first global estimate of over-night sleep duration in 645 cities over 7 years. We find statistically significant variation between continental, national and regional sleep durations including some evidence of global sleep duration convergence. Finally, we estimate the relationship between internet concentration and economic outcomes in 411 OECD regions and find that the internet's expansion is associated with negative or positive productivity gains, depending strongly on sectoral considerations. To our knowledge, our study is the first of its kind to use online/offline activity of the entire internet to infer social science insights, demonstrating the unparalleled potential of the internet as a social data-science platform.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge