Param Raval
Frequency Centric Defense Mechanisms against Adversarial Examples
Oct 26, 2021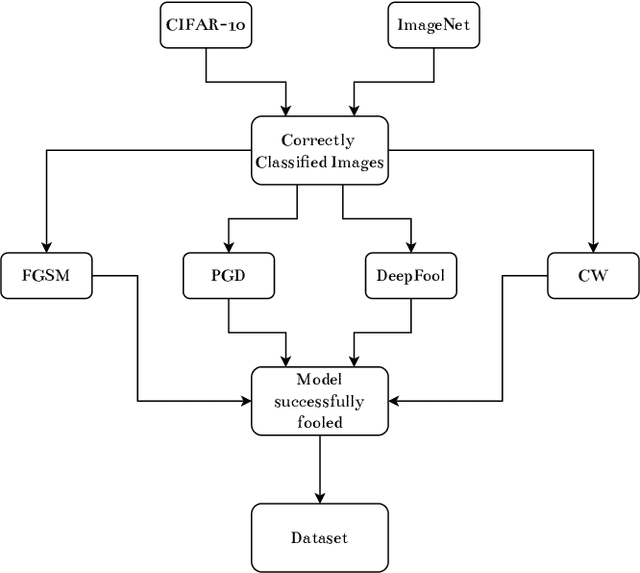
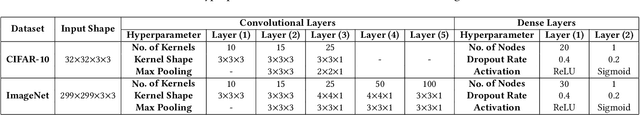
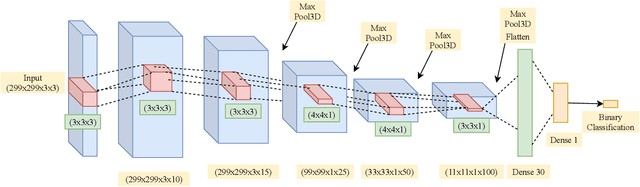
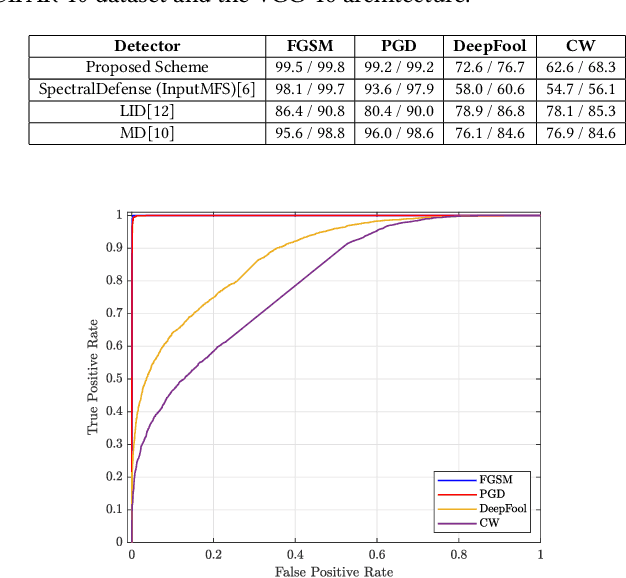
Abstract:Adversarial example (AE) aims at fooling a Convolution Neural Network by introducing small perturbations in the input image.The proposed work uses the magnitude and phase of the Fourier Spectrum and the entropy of the image to defend against AE. We demonstrate the defense in two ways: by training an adversarial detector and denoising the adversarial effect. Experiments were conducted on the low-resolution CIFAR-10 and high-resolution ImageNet datasets. The adversarial detector has 99% accuracy for FGSM and PGD attacks on the CIFAR-10 dataset. However, the detection accuracy falls to 50% for sophisticated DeepFool and Carlini & Wagner attacks on ImageNet. We overcome the limitation by using autoencoder and show that 70% of AEs are correctly classified after denoising.
Comparative Study of Machine Learning Models and BERT on SQuAD
May 22, 2020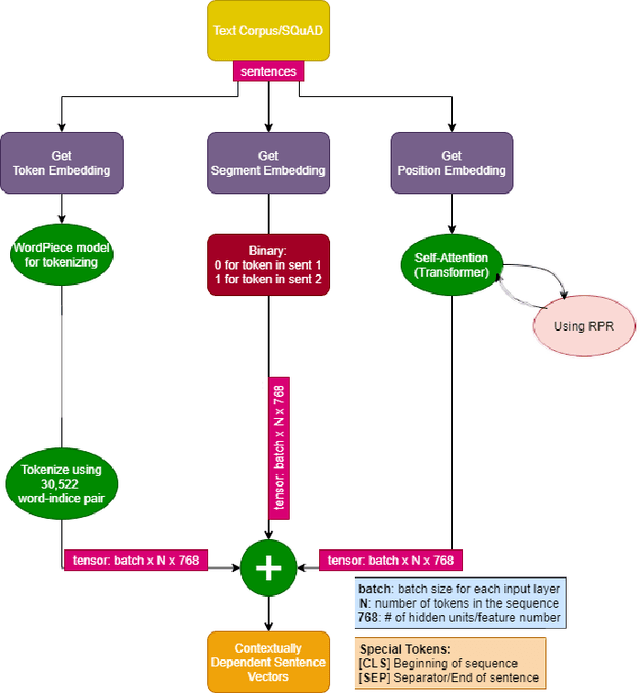
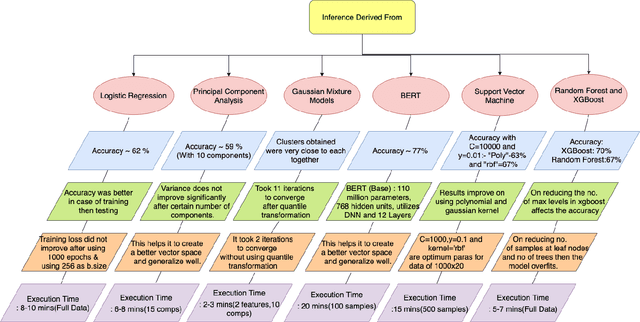
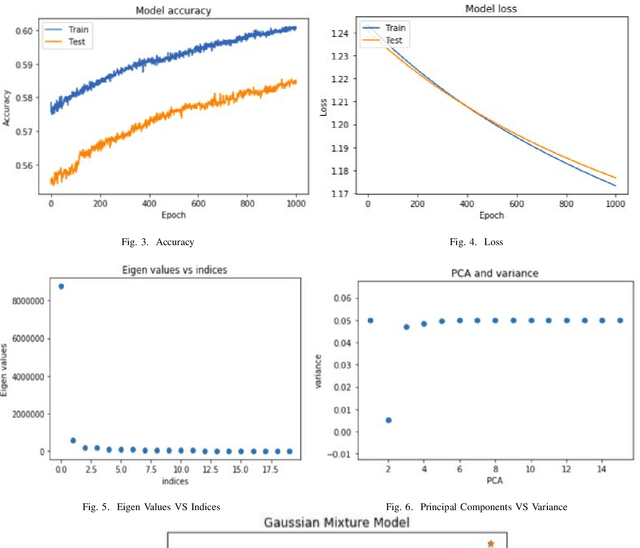
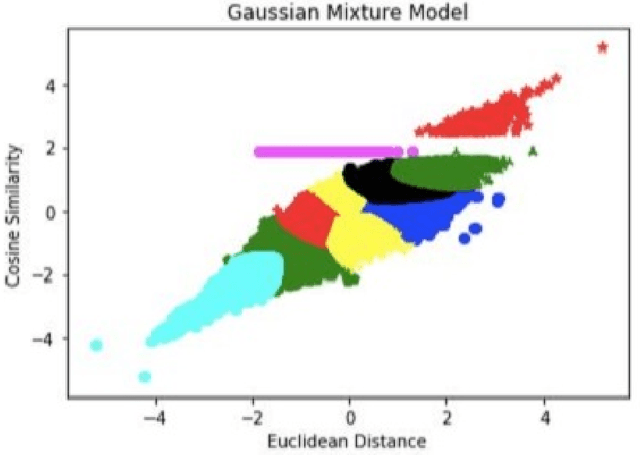
Abstract:This study aims to provide a comparative analysis of performance of certain models popular in machine learning and the BERT model on the Stanford Question Answering Dataset (SQuAD). The analysis shows that the BERT model, which was once state-of-the-art on SQuAD, gives higher accuracy in comparison to other models. However, BERT requires a greater execution time even when only 100 samples are used. This shows that with increasing accuracy more amount of time is invested in training the data. Whereas in case of preliminary machine learning models, execution time for full data is lower but accuracy is compromised.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge